The_Soviet_Army_troops_organization_and_equi
.pdf
Ditching Machines
Ditching machine characteristics
CHARACTERISTICS |
MDK - 2 M |
|
MDK-3 |
BTM3 |
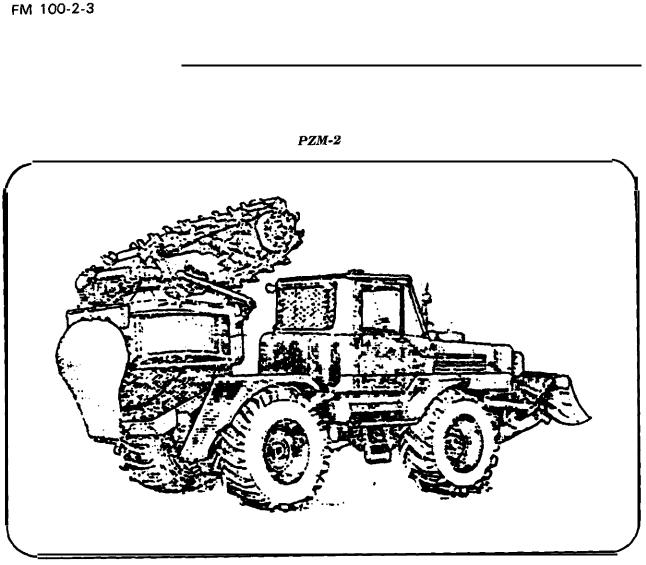
PZM-2 |
TMK - 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAXIMUM DIGGING DEPTH (m) |
3.5 |
|
3.0 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
DIGGING WIDTH (m) |
3.5 |
|
3.5 |
0.6 |
0.8-3.5 |
1.1 |
DIGGING CAPACITY (m3/hr) |
120.300 |
|
400.500 |
220-600 |
80-250 |
200-600 |
WORKING SPEED (m/hr) |
200.800 |
|
400-500 |
600 |
180 |
450 |
MAXIMUM ROAD SPEED |
36 |
|
70 |
36 |
45 |
60 |
(km/hr) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RANGE (km) |
500 |
|
500 |
500 |
500 |
500 |
CREW |
2 |
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
WEIGHT (mt) |
28 |
|
INA |
26.7 |
12.8 |
26.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE. Excavation capabilities depend on soil type, depth of |
cut, and other |
factors. |
|
|
||




Antipersonnel Mines
Antipersonnel mine characteristics
CHARACTERISTICS |
PMN |
PMD-6M |
POMZ-2M |
OZM-3 |
KhF-1/KhF-2 |
TYPE |
antipersonnel |
antipersonnel |
antipersonnel |
bounding |
chemical |
|
|
|
|
antipersonnel |
bounding |
|
blast |
blast |
fragmentation |
bounding |
chemical |
|
|
|
stake mine |
fragmentation |
(mustard) |
MAXIMUM DIAMETER |
110 |
length-191 |
60 |
75 |
150/190 |
(mm) |
|
widtin.89 |
|
|
|
HEIGHT (mm) |
56 |
64 |
107 (not |
120 |
245/280 |
|
|
|
including |
|
|
WEIGHT (kg) |
|
|
stake) |
|
|
0.55 |
0.4 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
15 |
|
ACTUATING FORCE |
8-25 |
1 0 |
1.0 |
varies |
varies |
(kg) |
|
|
|
|
|
FUZING SYSTEM |
pressure |
pull |
trip wire |
trip wire or |
electronic, |
|
plate |
|
pull |
electronic |
pressure |
|
|
|
|
|
delay |
DOI |
1960 |
1939 |
1951 |
1950 |
1941-1942 |
STATUS |
standard |
l i m i t e d |
l i m i t e d |
standard |
obsolete |
|
|
standard |
standard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CHARACTERISTICS |
PFM-1 |
MON-50 |
MON-100 |
MON-200 |
TYPE |
anitpersonnel |
antipersonnel |
antipersonnel |
antipersonnel |
|
scatterable |
d i r e c t i o n a l |
d i r e c t i o n a l |
d i r e c t i o n a l |
|
blast |
fragmentation |
fragmentation |
fragmentation |
MAXIMUM DIAMETER |
120 4 |
220 105 |
220 |
520 |
(mm) |
|
|
|
|
HEIGHT (mm) |
60 96 |
INA |
80 |
INA |
WEIGHT (kg) |
0 074 |
INA |
5 |
25 |
ACTUATING FORCE |
5 |
1 0 |
1 0 |
1 0 |
(kg) |
|
trip wire or |
trip wire or |
trip wire or |
FUZING SYSTEM |
delay, |
|||
|
pressure |
electronic |
electronic |
electronic |
DOI |
1978 |
1970 |
1970 |
1970 |
STATUS |
standard |
standard |
standard |
standard |
.