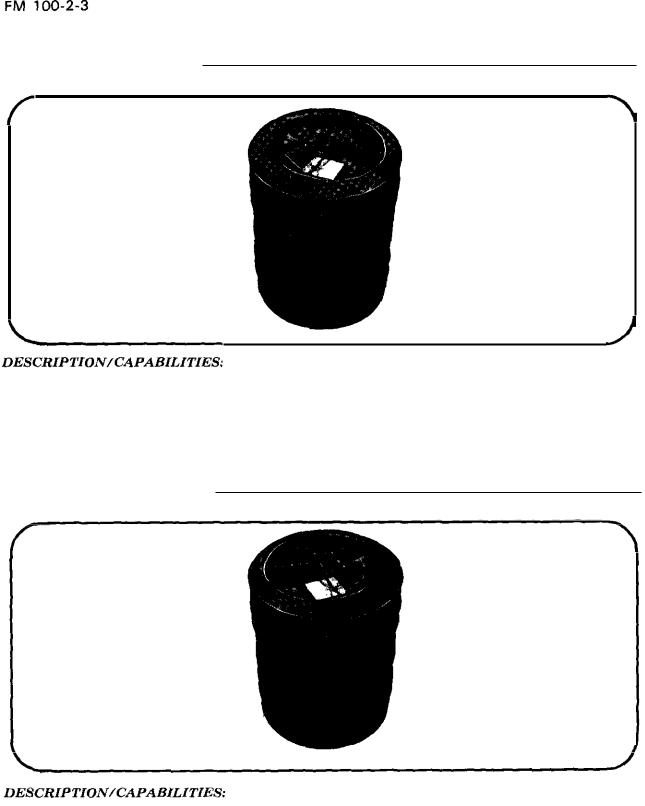
Large Smoke Barrel BDSh-5
BDSh-5
The BDSh-5 large smoke barrel is a cylinder filled with a smoke mixture; it has carrying handles on each end. A tube a t one end contains an ignition device with starter charge. The barrel, which will float in water, is balanced so that the smoke emission opening is always up. This is useful to
Large Smoke Barrel BDSh-15
screen water crossing operations by Iarge-scale forces. The BDShd will burn for 5 minutes. It has a delay time fuze of up to 39 seconds. The barrel is .49 meters long with a diameter of .4 meters. It weighs 40.1 kilograms when filled.
The BDSh-15 large smoke barrel produces white smoke for 14 to 16 minutes over an area of approximately 4180 square meters under favorable meteorological conditions. This smoke barrel is enclosed
in a steel container 48 centimeters long, with a diameter of 39.4 centimeters, and a weight of 38.6 kilograms with filling.
Incendiary Grenade, Fragible, Model?
No photograph available
This grenade has been standardized to permit launching from a cup-like launcher. The grenades are packed in earth or sand in wooden boxes. The Soviets use two known standard fillings. The first, "KS liquid (white phosphorous in carbon disulfide), ignites immediately upon exposure to air. A small amount of water or oil a n d a wooden stopper prevent the liquid from making contact with the air until the grenade ruptures against a target. This fill burns for approximately 2 minutes at a temperature of 850 to 1000 degrees Centigrade. The
Smoke Grenade RDG-1
second filling, "mixture No. 1," is a yellowish liquid which is ignited by a WP ampule inserted into the bottle just prior to firing. The fuel adheres to the surface of the target and burns for approximately one minute, producing a black smoke and temperatures of 700 to 850 degrees Centigrade.
REMARKS:
This incendiary grenade should not be confused with field expedients such as the "Molotov Cocktail" used by Soviet forces during World War II.
RDG-1
SMOKE COMPOSITION PELLETS
DESCRIPTION:
The RDG-I grenade is a burningtype smoke grenade made of cardboard with a wooden handle. It contains a black smoke mixture. A friction fuze with a 3.5-second delay ignites it. The grenade floats and can generate smoke over a large body of water. The RDG-1 weighs .50 to .59 kilograms and is 22 centimeters long.
CAPABILITIES:
The average hand-thrown range is 35 meters. Area coverage is approximately 460 square meters under favorable meteorological conditions. The 1.2 to 1.5 seconds burning time provides a quick screening device for attacking forces.
Incendiary Smoke Cartridge ZDP
ZDP
General view and main parts of an incendiary
|
|
smoke charge: |
1. |
launch tube |
4. |
cap with red marking |
2. |
generator |
5. |
cap with green marking |
3. |
motor |
6 & 7. cords with rings |
|
|
|
|
|
The ZDP incendiary smoke cartridge comes in a metal tube which weighs .75 kilograms, is 290 millimeters long, and has a diameter of about 50 millimeters. To activate the charge, the user must unscrew the green cap on one of the ends, pull the ring on the cord of the pressure-friction fuze, and handthrow the ZDP to a minimum of 25 meters. The ZDP can also be propelled by a rocket
motor up to 560 meters. I n this case, the user unscrews the red cap on the other end of the charge, pulls the ring on the cord, and rests the launch tube against one of the following: the swivel of a firmly seated automatic rifle, the safety catch of a rocket launcher, or the support of a machine gun.
Vehicle-Launched Smoke Grenades
T-72 variant with smoke grenade projectors
DESCRIPTION/CAPABILITIES:
Until the 1970s, the Soviets did not mount smoke grenade projectors on their combat vehicles. They did, however, put two smoke barrels on the rear of the T-54 and T-55 tanks. These obscured the tanks from the enemy while they maneuvered. This system was only effective when the tanks were retreating, because of the positioning of the smoke barrels. The new vehicle-launched smoke grenades provide a rapid means of shielding the vehicle and personnel during evasive maneuvers from antitank weapons. The grenades give some protection to crews when they are dismounting from disabled
vehicles. The grenade projector consists of two components: a tube assembly mounted on the exterior of the vehicle, and a firing mechanism or control unit mounted inside, where it is operated by the gunner or commander. The smoke grenade consists of a fuze, body, and fin asembly.
REMARKS:
The Soviets now mount this type of vehiclelaunched smoke grenade on some BMP-1s; on the BMP-2; on the BTR-80; and on the T-62, T-64, T.72 and T-80 tanks.
Advancements in the logistic equipment and capabilities of the Warsaw P a d countries have been continuous. Some new items have been introduced and older items upgraded. For a complete descrip-
tion of transport and other logistic equipment, see TB 381-5-22A and DST-1150528087. (Complete citations are given in the Reference section of this manual.)
Pipelaying Machines
TUM-160
Automatic Pipelaying Machines TUM-100 and TUM-150
Automatic Pipelaying Machines TUM-100 a n d TUM-150 (continued)
New TUM variant
The TUM-100 automatic pipelaying machine consists of a wheeled prime mover and a semitrailer with a pipe hopper, a n assembly device, and a crane. I t uses pipes which are 100 millimeters (approximately 4 inches) in diameter. Except for the size of pipes, the TUM-100 functions much the same as the TUM-150.
The TUM-150 automatic pipelaying machine consists of a tracked prime mover and a semitrailer
with a pipe hopper, a n assembly device, and a crane. It uses aluminum pipes which are 150 milli-
meters (approximately 6 inches) in diameter and 6 meters long.
Using the traversing crane, the machine loads pipes from a pipe-carrying tractor-trailer transport vehicle onto its integral hopper. It then feeds the pipe from the hopper into the assembly line, couples the pipe sections, and lays the pipe in place. It lays pipe at a rate estimated at one to three kilometers per hour.
The TUM-150 is organic to the pipeline brigade of a front. It is capable of laying tactical pipelines from front to army levels in an offensive operation a n d even down to division level i n a s t a t i c situation. A new variant of the wheeled TUM (which stands for trubo-ukladochnaya mashina, or pipe laying vehicle, in Russian) appeared in 1986.
Maintenance Support Vehicle
Amphibious Armored Maintenance Support Vehicle MTP
MTP
DESCRIPTION:
The MTP is a BTR-50P variant developed to provide servicing, maintenance, and recovery support of the BMP infantry combat vehicle. The power train compartment in the rear and the driver's compartment a t the front have retained the general characteristics of the BTR-50P.The centrally located working compartment has a n armored roof raised high enough to allow the maintenance crew to work while standing. The working and driver's compartments probably have a collective NBC filtration system. Firingports in
the hull sides are like a BMP's; they allow the crew to fire their personal weapons without disrupting the protective seal.
CHARACTERISTICS |
MTP |
Crew |
...................................... |
3-4 |
Weight ............................... |
(kg) |
16,000 |
Length .............................. |
(mm) |
6,910. |
Width ...............................(mm) |
3,140 |
Height ............................... |
(mm) |
2,500 |
Armored Recovery Vehicles
A r m o r e d recovery vehicle characteristics
CHARACTERISTICS |
T-54/55-T |
T-62-T |
BREM-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CREW |
|
|
3 - 5 |
3-5 |
2 - 3 |
WEIGHT (kg) |
|
Approximately32,000 |
Approximately 32,000 |
INA |
LENGTH, |
overall |
(m) |
7.47 |
6.63 |
INA |
WIDTH, |
overall |
(m) |
3.27 |
3.30 |
Approximately 3.46 |
HEIGHT, |
overall |
(m) |
1.89 |
1.90 |
INA |
ARMAMENT |
|
None |
None |
1-2 machineguns |
DOI |
|
|
1965? |
1977 |
1984 |
STATUS |
|
|
Standard |
Standard |
Standard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A r m o r e d Recovery Vehicle T-54/55-T
T-54-T
The T-54-T and T-55-Tarmored recovery vehicles are based on modified chassis of the T-54 and T-55 medium tanks, respectively. The recovery vehicle variants have a crane able to lift up to 3,000 kilograms, a loading platform, and a spade on the
rear of the vehicle. They can mount a snorkel for deep fording. Performance figures are the same a s for the T-54 and T-55 tanks. They have been in service since around 1965, replacing older tank recovery vehicles based on the T-34 tank chassis.
Armored Recovery Vehicle T-62-T
T-62-T
The T-62-T armored recovery vehicle is based |
first observed in the November 1977 Moscow Red |
on a modified T-62 medium tank chassis. It was |
Square parade. |
Medium TankRecovery Vehicle BREM-1
BREM-1
The BREM-1 is based on the T-72 tank chassis. Instead of a turret, it has a rectangular platform on top of the hull for work and loading. It has a 19-mtcapacity hydraulic crane, a 25-mt capacity winch with 200 meters of cable, a hydraulically operated dozer blade, as well as a telescoping
snorkel. It probably has collective NBC protection for its crew of two to three. It mounts one or two machine guns of unknown type and caliber.
REMARKS:
The BREM-1 was introduced in 1984.

CHARACTERISTICS |
Mi-2/ |
Mi-6A/ |
Mi-8T/ |
Mi-17/ |
Mi-24/ |
Mi-26/ |
Mi-28/ |
Ka-?/ |
HOPLITE |
HOOK |
HIP |
HIP H |
H I N D |
HALO A |
HAVOC A |
HOKUM A |
CREW |
1 |
5 |
2-3 |
2-3 |
3 |
5 |
2 |
2 |
PASSENGERS (troops) |
6-8 |
65 |
24 |
24 |
8-10 |
100+ |
0 |
0 |
NORMAL PAYLOAD (kg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hovering takeoff |
700/800* |
8,000 |
4,000/3,000* |
4,000/3,000* |
3,600 |
20,000 |
0 |
0 |
Rolling takeoff |
INA |
12,000 |
INA |
INA |
3,800 |
20,000 |
0 |
0 |
NORMAL TAKEOFF WEIGHT (kg) |
3,300 |
39,000 |
11.100 |
11.100 |
10,000 |
49,500 |
INA |
INA |
MAXIMUM TAKEOFF WEIGHT (kg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hovering takeoff |
3,500 |
42,500 |
12,000 |
13,000 |
12,000 |
56,000 |
INA |
5,500 |
Rolling takeoff |
INA |
46,800 |
INA |
INA |
12,200 |
INA |
11.400 |
INA |
SERVICE CEILING (m) |
4.000 |
3,000 |
3,500/4,500** |
5,000 |
2,100 |
4,500 |
INA |
INA |
SPEED (km/hr) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum @ sea level |
210 |
300 |
250 |
250 |
320 |
295 |
300 |
350 |
Cruising |
190 |
250 |
225 |
240 |
310 |
255 |
280 |
INA |
RANGE ( k m ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum payload |
340 |
200 |
160 |
460 |
490 |
800 |
INA |
INA |
Maximum fuel |
580 |
610 |
410 |
495/950*** |
540 |
1,200 |
INA |
INA |
COMBAT RADIUS (km) |
170 |
300 |
200 |
INA |
160 |
300+ |
240 |
250 |
DIAMETER, main rotor (m) |
14.50 |
35.00 |
21.30 |
21.30 |
17.00 |
32.00 |
17.20 |
INA |
LENGTH, fuselage (m) |
12.00 |
33.00 |
18.20 |
19.30 |
1900 |
33.727 |
16.85 |
INA |
HEIGHT, overall (m) |
3.80 |
9.90 |
5.70 |
5.60 |
4.30 |
8.145 |
4.81 |
INA |
DOI |
1965 |
1961 |
1963 |
1981 |
1972 |
1982 |
early 1990s |
early 1990s |
FOOTNOTES *Internal/sling
**Depending on role
***Without/withauxiliaryfuel tanks