
- •Вопрос 9. The Adjective. Its general characteristics, the word order and the Degrees of Comparison. Substantivized Adjectives.
- •Вопрос 10. The Adverb. Its general characteristics, place in the sentence and the Degrees of Comparison. Adverbs having two forms different in meaning.
- •Вопрос 11. The Verb. Its general characteristics and categories.
- •Is notional PoS which identifies actions
- •Finite forms (categories)-конечная форма
- •Synthetic and analytical forms
- •Tense – indicate the time of the actions
- •6. Direct moods
- •7. Cat. Of Voice
- •Вопрос 12. The Pronoun and its classification.
- •Number -in the system of pronouns can be expressed in different ways:
- •Indefinite Pronouns
- •A reflexive pronoun can be used in the sentence as an object, attribute, predicative, an adverbial modifier
- •The Russian reflexive meaning (ся) can be expressed in English by:
- •Interrogative (Question) Pronouns
- •Numerals may be used in the sentence in the function of:
- •Numerals fall into cardinals and ordinals.
- •Ordinal numerals denote order or position and answer the question “Which?”
- •Fractional numbers.
- •In fractional numbers the numerator is a cardinal numeral and the denominator is an ordinal (used as a noun):
- •The spoken forms of 0 are:
- •Classification of sentences.
6. Direct moods
The subjunctive The conditional mood
I wish this day wasn’t so cold –Subjunctive
If I were you I wouldn’t do it – Conditional
7. Cat. Of Voice
It’s form of the verb which shows the relation between the subject and the action
Active voice Passive Voice
The verb shows the subject is the doer shows that the subject
Of the action (Испольнитель действия) is acted upon (Подвергается действию)
We won the competition The car is being washed
Вопрос 12. The Pronoun and its classification.
The Pronoun
The Pronoun is a part of speech which points out things and qualities of things without naming them directly like nouns and adjectives do.
Grammatical categories of Pronouns:
Gender
he — masculine
she — feminine
it — neuter
they — refers to all of them in the plural
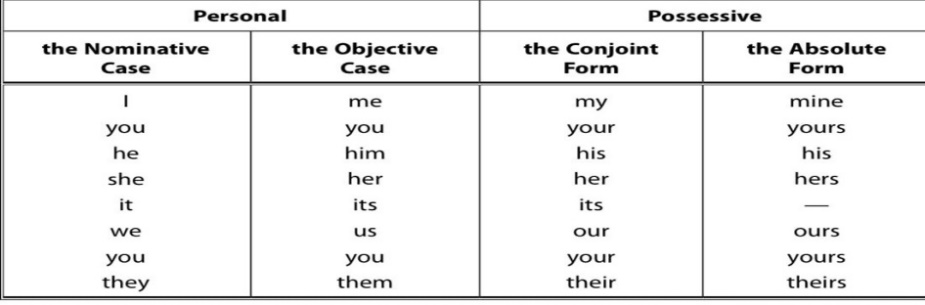
Case: only personal pronouns have cases — the Nominative Case and the Objective Case.
1)Nominative Case- именительный падеж : I, he she, they, we, you
2)Objective Case- Объектный падеж : me, him, her, them, it, us, you
Number -in the system of pronouns can be expressed in different ways:
Singular form- this, that, myself, herself
Plural form- these, those, ourselves, themselves
Groups of pronouns:
1. Personal: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they
2. Possessive: me, your, his, her, its, our, your, their mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, yours, theirs
3. Demonstrative: it, this, these, that, those, same, such
4. Interrogative: who (whom), whose, which, what (in questions)
5. Relative: who (whom), whose, which, that (in attributive clauses)
6. Conjunctive: who (whom), whose, which, what (in diff erent subordinate clauses)
7. Self-pronouns: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
8. Reciprocal: each other, one another
9. Negative: no, nobody (no one), none, nothing (in negative sentences)
10. Indefinite: some, any, no (and their compounds), all, both, each, every (and its compounds), other, another, one, much, many, (a) little, (a) few
Personal Pronouns
Personal Pronouns have two cases — the Nominative Case and the Objective Case.
When a personal pronoun is a subject, or a predicative of the sentence, it is used in the Nominative Case in official, formal style.
In informal, colloquial style the use of the objective case of the personal pronoun has become standard in Modern English.
The Objective Case of the personal pronoun is used after such prepositions as between, up, but (in the meaning of except), except, without.
If the pronoun follows than or as we can use me, him, etc. (informal style) or I, he, etc. with a verb (more formal). Also in short answers.
Possessive Pronouns
The Possessive Pronouns have two forms — the Conjoint Form and the Absolute Form
the Conjoint Form ( pronoun+noun ): my, your, his, her, its, our , their
the Absolute Form (pronoun — no noun): mine ,yours, his ,hers, — ,ours , theirs
The conjoint form of the pronoun is always followed by a noun.
The absolute form is used absolutely, without any noun and may have different functions in the sentence.
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative Pronouns have number — the singular and the plural. (this — these, that — those)
The general demonstrative meaning of these pronouns is near and distant reference in time and space.
This/these identify something near to the speaker, they are associated with “here”.
That/those identify something farther from the speaker; they are associated with “there”. (this room — that house; this year — that day)
