
- •1. Review of current systems for broadband wireless access
- •1.1 Comparison of key technologies WiMax and hspa
- •1.2 Comparison of the key technologies for WiMax and lte
- •1.3 Comparison of key technologies WiMax and Wi-Fi.
- •2.2 Standard 802.16: physical layer
- •2.3 Standard 802.16 Protocol mac sublayer
- •2.4 Standard 802.16: frame structure
- •In addition to the data ofdm6символ includes a guard interval duration Tg, so that the total duration of the ofdm symbol
- •3.2 Mesh network
- •3.3 Application Features multiple access ofdma
- •In addition to reviewing the methods of distribution of bearing, the standard and optional mechanisms - in particular, the so-called optional fusc, not fundamentally different from that considered.
- •3.4 Support for adaptive antenna system
- •In more detail the network architecture shown in figure 19:
- •Variant mimo with a single receiving antenna also known as the mode stc (Space Time Coding with space-time coding) and are particularly suitable in nlos conditions.
- •In turn, the values and are defined by the formulas
- •7.2 The choice of the equipment of base stations
1.3 Comparison of key technologies WiMax and Wi-Fi.
Comparisons and confusion between WiMAX and Wi-Fi are frequent because both are related to wireless connectivity and Internet access.
WiMAX uses spectrum to deliver a point-to-point connection to the Internet. Various 802,16 standards require different types of mobile switches (similar to a cordless telephone) for fixed (alternative to wired access where wireless connection point end users recorded in the region.)
Wi-Fi uses unlicensed spectrum to provide access to the network. Wi-Fi is more popular in end user devices.
WiMAX and Wi-Fi have quite different quality of service (QoS) mechanisms. WiMAX uses a mechanism based on communication between a base station and a user device. Each connection is based on specific scheduling algorithms. Wi-Fi has QoS mechanism similar fixed Ethernet, where the packets can get different priorities based on their tags.
Wi-Fi runs on the Media Access Control's CSMA / CA Protocol, which is connectionless and statements are based, while WiMAX works connection-oriented MAC.
Standard 802,16 spreading across a wide bandwidth in the RF spectrum and WiMAX can operate on any frequencies below 66 GHz (higher frequencies would lead to a decrease in the operating range of the base station to several hundred meters in an urban environment).
WiMAX profiles define channel size, TDD / FDD and other necessary attributes in order to have Inter-operating products. The current fixed profiles are determined both for FDD and TDD profiles. Currently, all mobile profile TDD only. The profiles have a fixed size channel 3.5 MHz, 5 MHz, 7 MHz and 10 MHz. Mobile profiles 5 MHz, The 8.75 MHz and 10 MHz. (Note: 802,16 standard allows a much wider range of channels, but only the above subsets are supported WiMAX profiles.)
It is expected that WiMAX will be able to provide high-speed Internet access easier and cheaper than existing cellular technologies. This technology also has the capability of zooming through which you can arrange affordable broadband access across India. WiMAX wireless infrastructure can be extended to provide support for handheld and mobile devices that will emerge in the future. This provides additional benefits for countries with developing economies like India that do not yet have a well-developed broadband infrastructure.
Due to the fact that WiMAX technology is based on standards, it allows for economies of scale that can reduce the cost of broadband access, to ensure interoperability and to simplify the implementation. In the absence of standards, manufacturers of specialized equipment offer a full range of hardware and software components, and because of the restrictive licensing expenditures increase. Service providers more profitable to work with standard products, because the compatibility of various devices and large production volumes allow to reduce the cost of equipment.
2. SHIROKOPOLOSNYI MOBILE ACCESS UNDER THE CONTROL OF IEEE 802.16
2.1 Standard 802.16: a Protocol stack.
The set of protocols used by the 802.16 standard, is shown in figure 3. The overall structure is similar to other 802 series standards, but more Sublevels. The lower sublayer is involved in the physical transfer of data. Using conventional narrowband radio system with the ordinary schemes of modulation of the signal. Above the physical layer is a sublayer of the data (with the accent on the second syllable), hiding from the level of data transmission technology differences.
The data consists of three sublevels. The lower one refers to the protection of information in which Data transfer is carried out in the ether, not physically protected from eavesdropping. This sublevel is citrate, decoding the data, and also control keys.
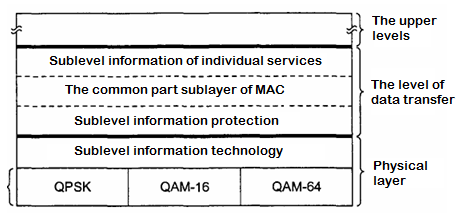
Figure 3 - Standard 802.16: a Protocol stack.
Then, the General part of the MAC sublayer. It is at this level of the hierarchy are the main protocols - in particular, the protocols of the control channel. Here the station in control of the entire system. She very effectively distributes the order of transmission of the incoming traffic to subscribers, plays a significant role in the management of outbound traffic (from the subscriber to the base station). From all other 802 standards.x MAC sub-layer the 802.16 standard is different in that he is fully focused on the connection. Thus, it is possible to guarantee a certain quality of service in the provision of telephone services and the transfer media.
