
- •Apple pie
- •Предисловие
- •14 20 27 206 300 Strong long wider
- •1V ocabulary
- •4. 5.
- •I met a man with seven wives,
- •Sport or craziness?
- •Optimist or Pessimist?
- •This is london!
- •Weddings in Indonesia
- •Holidays and festivals in the uk.
- •Veteran’s Day
- •Independence Day
- •Vocabulary
- •Anxiety
- •Vocabulary
- •Grammar
- •Reading
- •123. Выберите заголовок.
- •Classroom instructions
- •1.Образование множественного числа существительных.
- •2. Притяжательный падеж
- •6. Present Simple
- •7. Present Continuous
- •8. Past Simple
- •9. Past Continuous
- •10. Future Simple
- •12. Modal Verbs
- •13. Вопросы
- •Irregular verbs
- •Contents
1V ocabulary
|
In this unit you will…
and Indefinite Pronouns |
3 2
1. Match the shops from the box to the pictures 1-3. Study the rest of the key words. Use your dictionary if necessary. Learn the words.
|
Shops: department store, supermarket, newsagent, butcher’s, chemist’s, baker’s, dairy, grocer’s, greengrocer’s, cookery. Note: most other shops are just “+ shop (shoe shop, furniture shop, etc.) Shopping: shop assistant, cash-desk (till), price, change, size, shopping list, shop window, counter, changing-room. Clothes: skirt, trousers, blouse, suit, jacket, sweater, socks, jumper, coat (raincoat, fur-coat), dress, tie, scarf, jeans, shirt, T-shirt, gloves, hat, stockings. Footwear: shoes, boots, sneakers, slippers. Accessories and jewels: belt, umbrella, handbag, lace, earrings, ring, necklace. Food: milk, bread, cheese, meat (pork, lamb, beef), fish, chicken, sausages, eggs, rice, bacon, honey, cereal, crisps, jam, youghurt, oil, butter, cake, ice-cream, fruit (apple, pear, peach, lemon, orange, grapes, melon, pine-apple), berries (strawberry, raspberry, cherry), vegetables (carrot, potato, tomato, cabbage, cucumber, onion, pepper, mushrooms), tea, coffee, juice, beer, cola, sugar, salt, flour. Adjectives: fresh, comfortable, loose, tight, expensive, cheap, tasty, stylish. Expressions: do shopping, go shopping, shop around for, go window shopping, buy, sell, cost, pay, try on, wear, match, fit well, look for, put on, take off, do up, undo. |
2. Give it a name:
a large shop
a sum of money for which a thing is sold
a large shop with many departments
something that is used to keep people warm
something that you put on your head
footwear for sport
a place where you try on your new clothes
something that is produced by bees
a shop where you can buy ready-made food (salads, pies, roast meat)
something that saves from the rain
3. Write down:
5 things usually worn by women only
5 things worn by men and women
5 more things you have at home
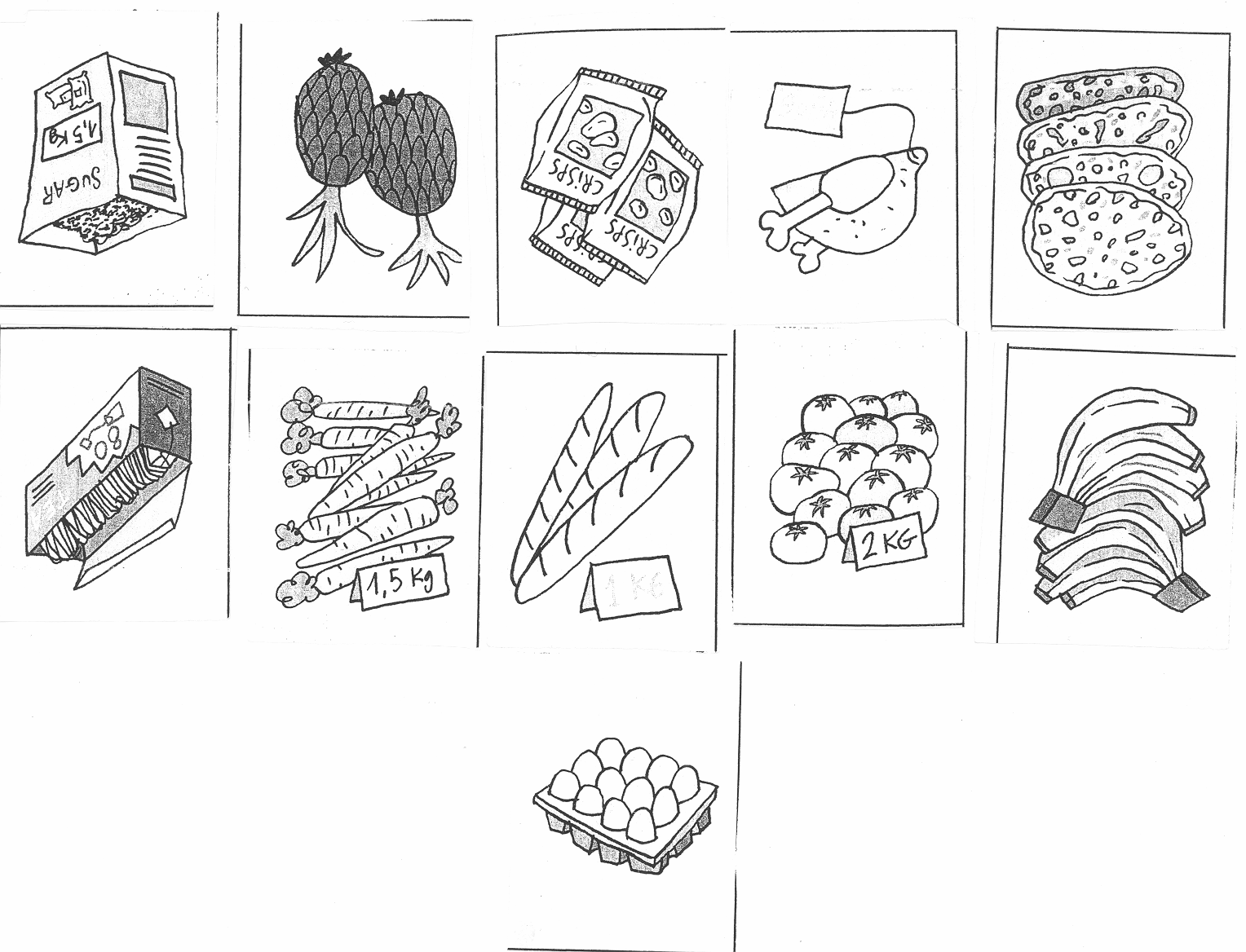
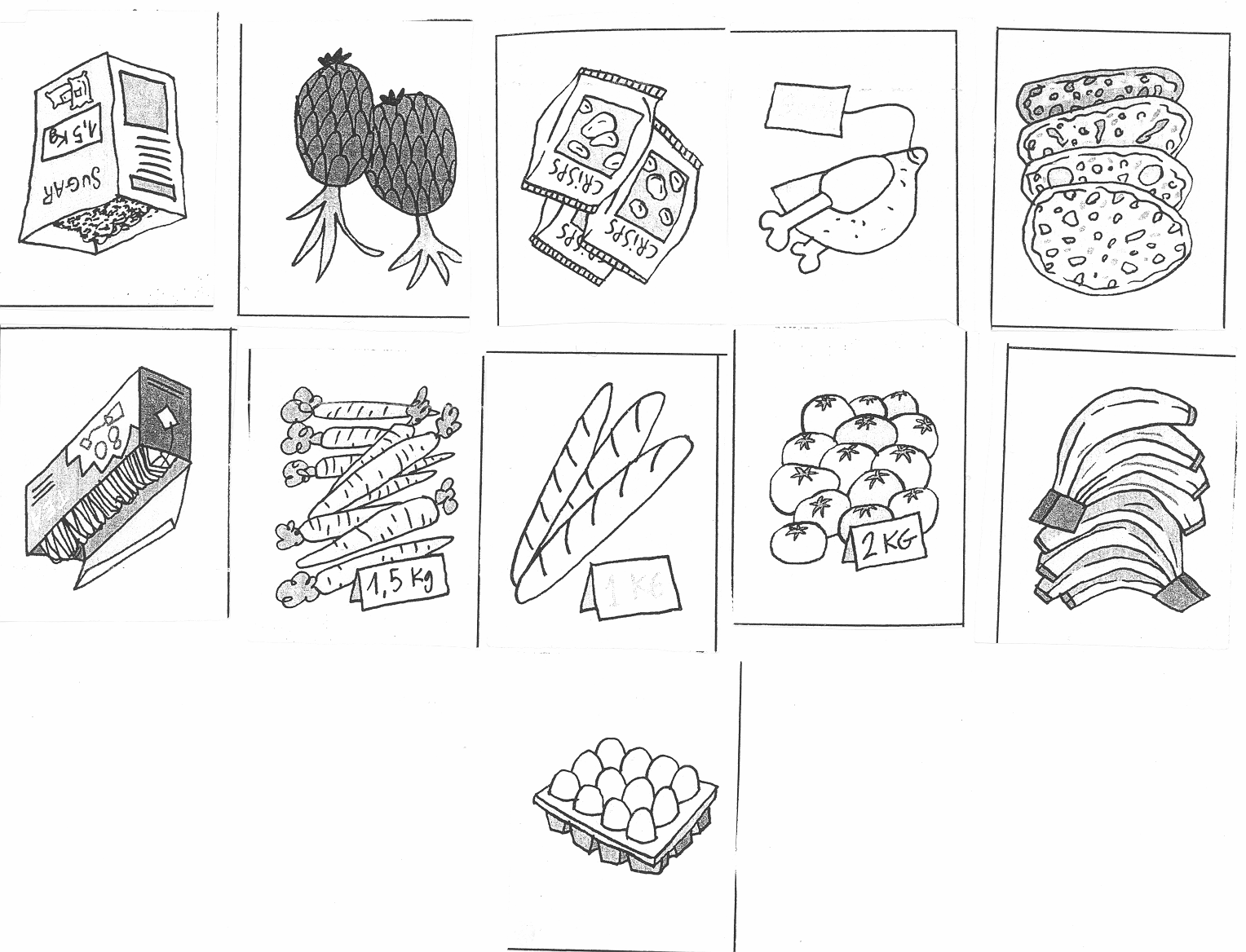
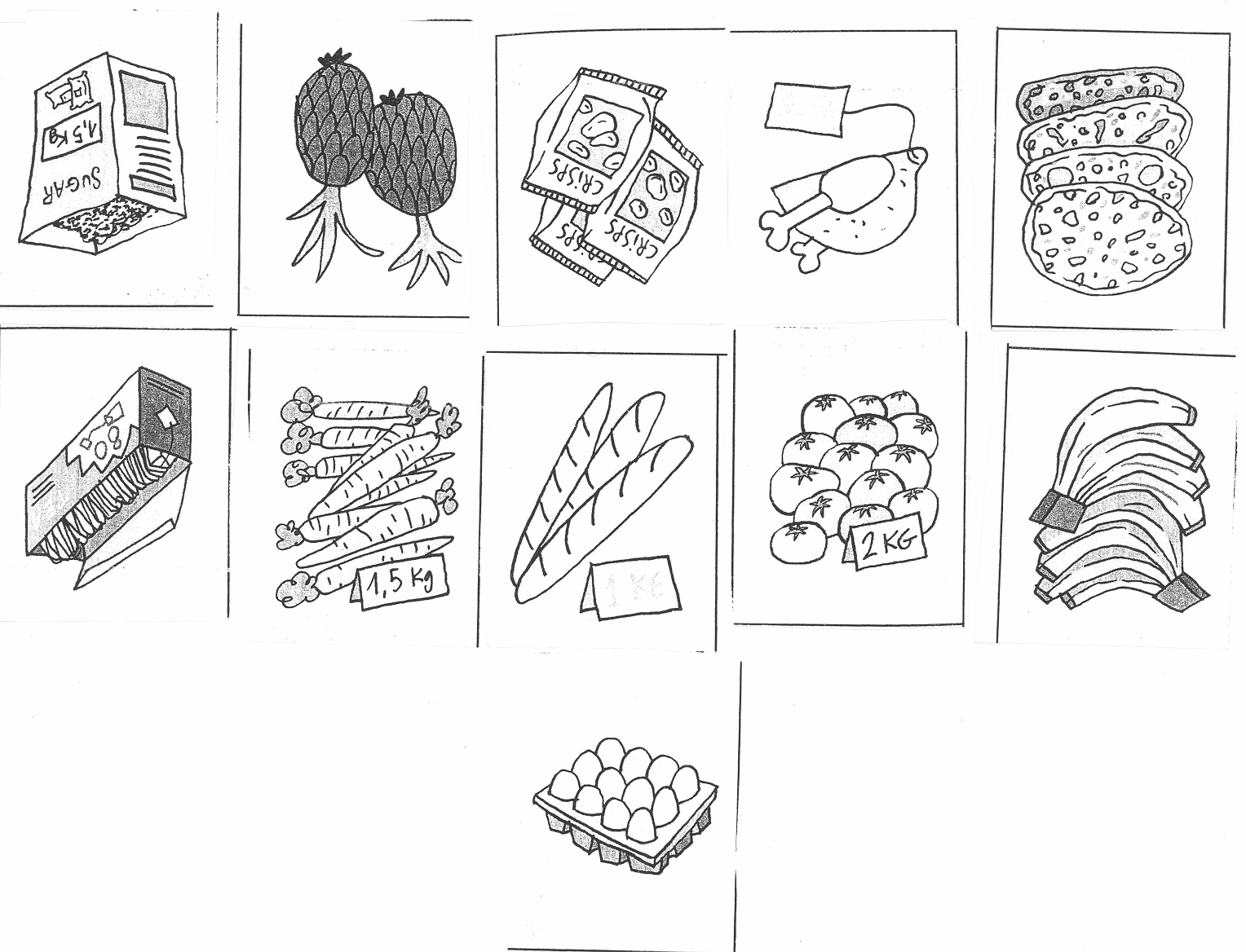
4. Look at the pictures and say what their prices are.
Example: These crisps cost 25 rubles.











5. Fill the gaps with suitable words. See key words:
wear fit low heel feet pair size high heel comfortable try on tight
- What kind of shoes do you want, miss?
- I need walking shoes with ……………… . …………… are not good for country ………. . You see I have rather smack …………. .
- Here is a………….. about your …………. . ……… them …… . How are they?
- They are rather ……………………, but they are a little ……………, can you show me another pair in a bigger…….., please?
- Certainly, miss. How do you find these?
- They …………… me very well, thank you (18).
6. Look at the word search below. There are 17 words connected with food. They go across and down. Find them and write them here. The words begin with these letters.
M………. B…………. C……….. F………… H……….. STEAK…
C………. R…………. L……….. B………... V……….. Y………...
P……….. E………….. G……….. B………… J……….. T…………
L C Y P N C R I S P S M
A V Z O B P B A N A N A
M U S T E A K N B T R R
B Z Q A M O Y R Y J A M
K G F T G H O D F G H A
B A C O N F G R A P E L
H J K F I S H T Y U I A
H O N E Y B U B R E A D
R A S D F G R Z K L P E
I B V E G E T A B L E I
C Z X C V B N M L P G J
E W E C E R E A L B G U
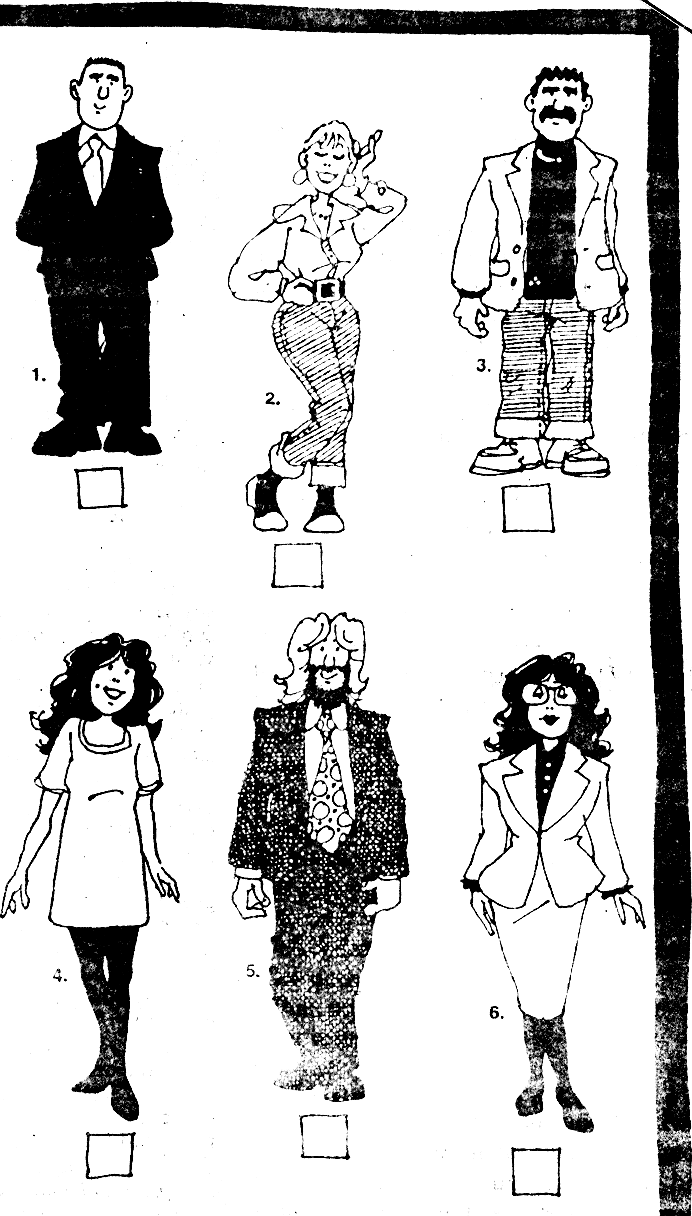
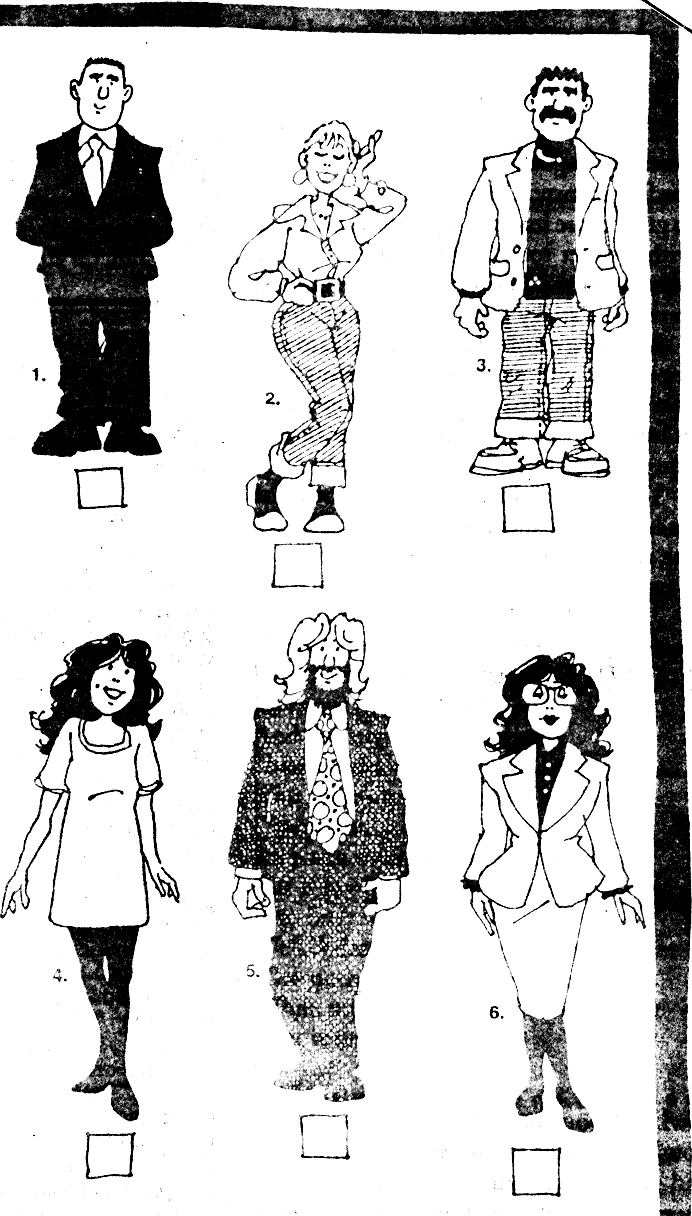
7. Join the pictures to the correct description. There are more descriptions than pictures. You don’t need to use all of them (12).
1) 2) 3) 4)
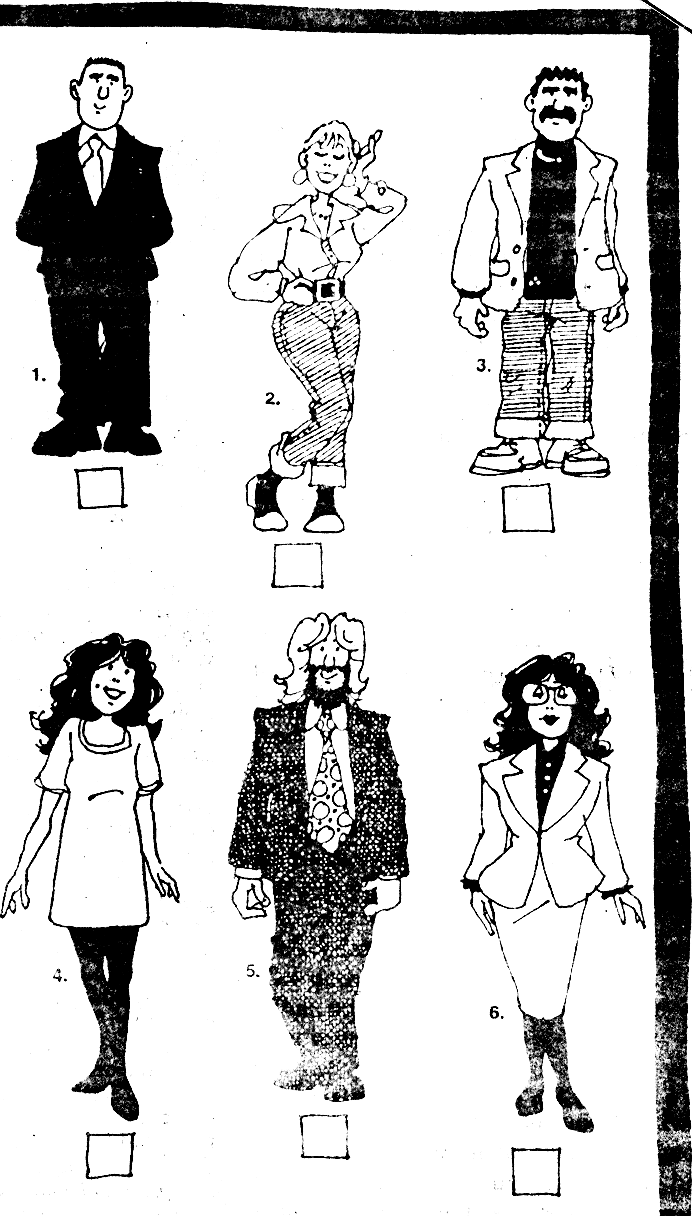


a) He has got short dark straight hair. He is wearing a jacket and a black sweater.
b) She has got long dark wavy hair. She is wearing black stockings and a white dress. She is wearing glasses.
c) She has got dark wavy hair. She is wearing a dark blouse and a white suit.
d) He has got dark hair. He is wearing a white shirt and a tie.
e) He has got dark hair. He is wearing a white suit.
f) She has wavy hair and a pleasant smile. She is wearing a white dress.
Grammar Focus
Presentation Present Simple/ Present Continuous
1. Solve the riddle below (answer p.120).
Old Horace lives with me.
When he comes home at three,
He knocks at the door,
He rolls on the floor
And comes to sit with me.
He is watching my TV now,
He is sitting on my knee now,
He is napping on my lap
Old Horace is my …….!
by I. Vereshchagina
Look at the riddle. Can you translate the verbs in italics?
2. Complete the table with these words: lives, knock, roll, is, am, are.
|
Present Simple |
Present Continuous | ||
|
Affirmative
|
Old Horace …. with me.
|
Affirmative
|
He/she is watching my TV now. I/am watching … You/we/they are watching … |
|
Question
|
Does he ….. at the door?
|
Question
|
… he/she watching my TV now? … I watching…? … you/we/they watching …? |
|
Negative
|
He does not …. on the floor.
|
Negative
|
He/she … not watching my TV now. I … not watching my TV now. You/we/they … not watching my TV now.
|
See Grammar Summary p.112
3. Write the –ing form of the verbs. Mind your spelling.
|
wear – wearing write – writing sit – sitting go – going hold – holding run - running
|
1. walk ……. 2. read ……. 3. use ……. 4. buy ……. 5. do …….
6. sing ……. 7. stop ……. 8. listen ……. 9. sell ……. 10. drive ……
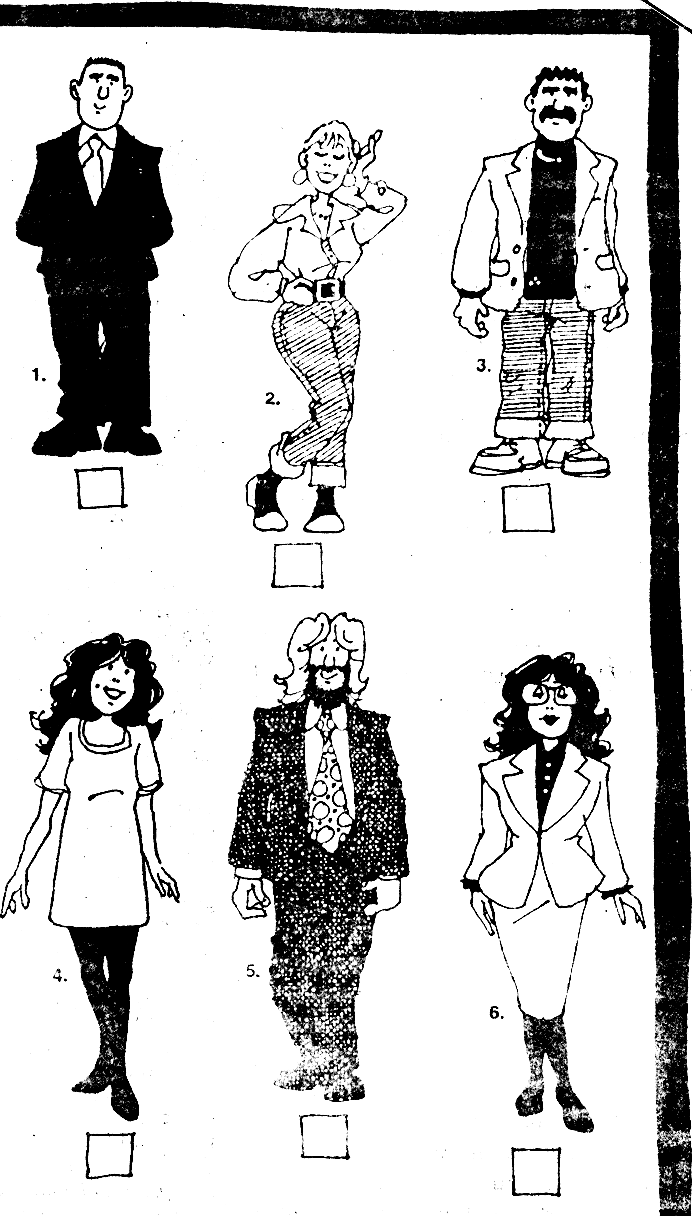
4. Look at the people in the pictures (22). What are they wearing? What are they doing?



5. Look at the sentences below. Which of them are true for you now?
wearing jeans 11. sitting at the cash-desk
wearing trousers 12. standing in the changing-room
wearing slippers 13. doing up my buttons
wearing a T-shirt 14. trying on a new dress
wearing a suit 15. drinking coffee
wearing earrings 16. buying tomatoes and cucumbers
wearing a coat 17. looking for a newsagent
wearing a blouse 18. taking off my coat
wearing a skirt 19. choosing carrots at greengrocer’s
wearing a jacket 20. doing an exercise
6. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct tense (Present Simple/Present Continuous) (18).
a) We usually ………………. (go) to Spain on holiday, but this year we ………… (go) to Florida.
b) A Why ………….. you ………….. (buy) so much food?
B Because we …………. (have) a party tonight.
c) My father ………………(live) in a house near the sea because he …………… (like) sailing.
d) …………… you ……………. (watch) the television? Can I turn it off?
e) A How often …………….. you ………….. (go) swimming?
B About once a week.
f) A What newspaper …………. you usually …………. (read)?
B The Times.
g) A The telephone …………………. (ring)!
B OK. Hello? No, Sally is not here at the moment. She ………………. (play) tennis.
Presentation many/much/a little/a few
7. a) Read the following dialogue. What do words in italics mean?
|
|
Countable nouns |
Uncountable nouns |
|
Much |
|
|
|
Many |
|
|
|
(a) few |
|
|
|
(a) little |
|
|
How much sugar should I put in the cake?
Just a little, not too much.
How many cherries should I put in the cake?
Just a few, not many.
b) Read the dialogue again and tick the right boxes See Grammar Summary p. 110.
in the table.
8. Who could say these words? A millionaire or a poor person? Why?
1. I have many cars in my garage.
2. I have many problems with banks.
3. When I get a present of money I try to save as much of it as possible.
4. I have a few friends in London, Paris and New York.
5. I have little time to discuss this question. I’ll call you later.
6. I have little money in my wallet.
9. Make up sentences using much, many, (a) few or (a) little and the words bellow.
1) size; 2) furniture; 3) lemon; 4) rice; 5) yoghurt; 6) supermarket; 7) cheese; 8) tomato; 9) sausage; 10) strawberry; 11) flour; 12) lace; 13) umbrella; 14) jeans; 15) tea.
10. Complete the sentences using: many, much, few, little, a few, a little, a lot of.
1) Is there …… furniture in your cottage? 2) I put …… salt in my soup, perhaps, too …… . 3) Has he …… or …… free time? 4) Don’t put …… milk into his coffee. 5) She has …… beautiful dresses. 6) Jane drinks …… coffee and …… tea. 7) How …… money do you need to buy this necklace? 8) Please give me …… water. 9) I need …… tomatoes to prepare this salad. 10) There is …… sugar in the bowl, and we should put …… sugar there. 11) Tom has …… clothes; 12) I never eat …… bread with soup; 13) Please don’t put …… pepper on the meat; 14) He has …… pairs of socks; 15) There is only …… soup in the saucepan.

11.
Game «Just 18
mistakes»
Work in groups of 4 (3 players and a referee). Each group will need
a dice and 4 counters. The aim of the activity is to put the
counters in the Start Box, roll the dice and move to the Finish Box
correcting the sentences on the way. The first one to come is the
winner. The referee tells the players if their answers are right or
wrong, but doesn’t give them the answer. If a player cannot find
a mistake he/she moves back to the same number he/she moved forward
and waits for the next turn. Players
see p.104
Referees
see p.120

Reading
1. How much money do you spend monthly on cosmetics, clothes, food? Compare your list with others.
|
Cosmetics |
Clothes |
Food |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Skim through the first paragraph and say what the text is about, then read the text and check your guesses.
New Social Disease
Shopomania has come to Russia. Uncontrollable passion for shopping brought to ruin many Europeans and Americans. Now it’s our turn. Even experienced foreigners get a shock when they see the way some Russians behave in shops. Shopomania went pear-shaped in our country. Not only oligarchs’ wives but also common people suffer from this new social disease: they manage to leave incredible sums of money in shops and widespread consumer credits tempt them to waste more and more. The vast majority of people realize that they are sick only at the moment of payoff, but sometimes it may be too late.
Oniomania has plenty of reasons. People deprived of something in the childhood are the first victims. The most part of shopaholics are people with serious complexes, thinking that they don’t meet the modern life standards. These days glamour ideology prevails in the society, which makes a person earn money in order to spend all it on houses, cars or expensive clothes. Russia is a country of extremes. During shop-tours abroad Russian people behave like barbarians.
Another reason of oniomania is great amount of commercials and advertisements. Billboards, beautiful pictures of basically useless products drive Russians crazy.
The interesting fact is that Russian female student spend about 20 percent of their salary on cosmetics and very often these are high-class products. Sometimes this kind of passion may even destroy lives or relationships as the vast majority of Russian men can’t understand why a young beautiful girl should waste money on a cream priced at 900 rubles (33dollars).
Nevertheless, oniomania overcame not only the fair sex but lots of men, too, and their number is increasing. Generally men are addicted to purchasing cars, books, technical equipment and its constituents. In some forms of oniomania men have surpassed women.
Should one take this phenomenon as a disease? Scientists note: craft of oniomania lies in the fact that Russian people don’t consider it to be a disease. However, any person is able to get over the addiction; success is very often directly connected with a shopaholic’s capability to give a negative answer to the question: do I really need this thing?
3. Read the statements. Decide whether each statement is true or false.
a. Uncontrollable passion for shopping isn’t a social disease for Russia, only Europeans and Americans suffer from it.
b. Not only oligarchs’ wives but also common people suffer from oniomania.
c. The first victims of oniomania are people who had everything in their childhood.
d. The most part of shopaholics are people with serious complexes, thinking that they don’t meet the modern life standards.
e. During shop-tours abroad Russians behave like cultural people.
f. Great amount of commercials and advertisements isn’t a reason of oniomania.
g. Oniomania overcame not only the fair sex but lots of men, too.
4. Answer the following questions:
a. Why do experienced foreigners get a shock when they see Russians in shops?
b. When do people begin to understand that they are shopaholics?
c. What kind of ideology does prevail in our society?
d. What kind of female passion, according to the text, is harmful for relationships between men and women?
e. What goods do men generally spend money on?
f. What question is very useful to get over the oniomania’s addiction?
5. What is your own attitude to shopaholics? Are they really sick people? Is shopomania a social disease or just a normal way of living for many people? Discuss each of the arguments in the table carefully. Think of any new arguments you can add. See p.103
-
Against
For
1. It is not normal for people to want to buy basically useless products, it is craziness.
2. Clothes, technical equipment and other goods are things that help people feel comfortable. And it is enough to have only one fur-coat, one television, one car, etc.
3.
4.
1. We live only once and it is normal to buy everything we want.
2. Shopomania isn’t a disease. Shopping is a good way to relax and to forget about problems, even if you buy useless things.
3.
4.
Writing
-

The Manager
Sportscene 66 Chapel Road
Long Street CARDIFF
CARDIFF
21st May 2006
Dear Sir/Madam,
I’m writing to complain about a pair of Nike sneakers I
bought in your main shop two Saturdays ago and the way
your assistant spoke to me when I called in it the
following Monday to return them.
I bought this pair – they were very fashionable ones –
after I saw you were advertising a sportswear sale.
However, the first time I wore them I realized that there
were different in colour laces in them.
When I explained it to the assistant he told me he couldn’t
give me my money back because I don’t have a receipt.
I demanded to see the manager but I was told that it
wasn’t possible because you were on holiday.
I insisted that as you weren’t there he should give me my
money back but unfortunately he became extremely rude.
I enclose the pair of sneakers and I must ask you to let me
have a full refund immediately (5,6).
Yours faithfully,
Stuart Blake

1. Give at least one reason why you might write to complain to:
a shop
a telephone company or the Post Office
a transport company (taxi, bus, train)
a builder, plumber or electrician
a language school
2. Write a letter of complaint
a) Choose a situation from Exercise 1 and make notes.
b) Divide your letter into three paragraphs (see the boxes below)
Use the expressions in brackets if you wish (5, 6).
|
PARAGRAPH 1 Say why are you complaining. (I’m writing to draw your attention to… /to object to…)
|
|
PARAGRAPH 2 Give background Information, such as precise details of the problem, how you discovered it and how you feel about it. (I think it’s awful that…; I’m very surprised that such a reputable organization as yours...) |
|
PARAGRAPH 3 Request action. (I feel Something ought to be done to…; It’s time you…; I will take further action if…; I demand that you…; Please replace…; I would be grateful if you could…) |

Speaking
1. Read the dialogue ‘In a clothes shop’. Underline the expressions which help you to buy a necessary thing.
Assistant: Can I help you?
Customer: Yes I’m looking for a white blouse. or
No, I’m just looking, thanks. or
I’m being served, thanks.
Assistant: What size are you?
Customer: Er, 46 usually.
Assistant: OK. Here we are. The last one in stock.
Customer: Great. Where is the changing room? I want to try it on.
Assistant: It’s down there on the right. Well, how is it?
Customer: Fine. I’ll take it. Where do I pay for it?
Assistant: Over at the cash desk.
Customer: And can I pay by credit card?
Assistant: Surely.
2. Look at the lines of some conversations in a clothes shop. a) Who says them, the customer or the shop assistant? Put C or A.
Can I try it on? Yes, it feels fine.
Mm, that’s nice. It is a bit too big/small/long/short.
Medium. $ 25.
Can I help you? Yes, I’m looking for a jumper.
Is it the right size? No, I don’t like the colour.
How much is it? What about this one?
Have you got something bigger? That’s the last we have got.
By credit card. I’ll have it, please.
This one is a bit darker. I’ll leave it, thanks.
What size are you? What colour are you looking for?
Blue. Thank you. How would you like to pay?
Yes, the changing rooms are over there.
b) Match the lines to make short dialogues.
3. Work in pairs. Make a big conversation using real clothes.

1. Put the verbs in brackets in the correct form (Present Simple or Present Continuous).
1 .
We (go) to the seaside every summer. 2. Listen! Somebody (knock) on
the door. 3. How often you (wash) your dog? 4. She can’t come to
the phone. She (wash) her hair. 5. Where (be) Kate? She usually
(sit) in the front row. I (not know) why she (sit) here now. 6.
Please be quiet! The baby (sleep). 7. What you (laugh) at? 8. I
hardly ever (work) on Mondays now. 9. The countryside (be) wonderful
especially when it (snow). 10. Why you (smoke) here? – And where
people usually (smoke) in this building?
.
We (go) to the seaside every summer. 2. Listen! Somebody (knock) on
the door. 3. How often you (wash) your dog? 4. She can’t come to
the phone. She (wash) her hair. 5. Where (be) Kate? She usually
(sit) in the front row. I (not know) why she (sit) here now. 6.
Please be quiet! The baby (sleep). 7. What you (laugh) at? 8. I
hardly ever (work) on Mondays now. 9. The countryside (be) wonderful
especially when it (snow). 10. Why you (smoke) here? – And where
people usually (smoke) in this building?
2. Each sentence has a mistake. Find it and correct it.
a) I’m going to the cinema tonight.
b) How much you earn in your job?
c) We no wear a uniform at my school.
d) That’s my husband over there. He stands near the window.
e) Sorry. You can’t speak to Jenny. She’s have a bath.
f) Peter is a businessman. He’s work all over the world.
g) At the moment Peter’s work in Russia.
h) Where your sister work? (19).
3. Imagine that you are at a party. Look around and say what the guests are doing and what they are wearing.
4. How much or how many?
1) ……………………………… cups of tea does your father drink at teatime?
2) ……………………………… kittens has your cat got?
3) ……………………………… bread do you eat with soup?
4) ……………………………… books do you carry in your schoolbag?
5) ……………………………… milk did your mother put in your porridge?
6) ……………………………… salt does your granny usually put in your salad?
7) ……………………………… snow is there in the streets of Moscow in winter?
8) ……………………………… skates have you got?
9) ……………………………… moons are there in the sky?
10) ……………………………. children has your aunt got?
11) ……………………………. juice can you drink when you are thirsty?
12) ……………………………. spaghetti does your mother buy?
13) ……………………………. days are there in September?
1 4)
……………………………. apples grow on your apple-tree?
4)
……………………………. apples grow on your apple-tree?


The Christmas season has an early start in England. In October the first Christmas cards appear in the shops. As early as the beginning of December, Christmas trees are already glittering in most homes.
Christmas Eve is on the 24th of December. On this day everybody is very busy and in a hurry. On Christmas Eve children hang their Christmas stockings on their beds or fireplace. They wait for Santa Claus.
Christmas Day is on the 25th of December. British people celebrate this holiday with big family dinners. Traditionally they eat Christmas pudding and a big roast turkey. Most people do not go to work on that day.
Every English family sends and receives many Christmas cards. Traditionally there is robin on a card, as it is a Christmas bird. Many years ago postmen had bright red coats. They looked like robins.
T raditionally
people put their Christmas presents into boxes. That is why the day
on which they give and receive these boxes is called Boxing Day. It
comes after Christmas Day. It is on the 26th
of December. But the name of this day also goes back to the past
when boxes of food and gifts were given to the poor. Today this is a
day of relaxation, sporting events, dances or maybe going to the
theatre. Families with children often go to see pantomimes – often
shortened to ‘panto’ – which is a very popular custom.
raditionally
people put their Christmas presents into boxes. That is why the day
on which they give and receive these boxes is called Boxing Day. It
comes after Christmas Day. It is on the 26th
of December. But the name of this day also goes back to the past
when boxes of food and gifts were given to the poor. Today this is a
day of relaxation, sporting events, dances or maybe going to the
theatre. Families with children often go to see pantomimes – often
shortened to ‘panto’ – which is a very popular custom.
Words:
1. glitter – блестеть, сверкать
2. turkey – индейка
3. robin – малиновка
4. poor - бедняки



|
In this unit you will…
|
1.
3.
2.

7.
