
- •1. Review of current systems for broadband wireless access
- •1.1 Comparison of key technologies WiMax and hspa
- •1.2 Comparison of the key technologies for WiMax and lte
- •1.3 Comparison of key technologies WiMax and Wi-Fi.
- •2.2 Standard 802.16: physical layer
- •2.3 Standard 802.16 Protocol mac sublayer
- •2.4 Standard 802.16: frame structure
- •In addition to the data ofdm6символ includes a guard interval duration Tg, so that the total duration of the ofdm symbol
- •3.2 Mesh network
- •3.3 Application Features multiple access ofdma
- •In addition to reviewing the methods of distribution of bearing, the standard and optional mechanisms - in particular, the so-called optional fusc, not fundamentally different from that considered.
- •3.4 Support for adaptive antenna system
- •In more detail the network architecture shown in figure 19:
- •Variant mimo with a single receiving antenna also known as the mode stc (Space Time Coding with space-time coding) and are particularly suitable in nlos conditions.
- •In turn, the values and are defined by the formulas
- •7.2 The choice of the equipment of base stations
In turn, the values and are defined by the formulas
 ,
(15)
,
(15)
 ,
(17)
,
(17)
 -
the parameter that determines the range of random fluctuations of the
signal level at the receiving end:
-
the parameter that determines the range of random fluctuations of the
signal level at the receiving end:
 .
(18)
.
(18)
The
coefficient
 in (17) is the median attenuation of radio waves in the i-th
direction you increase the noise. These factors are inversely
proportional to the quarters of the degrees of the distance to the
source of interference. The value M represents the number of base
stations that are "disturbing", located in the neighbouring
clusters.
in (17) is the median attenuation of radio waves in the i-th
direction you increase the noise. These factors are inversely
proportional to the quarters of the degrees of the distance to the
source of interference. The value M represents the number of base
stations that are "disturbing", located in the neighbouring
clusters.
First consider the case for Omni-directional antennas, where
 ,
,
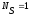 ,
,
 и
и
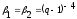 ,
,
 ,
,
 ;
;
where
 is the number of sectors.
is the number of sectors.
We choose the value C=3.

 ,
(19)
,
(19)

Define


Calculating the square root of the resulting value obtained

It follows
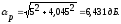
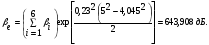
Now we calculate the lower boundary of the Q-function:

This
value in the table corresponds to the value , this
 value is approximately equal to one. Considering the equation (3.2),
we obtain
value is approximately equal to one. Considering the equation (3.2),
we obtain

The
resulting value is clearly more
 which job is 10. Hence, this type of antenna and the selected value
of the cluster is not suitable for the specified standard.
which job is 10. Hence, this type of antenna and the selected value
of the cluster is not suitable for the specified standard.
Now
consider the case for a directional antenna, in which the angle of
directivity pattern
 ,
,
 ,
М=2 и
,
М=2 и
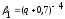 ,
,
 .
.
We choose the value C=4.

Define

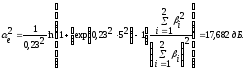
Calculating the square root of the resulting value obtained

It follows:


Now we calculate the lower boundary of the Q-function:

This value in the table corresponds to a value equal 0,0838. Considering the equation (3.2), we obtain

The
resulting value is slightly smaller hence
 ,
this type of antenna is the best.
,
this type of antenna is the best.
5.4 calculation of the frequency channels that are used for customer service BS
The number of frequency channels that are used for customer service in one sector is determined by the formula:
 (20)
(20)

где
 - the number of sectors.
- the number of sectors.
5.5 Calculation of the allowable load of BS
The value of the permissible load in one sector is determined by the ratio:
 (21)
(21)
provided that
 ,
(22)
,
(22)
where
 ;
;
 -
the number of subscribers that can simultaneously use the same
frequency channel. In this case, the value of =1 because you are
using the analog standard.
-
the number of subscribers that can simultaneously use the same
frequency channel. In this case, the value of =1 because you are
using the analog standard.

Radical
expression greater than the magnitude of
 ,
because
,
because
 .
.

5.6 Calculation of the number of subscribers served by one BS
For
a given activity per subscriber per hour maximum load you can
calculate the number of subscribers served by one BS to the formula
(23)

5.7 calculation of the number of BS
The required number of base stations in a given service area is determined by the ratio:
 ,
(24)
,
(24)
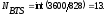
where
 is a specific number of subscribers, which serves the cellular
network connection.
is a specific number of subscribers, which serves the cellular
network connection.
5.8 calculation of the radius of the service area of BS
The radius can be determined using the expression

(25)
 km
km
6. CHECKING CALCULATION OF NOISE IMMUNITY TO THE NETWORK
6.1 the Calculation of the size of the clearance distance
The magnitude of the clearance distance between the BTS with the same frequency channels is determined by the ratio

(26)

6.2 Calculation of the signal level at the receiver input
The
required power at the receiver input
 when
when
 and
and
 determine, using the so-called first equation of transfer.
determine, using the so-called first equation of transfer.
 (27)
(27)

where
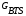 - gain base station antennas, dB;
- gain base station antennas, dB;
f - the average frequency of the selected frequency range;
 -
the BTS transmitter power, dBW;
-
the BTS transmitter power, dBW;
 -
losses in the feeder BTS, dB;
-
losses in the feeder BTS, dB;
 -
long feeder, which may be equal to or greater than the height of the
BTS antenna;
-
long feeder, which may be equal to or greater than the height of the
BTS antenna;
 -
linear attenuation of the feeder, dB/m.
-
linear attenuation of the feeder, dB/m.
6.3 Calculation of error probability
To determine the probability of error when the MS is located on the border of the service area of the BTS, you must use the ratio
 (28)
(28)

6.4 Calculation of efficiency of use of radio spectrum
An important parameter of the cellular network connection is efficient use of radio spectrum , due to the number of active subscribers at 1 MHz frequency band for transmission (or reception) BTS, that is
![]() (29)
(29)
where
the frequency band for transmission (or reception)
 the number of active subscribers
the number of active subscribers

 (30)
(30)
where
 is the radius of the territory that is served by,
is the radius of the territory that is served by,

Here

(31)
 .
.
7. THE CHOICE OF THE BASIC EQUIPMENT OF THE SUBSCRIBER STATIONS
Functionally, the WiMAX equipment is divided into base and subscriber. The first generation of chips for base stations has a lower level of integration than for subscriber stations. To implement the MAC Protocol of the base station need to increase performance of these solutions. For this purpose, external processors that perform the top-level MAC Protocol. Thus, the WiMAX chipsets implement the functions of the physical layer and lower MAC layer Protocol.
7.1 Selection of equipment subscriber stations
For developers WiMAX subscriber equipment, the most promising are "systems on a chip" from four manufacturers: Fujitsu, Intel, Sequans, and Wavesat.
Intel first offered to the developers of "system on chip" PRO/Wireless 5116 for WiMAX mobile stations, which were integrated functions, both physical and MAC levels. Chip MB87M3400 Fujitsu is designed for a wider range of applications and allows you to develop both basic and subscriber equipment. The company Sequans has developed separate chips SQN1010 and SQN2010 - for base and subscriber equipment, respectively.
"The SOC from Fujitsu, Intel and Sequans fully implement the functions of the MAC Protocol for WiMAX mobile stations. Another approach to the development said the company Wavesat, releasing two chips: OFDM modem DM256 (implements the functions of the physical layer) and MC336 (is a computational kernel that implements the lower level of the MAC Protocol). To develop a subscriber modem on the basis of the SOC from Fujitsu, Intel and Sequans not require an additional external processor.
Characteristics of these chips, depending on the type of duplex, channel width and other parameters are very different. For the organization full-duplex operation based on Fujitsu MB87M3400 requires two chips. Sequans chip SQN1010 is the first "system on a chip", which supports full-duplex mode. The company's decision Wavesat DM256/MC336 also allows for full duplex mode based on the single chip OFDM modem DM256.
Chip companies Fujitsu and Sequans allow you to organize the channel width to 20 and 28 MHz respectively, while the maximum width of the channel for Intel chips and Wavesat is 10 MHz with intermediate values of 3.5 and 7 MHz.
The air is considered "systems on chip" contains blocks ADC/DAC for direct analog connection to an external transceiver. In table. 2 presents the main parameters of solutions for WiMAX subscriber equipment [6].
Table 6. The main parameters of solutions for WiMAX subscriber equipment.
|
Option |
Fujitsu MB87 |
Intel PRO/Wireless 5116 |
Sequans SQN1010 |
Wavesat DM256/MC336 |
|
Function |
PHY/MAC |
PHY/MAC |
PHY/MAC |
PHY/MAC |
|
Maximum channel width |
20 MHz |
10 MHz |
28 MHz |
10 MHz |
|
Duplex |
H-FDD, TDD, FDD (2 chip) |
H-FDD, TDD |
H-FDD, TDD, FDD |
H-FDD, TDD, FDD |
|
System interface |
Mill, 32-bit generic |
Mll |
RMLL, PCI |
PCI |
