
- •MicroRna (miRna)
- •Splicing
- •Editing
- •Polyadenylation
- •Transport
- •A hairpin loop from a pre-mRna. Highlighted are the nucleobases (green) and the ribose-phosphate backbone (blue).
- •Three-dimensional representation of the 50s ribosomal subunit. Rna is in ochre, protein in blue. The active site is in the middle (red). Translation
- •Inside the ribosome
- •Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
- •Key discoveries in rna biology
- •TRna Function: Synthetases
- •Accuracy & Proofreading
Transport
Another difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes is mRNA transport. Because eukaryotic transcription and translation is compartmentally separated, eukaryotic mRNAs must be exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Mature mRNAs are recognized by their processed modifications and then exported through the nuclear pore. In neurons, mRNA must be transported from the soma to the dendrites where local translation occurs in response to external stimuli.[1] Many messages are marked with so-called "zip codes," which target their transport to a specific location.[2]
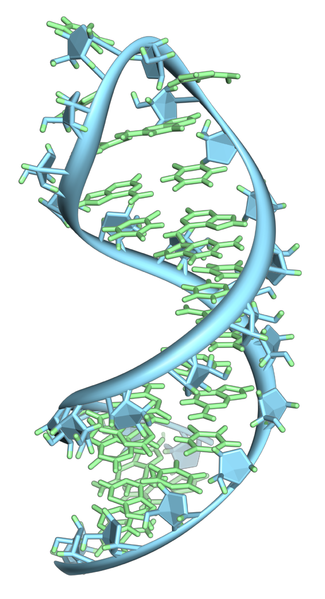
A hairpin loop from a pre-mRna. Highlighted are the nucleobases (green) and the ribose-phosphate backbone (blue).

Three-dimensional representation of the 50s ribosomal subunit. Rna is in ochre, protein in blue. The active site is in the middle (red). Translation
Main article: Translation (genetics)
Because prokaryotic mRNA does not need to be processed or transported, translation by the ribosome can begin immediately after the end of transcription. Therefore, it can be said that prokaryotic translation is coupled to transcription and occurs co-transcriptionally.
Eukaryotic mRNA that has been processed and transported to the cytoplasm (i.e., mature mRNA) can then be translated by the ribosome. Translation may occur at ribosomes free-floating in the cytoplasm, or directed to the endoplasmic reticulum by thesignal recognition particle. Therefore, unlike in prokaryotes, eukaryotic translation is not directly coupled to transcription.
rRNA

Inside the ribosome
The ribosomal RNAs form two subunits, the large subunit (LSU) and small subunit (SSU). mRNA is sandwiched between the small and large subunits and the ribosome catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the 2 amino acids that are contained in the rRNA.
A ribosome also has 3 binding sites called A, P, and E.
The A site in the ribosome binds to an aminoacyl-tRNA (a tRNA bound to an amino acid).
The amino (NH2) group of the aminoacyl-tRNA, which contains the new amino acid, attacks the ester linkage of peptidyl-tRNA (contained within the P site), which contains the last amino acid of the growing chain, forming a new peptide bond. This reaction is catalyzed by peptidyl transferase.
The tRNA that was holding on the last amino acid is moved to the E site, and what used to be the aminoacyl-tRNA is the peptidyl-tRNA.
A single mRNA can be translated simultaneously by multiple ribosomes.
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes can be broken down into two subunits (the S in 16S represents Svedberg units):
|
Type |
Size |
Large subunit |
Small subunit |
|
prokaryotic |
70S |
50S (5S, 23S) |
30S (16S) |
|
eukaryotic |
80S |
60S (5S, 5.8S, 28S) |
40S (18S) |
Note that the S units of the subunits cannot simply be added because they represent measures of sedimentation rate rather than of mass. The sedimentation rate of each subunit is affected by its shape, as well as by its mass.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosome, the sites of protein synthesis (translation) in the cell. The coding sequence of the mRNA determines the amino acidsequence in the protein that is produced.[20] Many RNAs do not code for protein however (about 97% of the transcriptional output is non-protein-coding in eukaryotes [21][22][23][24]).
These so-called non-coding RNAs ("ncRNA") can be encoded by their own genes (RNA genes), but can also derive from mRNA introns.[25] The most prominent examples of non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA(tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which involved in the process of translation.[1] There are also non-coding RNAs involved in gene regulation, RNA processing and other roles. Certain RNAs are able tocatalyse chemical reactions such as cutting and ligating other RNA molecules,[26] and the catalysis of peptide bond formation in the ribosome;[3] these are known as ribozymes.

Structure of a hammerhead ribozyme, a ribozyme that cuts RNA
