
MICROSOFT Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
.pdfMicrosoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. In UNIX and GNU, a collection of compressed files that has been prepared for transmission by an e-mail service using the shar command.
shell out
vb. To obtain temporary access to the operating-system shell without having to shut down the current application and return to that application after performing the desired shell function. Many UNIX programs allow the user to shell out; the user can do the same in windowing environments by switching to the main system window.
shell script
n. A script executed by the command interpreter (shell) of an operating system. The term generally refers to scripts executed by the Bourne, C, and Korn shells on UNIX platforms. Also called: batch file. See also batch file, script, shell1.
Shell sort
n. A programming algorithm used for ordering data in which data are sorted in subsets so that the process works its way from unsorted to progressively more sorted. Named after its inventor, Donald Shell, it is faster than the bubble sort and the insertion sort. See also algorithm. Compare bubble sort, insertion sort.
Sherlock
n. An advanced search mechanism included with the Macintosh OS. Sherlock provides the ability to search multiple Internet search engines simultaneously and incorporates the Macintosh Find File interface for searches of local volumes. Additional plug-ins can expand the number of search engines available for access and increase search options.
shielded twisted-pair wiring n. See twisted-pair wiring.
shift
vb. In programming, to move the bit values one position to the left or right in a register or memory location. See also end-around shift. Compare rotate (definition 2).
Shift+click or Shift click
vb. To click the mouse button while holding down the Shift key. Shift+clicking performs different operations in different applications, but its most common use in Windows is to allow users to select multiple items in a list, for example, to select a number of files for deletion or copying.
Shift key
n. A keyboard key that, when pressed in combination with another key, gives that key an alternative meaning; for example, producing an uppercase character when a letter key is pressed. The Shift key is also used in various key combinations to create nonstandard characters or to perform special operations. The term is adapted from usage in relation to manual typewriters, in which the key physically shifted the carriage to print an alternative character. See also Caps Lock key.
Shift-PrtSc
n. See Print Screen key.
shift register
n. A circuit in which all bits are shifted one position at each clock cycle. It can be either linear (a bit is inserted at one end and “lost” at the other during each cycle) or it can be cyclic or looped (the “lost” bit is inserted back at the beginning). See also register, shift.
Shockwave
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
781 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. A format for multimedia audio and video files within HTML documents, created by Macromedia, which markets a family of Shockwave servers and plug-in programs for Web browsers. See also HTML.
shopping cart
n. In e-commerce programs, a file in which an online customer stores information on potential purchases until ready to order. Usually represented on screen with a drawing of a shopping cart, the virtual shopping cart provides a recognizable point of reference to users new to the e- commerce experience. See also e-commerce.
short card
n. A printed circuit board that is half as long as a standard-size circuit board. Also called: halfcard. See also printed circuit board.
short-circuit evaluation
n. A form of expression evaluation that guarantees that Boolean expressions will be evaluated only far enough to determine their value. See also AND, Boolean operator, OR.
shortcut
n. In Windows 9x, Windows XP, Windows NT 4, and Windows 2000, an icon on the desktop that a user can double-click to immediately access a program, a text or data file, or a Web page. See also symbolic link.
shortcut key
n. See accelerator.
short-haul
adj. Of or pertaining to a communications device that transmits a signal over a communications line for a distance less than approximately 20 miles. Compare long-haul.
short message service
n. Service for wireless phones that allows users to send and receive brief messages consisting of text and numbers. Acronym: SMS.
shout
vb. To use ALL CAPITAL LETTERS for emphasis in e-mail or a newsgroup article. Excessive shouting is considered a violation of netiquette. A word can be more acceptably emphasized by placing it between *asterisks* or _underscores_. See also netiquette.
shovelware
n. A commercially sold CD-ROM containing a miscellaneous assortment of software, graphic images, text, or other data that could otherwise be obtained at little or no cost, such as freeware or shareware from the Internet and BBSs or public-domain clip art. See also BBS (definition 1), freeware, shareware.
ShowSounds
n. In Windows 9x and Windows NT 4, a global flag that instructs application programs to provide some kind of visual indication that the program is generating a sound in order to alert users with hearing impairments or those in a noisy location such as a factory floor.
shredder
n. An application designed to completely destroy digital data so it cannot be reconstructed with file recovery software.
shrinkwrap agreement
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
782 |

Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. A contract or license in or on a software box or package that sets forth conditions for use of the software. Typically, a shrinkwrap agreement states that a user accepts the terms of the agreement when he or she opens the box. A shrinkwrap agreement is a print version of an EndUser License Agreement. Also called: box-top license. See also End-User License Agreement. Compare clickwrap agreement.
shrink-wrapped
adj. Boxed and sealed in clear plastic film for commercial distribution. Use of the term implies a final version of a product as opposed to a beta version. See also beta1.
SHS virus
n. Any of a class of viruses that infect a user’s system by hiding in files with an .shs extension. These viruses typically spread through e-mail attachments. A widely distributed e-mail warning cautions readers to beware of the “SHS virus,” but no one specific virus by that name exists.
SHTML
n. Short for server-parsed HTML. Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) text that contains embedded server-side include commands. SHTML documents are fully read, parsed, and modified by the server before being passed to the browser. See also HTML, server-side include.
S-HTTP or SHTTP
n. Acronym for Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol. An extension to HTTP that supports various encryption and authentication measures to keep all transactions secure from end to end. S-HTTP is designed to ensure the security of individual transmissions over the Internet and has been approved as a standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). S-HTTP should not be confused with HTTPS, a Netscape-developed technology based on SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). HTTPS is also designed to ensure secure transmissions, but does so between communicating computers rather than on a message-by-message basis. Also called: Secure HTTP. See also SSL.
shut down
vb. To close a program or an operating system in a manner ensuring that no data is lost.
sibling
n. A process or node in a data tree that is descended from the same immediate ancestor(s) as other processes or nodes. See also generation (definition 2), node (definition 3).
sideband
n. The upper or lower portion of a modulated carrier wave. One portion can be processed while the other is used to carry separate data, a technique that doubles the amount of information that can be carried over a single line. See the illustration.
Sideband.
sidebar
n. A block of text placed to the side of the main body of text in a document, often set off by a border or other graphic element.
side-by-side execution
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
783 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. The ability to install and use multiple versions of an assembly in isolation at the same time. This can occur on the same machine, or in the same process or application domain. Side-by-side execution can apply to applications and components as well as the components of the .NET Framework. Allowing assemblies to run side-by-side is essential to support robust versioning in the common language runtime.
side effect
n. Any change of state caused by a subroutine, such as a routine that reads a value from a file and advances the current file position.
side head
n. A heading placed in the margin of a printed document and top-aligned with the body text, rather than being vertically aligned with text, as is a normal head.
sieve of Eratosthenes
n. An algorithm for finding prime numbers. It is often used as a benchmark in testing the speed of a computer or programming language. See also benchmark1.
.sig
n. A file extension for a signature file for e-mail or Internet newsgroup use. The contents of this file are automatically appended to e-mail correspondence or newsgroup articles by their respective client software. See also signature file (definition 1).
SIG
n. Acronym for special interest group. An e-mail online discussion group or a group of users who meet and share information, especially one of the groups supported by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), such as SIGGRAPH for computer graphics.
SIGGRAPH
n. Short for Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics, a part of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).
sigmoid function
n. A kind of S-shaped mathematical function arising in many dynamical systems, including neural networks, because it is the solution to a first-order differential equation. It typically maps a real value, which may be arbitrarily large in magnitude (positive or negative), to another real value, which lies within some narrow range. The sigmoid function, in neural network computation literature, is also sometimes referred to as the logistic function. The reason for its prevalence is that it is thought to resemble the probability that a true neuron generates as an action potential in response to particular input and output. See also artificial intelligence, neural network.
sign
n. The character used to indicate a positive or negative number. In assembly-level programming, the sign is indicated by the sign bit accompanying the number. See also sign bit.
signal
n. 1. Any electrical quantity, such as voltage, current, or frequency, that can be used to transmit information. 2. A beep or tone from a computer’s speaker or a prompt displayed on screen that tells a user that the computer is ready to receive input.
signal converter
n. A device or circuit that converts a signal from one form to another, such as analog to digital, or pulse code modulation to frequency modulation.
signal-to-noise ratio
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
784 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. The amount of power, measured in decibels, by which the signal exceeds the amount of channel noise at the same point in transmission. Abbreviation: S/N. See also noise (definition 2).
signature
n. 1. A sequence of data used for identification, such as text appended to an e-mail message or a fax. 2. A unique number built into hardware or software for authentication purposes.
signature block
n. A block of text that an e-mail client or a newsreader automatically places at the end of every message or article before the message or article is transmitted. Signature blocks typically contain the name, e-mail address, and affiliation of the person who created the message or article.
signature file
n. 1. A file that contains information inserted by a user and automatically appended to e-mail correspondence or newsgroup articles by client software. A signature file typically contains the name or nickname of the user and might include such information as the user’s e-mail address, Web page, company, or job title. 2. A file that updates an antivirus program so that the program recognizes signatures of new viruses and removes the viruses from the user’s computer. See also antivirus program, virus signature.
sign bit
n. The most significant, or leftmost, bit of a number field, usually set to 1 if the number is negative.
sign extension n. See sign bit.
significand
n. See mantissa.
significant digits
n. The sequence from the first nonzero digit to the last digit in a number (the last nonzero digit in an integer), used to express the number’s precision (for example, 12,300 has three significant digits, and 0.000120300 has six). See also floating-point notation.
sign off
vb. See log off.
sign on
vb. See log on.
sign propagation n. See sign bit.
SIIA
n. Acronym for Software & Information Industry Association. A nonprofit trade association representing over 1200 high-tech companies worldwide and charged with watching over the interests of the software and digital content industry. The SIIA was formed in 1999 when the Software Publishers Association (SPA) merged with the Information Industry Association (IIA). The SIIA focuses on three areas: providing information and forums in which to distribute information to the high-tech industry; protection in the form of an antipiracy program geared to help members enforce their copyrights; and promotion and education.
silica gel
n. A desiccant (moisture-absorbing substance) often packaged with optical or electronic equipment.
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
785 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
silicon
n. A semiconductor used in many devices, especially microchips. Silicon, with atomic number 14 and atomic weight 28, is the second most common element in nature. Compare silicone.
Silicon Alley
n. The Manhattan, New York, metropolitan area. Originally the term referred to the area of Manhattan below 41st Street, which had a heavy concentration of technology companies, but it now includes the entire island, reflecting the number of businesses involved in computer technology in that area. The name was inspired by Silicon Valley, the area of northern California that is home to many technology firms. See also Silicon Valley.
silicon chip
n. An integrated circuit that uses silicon as its semiconductor material.
silicon-controlled rectifier
n. A semiconductor rectifier whose conductance can be controlled by a gate signal. Acronym: SCR. See also gate (definition 1), rectifier.
silicon dioxide
n. An insulator used to form thin insulating layers in some types of semiconductors; also the primary component of glass.
silicone
n. A polymer in which silicon and oxygen are major components. Silicone is an excellent electrical insulator and conducts heat well. Compare silicon.
silicon foundry
n. A factory or machine used to create wafers of crystalline silicon.
silicon on insulator n. See SOI.
silicon-on-sapphire
n. A method of fabricating semiconductors in which the semiconductor devices are formed in a thin single layer of silicon that has been grown on an insulating substrate of synthetic sapphire. Acronym: SOS.
Silicon Valley
n. The region of California south of San Francisco Bay, otherwise known as the Santa Clara Valley, roughly extending from Palo Alto to San Jose. Silicon Valley is a major center of electronics and computer research, development, and manufacturing. See the illustration.
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
786 |

Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
Silicon Valley.
Silicorn Valley
n. Clusters of high-tech companies headquartered in small cities in the Midwestern United States, particularly in areas of rural Iowa.
SIM
n. See Society for Information Management.
SIM card
n. Short for Subscriber Identity Module card. A smart card designed for use with GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) mobile phones. SIM cards contain chips that store a subscriber’s personal identifier (SIM PIN), billing information, and data (names, phone numbers). See also Global System for Mobile Communications, smart card (definition 2).
SIMD
n. Acronym for single-instruction, multiple-data stream processing. A category of parallelprocessor computer architecture in which one instruction processor fetches instructions and distributes orders to several other processors. See the illustration. See also parallel processing. Compare MIMD.
SIMD.
SIMM
n. Acronym for single inline memory module. A small circuit board designed to accommodate surface-mount memory chips.
Simple API for XML n. See SAX.
Simple Authentication and Security Layer
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
787 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. See SASL.
Simple Control Protocol n. See SCP.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
n. A TCP/IP protocol for sending messages from one computer to another on a network. This protocol is used on the Internet to route e-mail. Acronym: SMTP. See also communications protocol, TCP/IP. Compare CCITT X series, Post Office Protocol.
Simple Network Management Protocol n. See SNMP.
Simple Object Access Protocol n. See SOAP.
simplex
n. Communication that takes place only from sender to receiver. Compare duplex2 (definition 1), half-duplex2.
simplex transmission n. See simplex.
SIMULA
n. Short for simulation language. A general-purpose programming language based on ALGOL 60, with special features designed to aid the description and simulation of active processes. Visual C++ is based on aspects of this language.
simulation
n. The imitation of a physical process or an object by a program that causes a computer to respond mathematically to data and changing conditions as though it were the process or object itself. See also emulator, modeling (definition 1).
simultaneous access n. See parallel access.
simultaneous processing
n. 1. True multiple-processor operation in which more than one task can be processed at a time. See also multiprocessing, parallel processing. 2. Loosely, concurrent operation in which more than one task is processed by dividing processor time among the tasks. See also concurrent, multitasking.
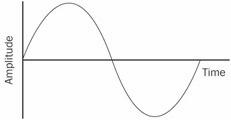
sine wave
n. A uniform, periodic wave often generated by an object that vibrates at a single frequency. See the illustration. Compare square wave.
Sine wave.
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
788 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
single attachment station
n. An FDDI node that connects to the primary ring through a concentrator. Compare dual attachment station.
single-board
adj. Of or pertaining to a computer that occupies only one circuit board, usually with no capacity for additional boards.
single-density
adj. Of or pertaining to a disk that is certified only for use with frequency modulation (FM) recording. A single-density disk can store much less data than a disk using modified FM encoding or run-length limited encoding. See also modified frequency modulation encoding, run-length limited encoding.
Single Image Random Dot Stereogram n. See autostereogram.
Single Image Stereograms n. See autostereogram.
single inline memory module n. See SIMM.
single inline package n. See SIP.
single inline pinned package n. See SIP.
single-instruction, multiple-data stream processing n. See SIMD.
single-line digital subscriber line n. See SDSL.
single-precision
adj. Of or pertaining to a floating-point number having the least precision among two or more options commonly offered by a programming language, such as single-precision versus doubleprecision. See also floating-point notation, precision (definition 2). Compare double-precision.
single-sided
adj. Of or pertaining to a floppy disk in which data can be stored on only one side.
single sign-on
n. A system enabling a user to enter one name and password to log on to different computer systems or Web sites. Single sign-on is also available for enterprise systems so a user with a domain account can log on to a network once, using a password or smart card, and thereby gain access to any computer in the domain. See also domain, smart card (definition 1).
single step
vb. To execute a program one step at a time, usually within the context of a debugger. See also debugger.
single switch device
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
789 |
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition
n. An assistive computer technology for people with mobility impairments. A single switch device allows users to interact with a computer by using slight body movements.
single threading
n. 1. Within a program, the running of a single process at a time. 2. A condition in which each leaf node of a tree data structure contains a pointer to its parent. See also node (definition 3), pointer (definition 1), threading.
single-user computer
n. A computer designed for use by a single individual; a personal computer. Compare multiuser system.
sink
n. A device or part of a device that receives something from another device. See also data sink, heat sink.
SIP
n. Acronym for single inline package. A type of housing for an electronic component in which all leads (connections) protrude from one side of the package. Also called: single inline pinned package. Compare DIP.
SIPP
n. Acronym for single inline pinned package. See SIP.
SIR
n. See Serial Infrared.
SirCam worm
n. A malicious worm that combines fast infection with the potential to deliver multiple malicious payloads. SirCam spreads through multiple means, both by mailing infected personal files from a compromised disk to other potential victims and through Windows network shares on unprotected machines. One time in 20 SirCam deletes the contents of the infected drive, and one time in 50 it fills all free space on the disk with trash data. SirCam was discovered in mid-2001 and has reappeared regularly since that time.
SIRDS
n. Acronym for Single Image Random Dot Stereogram. See autostereogram.
SIS
n. Acronym for Single Image Stereogram. See autostereogram.
.sit
n. The file extension for a Macintosh file compressed with StuffIt. See also StuffIt.
site
n. See Web site.
site license
n. A purchase agreement for using multiple copies of the same software at a business or an institution, usually at a volume discount.
size box
n. A control in the upper right corner of the frame of a window on the Macintosh screen. When the user clicks the size box, the window toggles between the size the user has set for it by dragging and the maximum size. Compare Maximize button.
Microsoft Computer Dictionary, Fifth Edition |
790 |
