
- •Межзвездная среда и звездообразование
- •Состав межзвездной среды
- •Двухфазная модель межзвездной среды
- •Основные компоненты МЗС
- •Фаза
- •Механизмы нагрева и охлаждения
- •Космические лучи
- •Происхождение космических лучей
- •Механизмы ускорения КЛ
- ••Статистический механизм ускорения (при хаотическом движении частицы между облаками). При встречных столкновениях с
- •Магнитные поля
- •Межзвездная пыль
- •Фрактальная модель
- •Туманность Ориона в оптике и в ИК диапазоне
- •Свойства пылинок
- •Ориентация несферических пылинок
- •Polarization of dust emission and magnetic fields in star forming regions
- •Области ионизованного водорода (зоны H II)
- •Зоны Стрёмгрена
- •Ультракомпактные зоны H II
- •How are hypercompact HII regions defined?
- •Молекулярные облака
- •Межзвездная химия
- •Крупномасштабная структура МЗС
- •Изофоты радиоизлучения Галактики на частоте 150 МГц
- •Распределение по небу нейтрального водорода (по данным обзоров в линии 21 см). Видна
- •Распределение нейтрального водорода в плоскости Галактики по данным Лейденского обзора в линии 21
- •Распределение молекулярного газа в Галактике: обзоры в линии СО
- •Межзвёздная среда в других галактиках
- •Межзвездная газодинамика
- •Теорема вириала
- •Волновые движения в МЗС
- •Ударные фронты
- •Основные неустойчивости МЗС
- •Неустойчивость Рэлея – Тэйлора
- •Неустойчивость Паркера
- •Неустойчивость Кельвина- Гельмгольца
- •Численный расчет неустойчивости Кельвина - Гельмгольца в магнитном поле. Эволюция плотности.
- •Численный расчет ионизационно-тепловой неустойчивости в магнитном поле (направлено по диагонали). Изображено распределение плотности.
- •Модели звездообразования
- •Гравитационное сжатие однородного сферического облака
- •Изотермичное облако, ограниченное внешним давлением
- •Распределение плотности для изотермичной ограниченной сферы, помещенной в среду с давлением Pext.
- •Пример наблюдаемой сферы Боннора-Эберта
- •Inside-out collapse of metastable sphere
- •Модель Шу (“inside-out” collapse)
- •Inside-out collapse model of Shu
- •Inside-out collapse model of Shu
- •Inside-out collapse model of Shu
- •Inside-out collapse model of Shu
- •Влияние магнитного поля
- •Уменьшение магнитного потока
- •Проблема углового момента
- •Фрагментация
- •The Star Forming Environment
- •Основные этапы звездообразования
- •The Formation Process
- •Stages of star formation
- •Linked Accretion & Outflow
- •Herbig Haro Objects
- •Accretion/Outflow – Low Mass
- •Высокоскоростные биполярные истечения
- •Структура
- •G192.163.82 – Artist view
- •Difficult to Form Planets?
- •Accretion Disks: Solar Type Stars
- •The 3D Structure of Orion
- •The Solar Neighborhood

The Star Forming Environment
The Eagle Nebula, Hester et al. (1995) |
Thackeray’s |
|
|
|
Globule in IC |
|
2944, Reipurth et |
|
al. (2002) |
Stars form within dense interstellar clouds of gas & dust that obscure our view at visible wavelengths.
The Horsehead Nebula, HST Heritage project

Основные этапы звездообразования
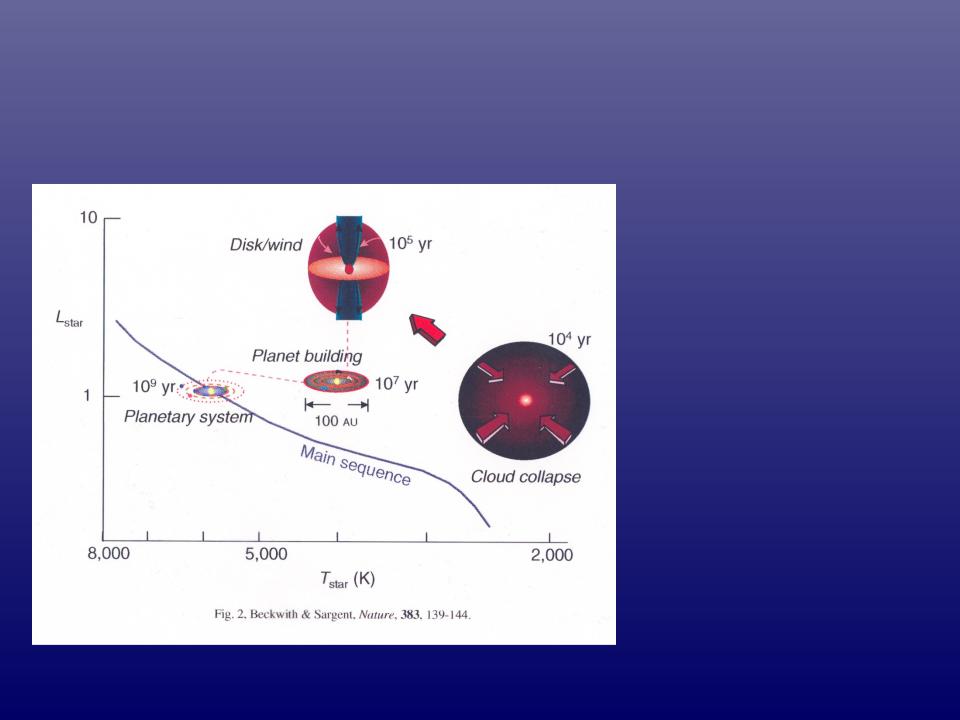
The Formation Process
For a “TTauri” star – how our Solar System formed
Scales:
Earth sun distance = 1 AU, Astronomical Unit (6 lt minutes)
Size of our Solar System = 80 AU (8 lt hours)
Size of typical accretion disks = 100 AU
Size of typical outflow = 1 parsec (pc) = 3.26 lt yrs = 200,000 AU
Closest star to Sun = 4.3 lt yrs = 1.3 pc ( Centauri)
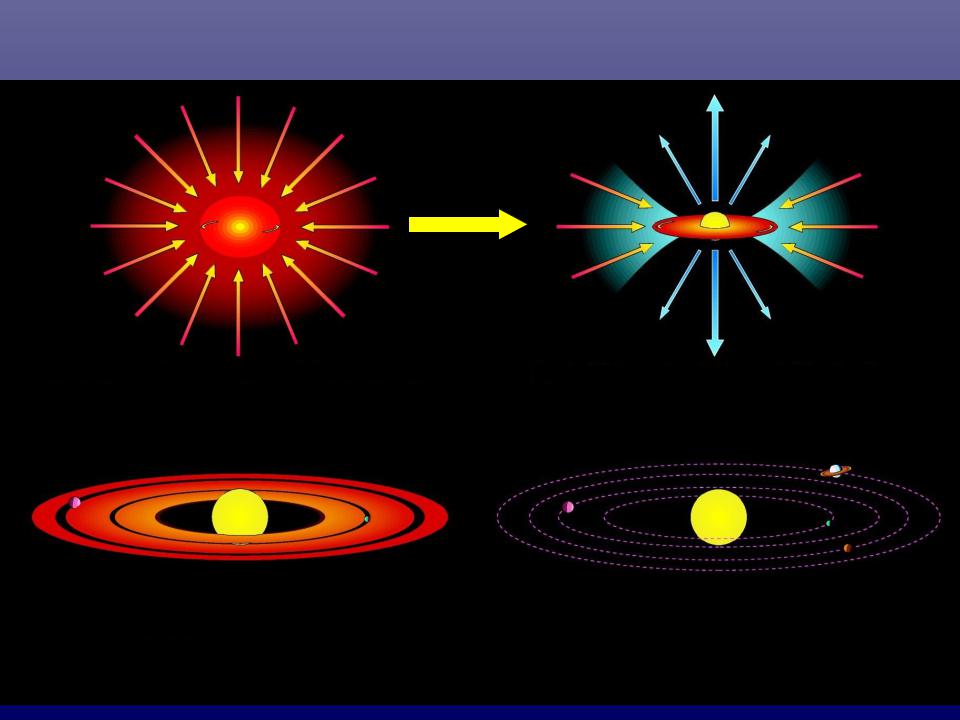
Stages of star formation
x1000 in scale
outflow
infall
Cloud collapse |
Rotating disk |
Planet formation Mature solar system Scenario largely from indirect tracers.
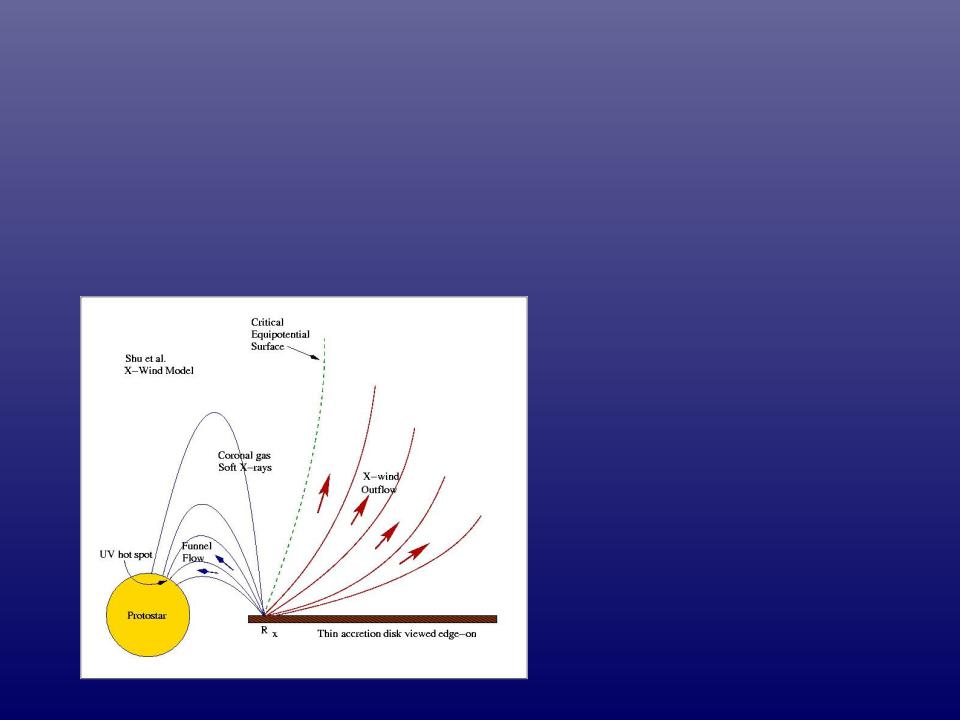
Linked Accretion & Outflow
Disk regulates accretion, acts as launching point for outflow. Disk remnant becomes planetary system.
Outflow carries away excess angular momentum from spinning cloud. Without outflow, star would rotate to “break up” speed and fly apart – no stars, no planets.
2 basic theories:
Xwind
(Shu and collaborators) – schematic shown. Protostar magnetic field links with disk field to control infall & outflow.
Diskwinds
(Konigl, Pudritz, Garcia, & collaborators).
Star does not have a magnetic field, disk field controls outflow over a range of radii.
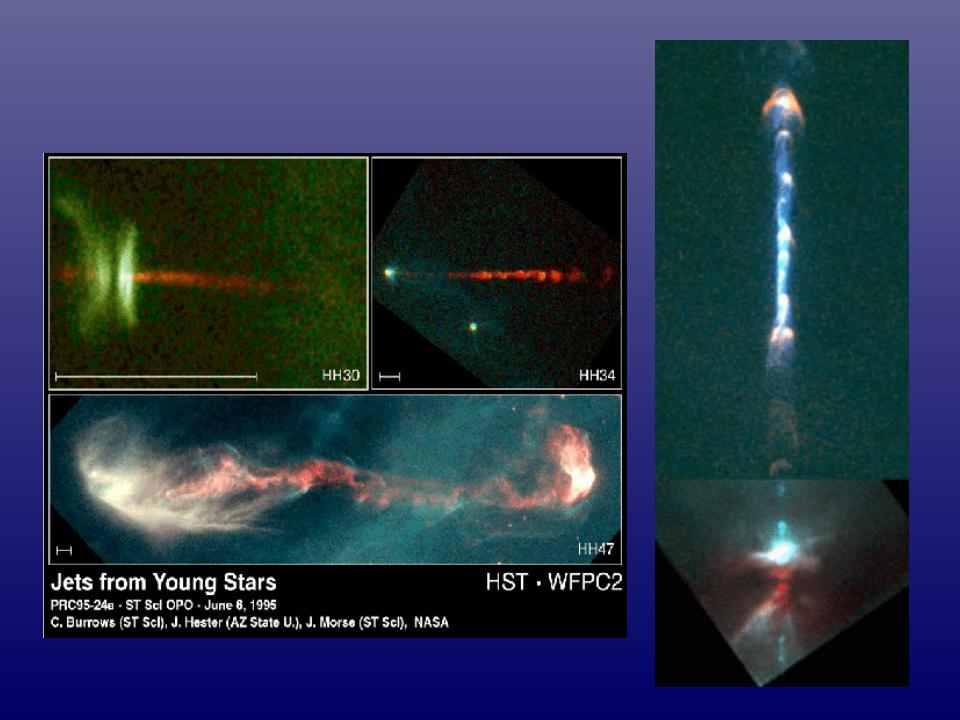
Herbig Haro Objects
HH 111
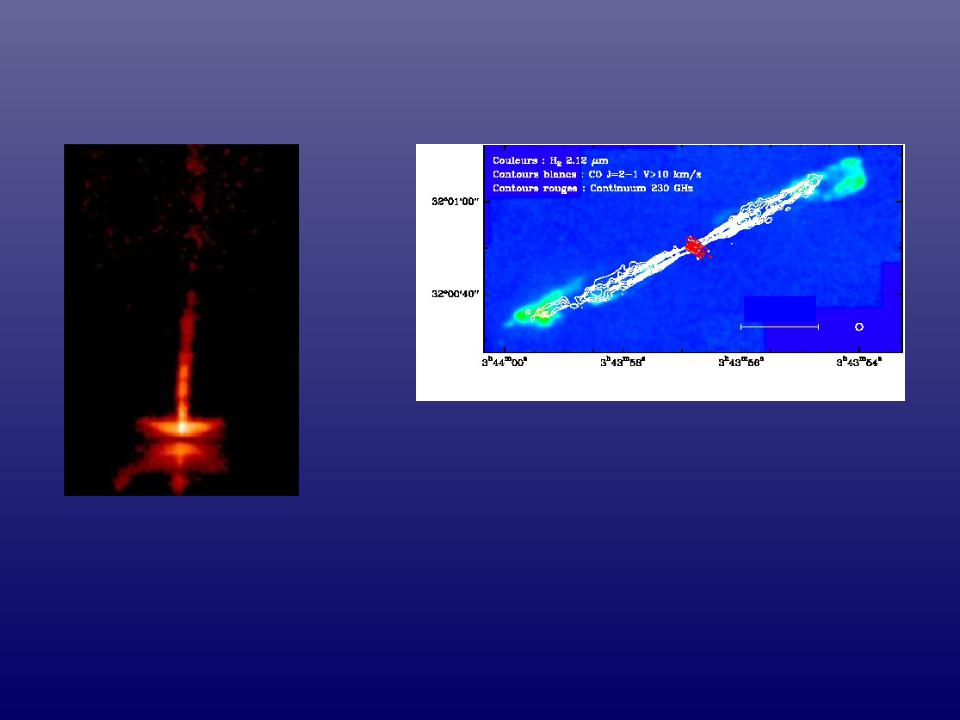
Accretion/Outflow – Low Mass
HH 30
HH 30: visible light (HST R band) showing jet & reflected light from surface of flared disk (Watson et al. 2000).
HH 211
Dec
5000 AU
RA
Top: Embedded outflow/accretion system HH 211: CO (molecular outflow), H2
(shocks), & 1 mm (230 GHz) continuum (warm dust) (McCaughrean et al. 1994, Gueth & Guilloteau 1999).
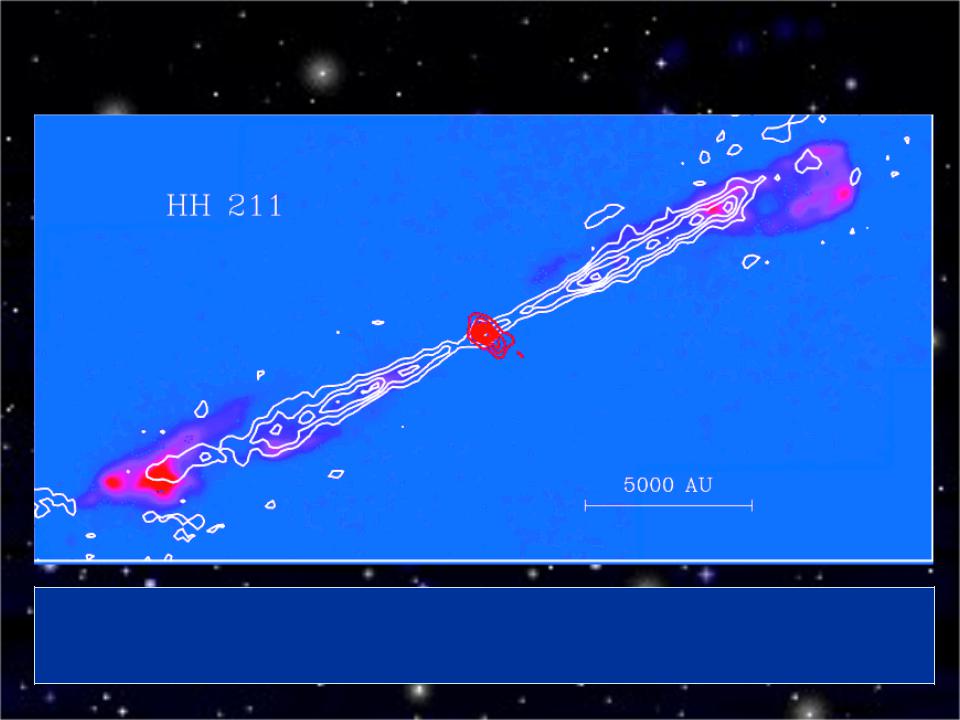
Высокоскоростные биполярные истечения
Interferometer map of the molecular jet in the HH211 outflow; the CO emission (white lines) is overlaid on a false color image of excited molecular hydrogen. The red lines delineate a flattened dust concentration around the protostar.
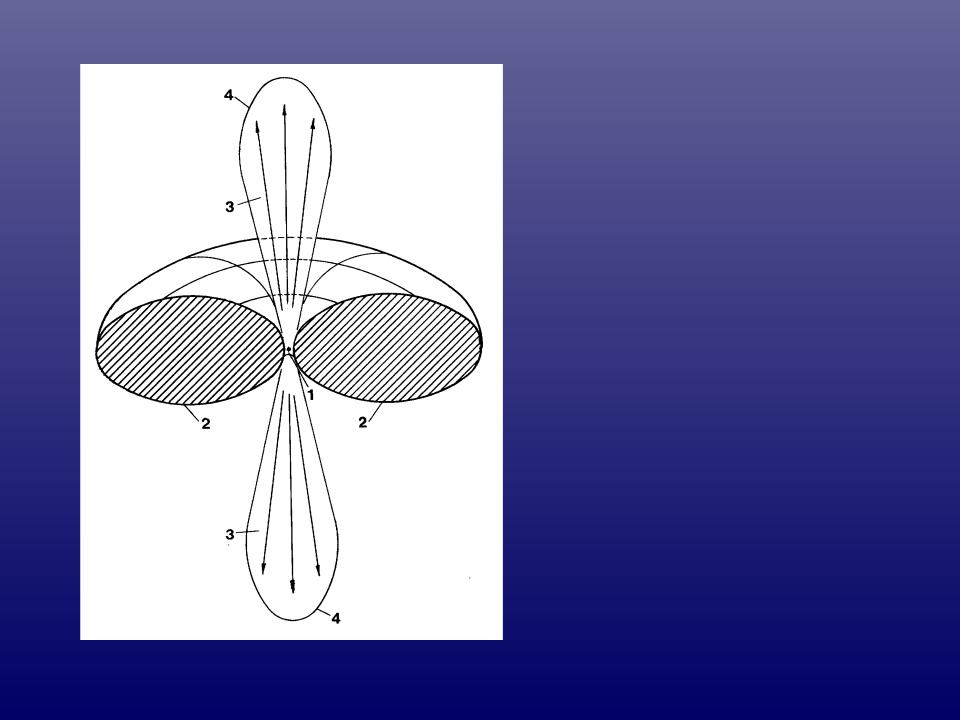
Структура
биполярного истечения из молодой звезды: 1 – звезда, 2 – околозвездный диск, 3 – поток
ускоренного молекулярного газа, 4 – ударная волна.

G192.163.82 – Artist view
Massive protostar with 130 AU diameter accretion disk and wideangle outflow.
Close binary companion,
100 AU separation – truncating inner disk?
Circumbinary torus – inferred from water maser emission.
Wellcollimated jet (mixed thermal and synchrotron emission) , actual location of protostar producing jet is unknown.
