
- •Radio Engineering for Wireless Communication and Sensor Applications
- •Contents
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgments
- •1 Introduction to Radio Waves and Radio Engineering
- •1.1 Radio Waves as a Part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
- •1.2 What Is Radio Engineering?
- •1.3 Allocation of Radio Frequencies
- •1.4 History of Radio Engineering from Maxwell to the Present
- •2.2 Fields in Media
- •2.3 Boundary Conditions
- •2.4 Helmholtz Equation and Its Plane Wave Solution
- •2.5 Polarization of a Plane Wave
- •2.6 Reflection and Transmission at a Dielectric Interface
- •2.7 Energy and Power
- •3 Transmission Lines and Waveguides
- •3.1 Basic Equations for Transmission Lines and Waveguides
- •3.2 Transverse Electromagnetic Wave Modes
- •3.3 Transverse Electric and Transverse Magnetic Wave Modes
- •3.4 Rectangular Waveguide
- •3.4.1 TE Wave Modes in Rectangular Waveguide
- •3.4.2 TM Wave Modes in Rectangular Waveguide
- •3.5 Circular Waveguide
- •3.6 Optical Fiber
- •3.7 Coaxial Line
- •3.8 Microstrip Line
- •3.9 Wave and Signal Velocities
- •3.10 Transmission Line Model
- •4 Impedance Matching
- •4.1 Reflection from a Mismatched Load
- •4.2 Smith Chart
- •4.3 Matching Methods
- •4.3.1 Matching with Lumped Reactive Elements
- •4.3.4 Resistive Matching
- •5 Microwave Circuit Theory
- •5.1 Impedance and Admittance Matrices
- •5.2 Scattering Matrices
- •5.3 Signal Flow Graph, Transfer Function, and Gain
- •6.1 Power Dividers and Directional Couplers
- •6.1.1 Power Dividers
- •6.1.2 Coupling and Directivity of a Directional Coupler
- •6.1.3 Scattering Matrix of a Directional Coupler
- •6.1.4 Waveguide Directional Couplers
- •6.1.5 Microstrip Directional Couplers
- •6.2 Ferrite Devices
- •6.2.1 Properties of Ferrite Materials
- •6.2.2 Faraday Rotation
- •6.2.3 Isolators
- •6.2.4 Circulators
- •6.3 Other Passive Components and Devices
- •6.3.1 Terminations
- •6.3.2 Attenuators
- •6.3.3 Phase Shifters
- •6.3.4 Connectors and Adapters
- •7 Resonators and Filters
- •7.1 Resonators
- •7.1.1 Resonance Phenomenon
- •7.1.2 Quality Factor
- •7.1.3 Coupled Resonator
- •7.1.4 Transmission Line Section as a Resonator
- •7.1.5 Cavity Resonators
- •7.1.6 Dielectric Resonators
- •7.2 Filters
- •7.2.1 Insertion Loss Method
- •7.2.2 Design of Microwave Filters
- •7.2.3 Practical Microwave Filters
- •8 Circuits Based on Semiconductor Devices
- •8.1 From Electron Tubes to Semiconductor Devices
- •8.2 Important Semiconductor Devices
- •8.2.1 Diodes
- •8.2.2 Transistors
- •8.3 Oscillators
- •8.4 Amplifiers
- •8.4.2 Effect of Nonlinearities and Design of Power Amplifiers
- •8.4.3 Reflection Amplifiers
- •8.5.1 Mixers
- •8.5.2 Frequency Multipliers
- •8.6 Detectors
- •8.7 Monolithic Microwave Circuits
- •9 Antennas
- •9.1 Fundamental Concepts of Antennas
- •9.2 Calculation of Radiation from Antennas
- •9.3 Radiating Current Element
- •9.4 Dipole and Monopole Antennas
- •9.5 Other Wire Antennas
- •9.6 Radiation from Apertures
- •9.7 Horn Antennas
- •9.8 Reflector Antennas
- •9.9 Other Antennas
- •9.10 Antenna Arrays
- •9.11 Matching of Antennas
- •9.12 Link Between Two Antennas
- •10 Propagation of Radio Waves
- •10.1 Environment and Propagation Mechanisms
- •10.2 Tropospheric Attenuation
- •10.4 LOS Path
- •10.5 Reflection from Ground
- •10.6 Multipath Propagation in Cellular Mobile Radio Systems
- •10.7 Propagation Aided by Scattering: Scatter Link
- •10.8 Propagation via Ionosphere
- •11 Radio System
- •11.1 Transmitters and Receivers
- •11.2 Noise
- •11.2.1 Receiver Noise
- •11.2.2 Antenna Noise Temperature
- •11.3 Modulation and Demodulation of Signals
- •11.3.1 Analog Modulation
- •11.3.2 Digital Modulation
- •11.4 Radio Link Budget
- •12 Applications
- •12.1 Broadcasting
- •12.1.1 Broadcasting in Finland
- •12.1.2 Broadcasting Satellites
- •12.2 Radio Link Systems
- •12.2.1 Terrestrial Radio Links
- •12.2.2 Satellite Radio Links
- •12.3 Wireless Local Area Networks
- •12.4 Mobile Communication
- •12.5 Radionavigation
- •12.5.1 Hyperbolic Radionavigation Systems
- •12.5.2 Satellite Navigation Systems
- •12.5.3 Navigation Systems in Aviation
- •12.6 Radar
- •12.6.1 Pulse Radar
- •12.6.2 Doppler Radar
- •12.6.4 Surveillance and Tracking Radars
- •12.7 Remote Sensing
- •12.7.1 Radiometry
- •12.7.2 Total Power Radiometer and Dicke Radiometer
- •12.8 Radio Astronomy
- •12.8.1 Radio Telescopes and Receivers
- •12.8.2 Antenna Temperature of Radio Sources
- •12.8.3 Radio Sources in the Sky
- •12.9 Sensors for Industrial Applications
- •12.9.1 Transmission Sensors
- •12.9.2 Resonators
- •12.9.3 Reflection Sensors
- •12.9.4 Radar Sensors
- •12.9.5 Radiometer Sensors
- •12.9.6 Imaging Sensors
- •12.10 Power Applications
- •12.11 Medical Applications
- •12.11.1 Thermography
- •12.11.2 Diathermy
- •12.11.3 Hyperthermia
- •12.12 Electronic Warfare
- •List of Acronyms
- •About the Authors
- •Index
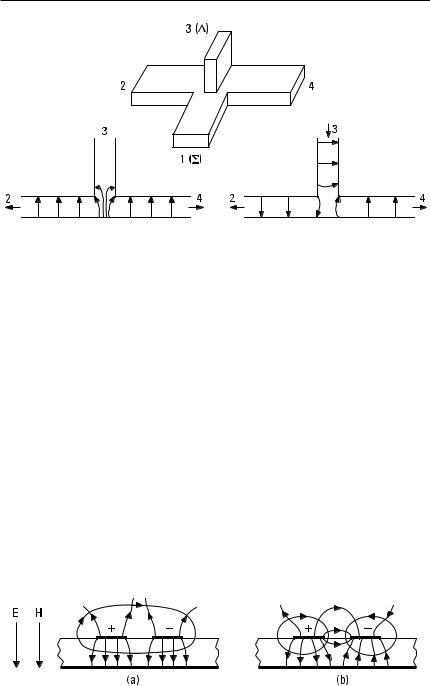
124 Radio Engineering for Wireless Communication and Sensor Applications
Figure 6.8 Magic T-junction and its field patterns.
divided into ports 2 and 4 equally and in the same phase, due to symmetry. The electric field distribution has an even symmetry with respect to the middle line of port 3, whereas the field of the TE10 mode has an odd symmetry. Therefore, a wave cannot couple from port 1 to port 3. Also, a wave applied to port 3 (D) is divided into ports 2 and 4 with equal amplitude, but now the output waves have an opposite phase.
6.1.5 Microstrip Directional Couplers
Let us consider two parallel microstrip lines that are placed so close to each other that the fields of the lines couple to each other. Then a wave propagating in one line can excite a wave in the other line. The fields of a coupled line can be presented as a superposition of an even mode and an odd mode, shown in Figure 6.9. In case of the even mode the currents of the lines are equal and in the same direction; in case of the odd mode they are equal but in the opposite directions. A coupled line may be represented with an even-mode characteristic impedance Z 0e and an odd-mode characteristic impedance Z 0o , which are characteristic impedances of one of the strip
Figure 6.9 Fields of (a) the even mode and (b) the odd mode in a coupled microstrip line.
Passive Transmission Line and Waveguide Devices |
125 |
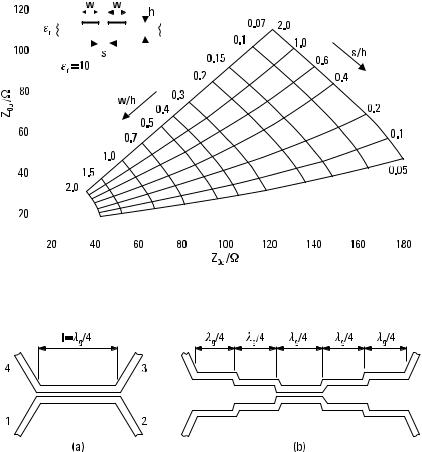
conductors relative to the ground when the coupled line is operated in the even mode or odd mode, respectively. The graph in Figure 6.10 gives these impedances when the relative permittivity of the substrate is 10.
The microstrip lines shown in Figure 6.11(a) are coupled to each other over a length of l . Let us assume that a signal source is at port 1 and other ports are terminated with loads having an impedance of Z 0 . It can be proven that all the ports are matched if
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z 0 = √ |
Z 0e Z 0o |
(6.20) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 6.10 Even-mode and odd-mode characteristic impedances of coupled microstrip lines; er = 10.
Figure 6.11 Directional couplers based on coupled microstrip lines: (a) single-element coupler; and (b) multielement coupler.
126 Radio Engineering for Wireless Communication and Sensor Applications
When l = l g /4 the coupling to port 4 reaches its maximum value and no signal is coupled to port 3. Thus, this device operates as a directional coupler. (Note that the coupled port is on the same end as the input port, unlike in Figures 6.6 and 6.7.) The characteristic impedances of the coupled line depend on Z 0 and on the voltage coupling coefficient K = | V4 /V1 | as
|
1 |
+ K |
|
|
|
|||
Z 0e = Z 0 √ |
|
|
|
|
|
(6.21) |
||
1 |
− K |
|||||||
1 |
− K |
|
|
|
||||
Z 0o = Z 0 √ |
|
|
|
(6.22) |
||||
1 |
+ K |
|
||||||
Equations (6.20) through (6.22) are valid if the even-mode and oddmode waves propagate at the same speed. In a coupled microstrip line, this is not exactly true, and the directivity is worse than in an ideal case. The structure of Figure 6.11(a) is best suited for realizing a weak coupling (large C ). The lines would be impractically close to each other to achieve a strong coupling. The single-element coupler has a bandwidth that may be too narrow for some applications. A broadband directional coupler is obtained by connecting quarter-wave sections with appropriate couplings, as in Figure 6.11(b).
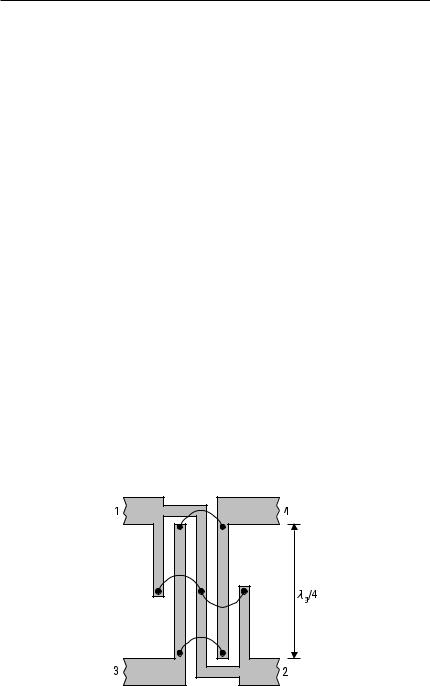
The directional coupler shown in Figure 6.12 is called the Lange coupler and is suitable for realizing strong couplings as 3 dB to 6 dB. It is made of several coupled lines bonded together with thin wires.
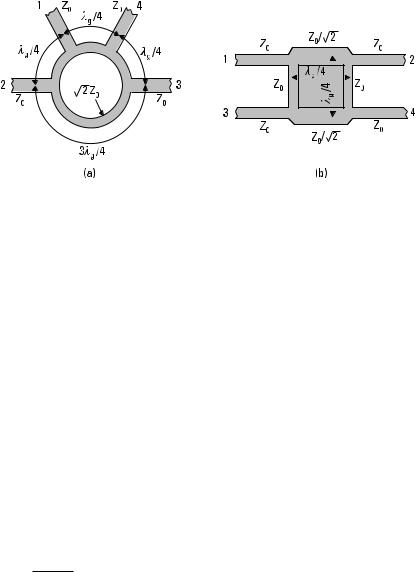
The ring coupler illustrated in Figure 6.13(a) is a 180° hybrid. Its scattering matrix is obtained by multiplying the matrix of (6.17) by −j , if
Figure 6.12 Lange coupler.
Passive Transmission Line and Waveguide Devices |
127 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 6.13 Hybrids: (a) ring hybrid; and (b) branch-line hybrid.
the reference planes are at the T-junctions. The characteristic impedances of the ports are Z 0 and that of the 3lg /2-long ring is √2Z 0 . A wave applied to port 1 (S) does not couple to port 3 because the two paths have a difference in length of lg − lg /2 = lg /2 , but it couples to ports 2 and 4 in the same phase. A wave applied to port 2 (D) couples to ports 1 and 3 in an opposite phase.
The branch-line coupler shown in Figure 6.13(b) is a 90° hybrid. The lg /4-long branches have characteristic impedances of Z 0 and Z 0 /√2 . For example, a wave applied to port 1 couples to ports 2 and 4 with a phase difference of 90°, and port 3 is isolated from port 1. Both ring and branchline couplers can be modified so that the ratio of output powers differs from 1.
Example 6.1
Design a 50-V microstrip directional coupler operating at 1 GHz with a coupling of C = 15 dB. The properties of the substrate are: er = 10, h = 0.254 mm, t = 5 m m. Use the structure presented in Figure 6.11(a).
Solution
The voltage-coupling coefficient corresponding to a 15-dB coupling is K = √1/101.5 = 0.1778. From (6.12) and (6.13) we get Z 0e = 59.8V and Z 0o = 41.8V. We use the graph of Figure 6.10 for er = 10, and read w /h = 0.9 and s /h = 0.9. Thus, both the width of strips forming the coupled line and their separation is 0.23 mm. According to (3.85), the effective
relative permittivity is e = 6.69. The length of the coupled line section
X C reff
is l/4 = c / 4f √ereff = 29.0 mm. The strip width of 50-V lines is 0.234 mm.
