
Marketing_L8_2013-2014
.pdfIden>fying Major Alterna>ves
When the company has defined its channel objec&ves, it should next iden&fy its major channel alterna&ves in terms of:
• the types of intermediaries
• the number of intermediaries
• the responsibili>es of each channel member
Evalua>ng the Major Alterna>ves
Suppose a company has iden&fied several channel alterna&ves and wants to select the one that will best sa&sfy its long-run objec&ves.
Each alterna>ve should be evaluated against criteria, such as
• economic
• control
• adaptability criteria

Designing Interna>onal Distribu>on
Channels
Interna&onal channel complexi&es:
When the Chinese government banned door-to-door selling, Avon had to abandon its tradi&onal direct marke&ng approach and sell through retail shops.

Channel Management Decisions
• Marke&ng channel management
Selec&ng, managing, and mo&va&ng individual channel members and evalua&ng their performance over &me.
Caterpillar works closely with PRM its worldwide network of
independent dealers to
find beeer ways to bring value to customers. When a big piece of CAT equipment breaks down, customers know they can count on Caterpillar and its outstanding
dealer network for support.
Marke&ng Logis&cs
and Supply Chain Management
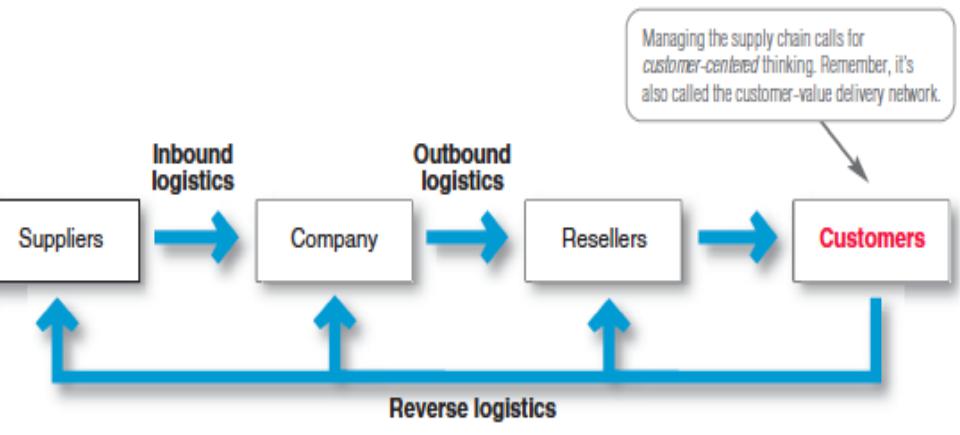
Supply chain management
Managing upstream and downstream valueadded flows of materials, final goods, and related informa&on among suppliers, the company, resellers, and final consumers.

• Marke&ng logis&cs
(physical distribu&on)
Planning, implemen&ng, and controlling the physical flow of materials, final goods, and related informa&on from points of origin to points of consump&on to meet customer requirements at a profit.
American companies spent $1.3 trillion last year—about 10 percent of the U.S. GDP—to wrap, bundle, load, unload, sort, reload, and transport goods.
• Marke>ng logis>cs addresses not only outbound distribu&on but also inbound distribu&on and reverse distribu&on. That is, it involves the en&re supply chain management—managing value-added flows between suppliers, the company, resellers, and final users.
• No logis&cs system can both maximize customer service and minimize distribu&on costs.
• The goal of logis&cs management is to provide a targeted level of service at the least cost.
• The major logis&cs func&ons include warehousing, inventory management, transporta&on, and logis&cs informa&on management.
• Improved logis&cs requires teamwork in the form of close working rela&onships across func&onal areas inside the company and across various organiza&ons in the supply chain.
• Companies can achieve logis&cs harmony among
func&ons by crea&ng cross-func&onal logis&cs teams, integra&ve supply manager posi&ons, and senior-level logis&cs execu&ves with crossfunc&onal authority.
• Channel partnerships can take the form of cross-
company teams, shared projects, and informa&onsharing systems.
• Today, some companies are outsourcing their logis&cs func&ons to third-party logis&cs (3PL) providers to save costs, increase e ciency, and gain faster and more e ec&ve access to global markets.
Thanks for your aPen&on!
