
Полезные материалы за все 6 курсов / Учебники, методички, pdf / INBDEBooster Oral Pathology
.pdf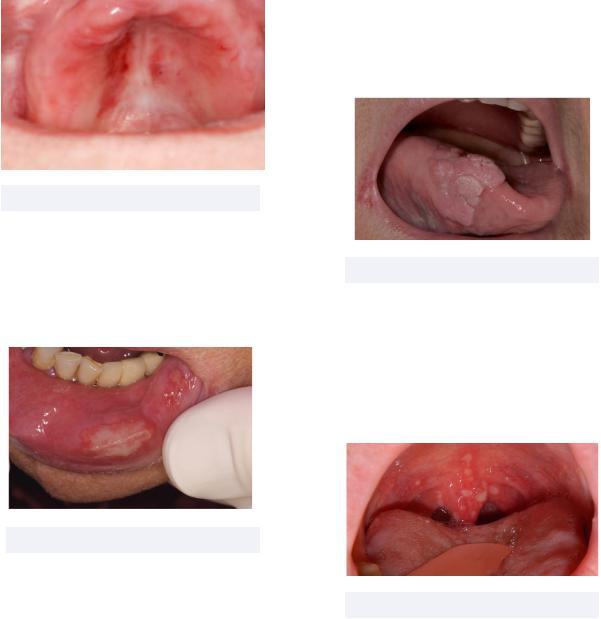
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES |
11 |
characterized based on size:
-Petechiae: 1 mm
-Purpura: slightly larger than petechiae
-Ecchymosis: 1+ cm
-Hematoma: mass of blood within tissue, often caused by trauma to oral mucosa
know for the INBDE!
Viral Infections
•Condyloma Acuminatum - papilloma caused by HPV infection, with strains 6 and 11 having the highest prevalence
Must know: This condition may manifest as a genital or oral wart, usually as a result of having oral sex with someone with genital warts
Treatment: Excision with high recurrence
Figure 2.09 Submucosal hemorrhage
•Traumatic Ulcer - a complete break through the epithelium
Must know: This common condition differs from erosion, which is an incomplete break of the epithelium
Figure 2.11 Condyloma Acuminatum
•Coxsackie Virus - an enterovirus causing hand-foot-and-mouth diseases
Must know: This virus can also cause herpangia, which results in small blisterlike sores in the posterior oral cavity (soft palate, throat, and tonsils)
Figure 2.10 Traumatic ulcer
That wraps up reactive mucosal lesions! Let’s move onto learning about high-yield infectious lesions!
Infectious Mucosal Lesions
This section will highlight various viral, bacterial, and fungal infections you’ll need to
Figure 2.12 Herpangia
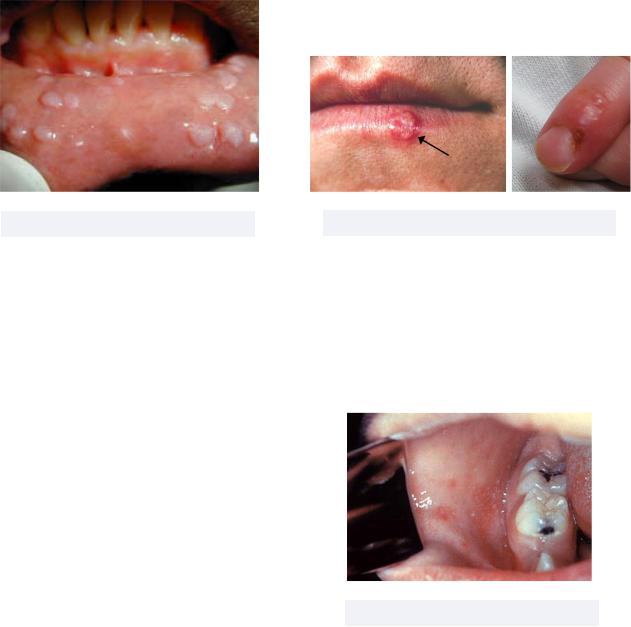
•Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia (Heck’s Disease) - papilloma caused by HPV 13 and 32
Must know: This condition presents as
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
multiple small dome-shaped warts on oral mucosa
Treatment: Excision with excellent prognosis
Figure 2.13 Focal epithelial hyperplasia
•Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) - a viral infection causing contagious genital and/or oral sores
Must know: There are two manifestations of HSV = primary and recurrent
-Primary: When you contract the virus for the first time in the oral region; this stage is self-limiting and occurs during childhood. Upon healing, the virus remains dormant, or latent, in the trigeminal ganglion
-Recurrent: When the virus is triggered by stress, sunlight, or immunosuppression; has the following different manifestations on keratinized tissue
Herpes gladiatorum - sores on lateral neck, sides of face, and forearm
Herpes labialis (recurrent extraoral herpes) - cold sores on the vermillion border
Herpetic whitlow (AKA an occupational disease of practicing dentists!) - sores on fingers; dentists with this condition should not contact
12
patients until it subsides
Recurrent intraoral herpes - sores form exclusively on attached gingiva or hard palate
Treatment: Antiviral such as acyclovir during the prodromal period, the period of itching and tingling 12-24 hours before
Figure 2.14 HSV (left), herpetic whitlow (right)
•Measles - a viral infection with oral manifestations including Koplik’s spots, or buccal mucosa dot ulcers, that precede the characteristic measles skin rash
Must know: The primary infection of measles is self limiting and occurs during childhood
Figure 2.15 Koplik’s spots
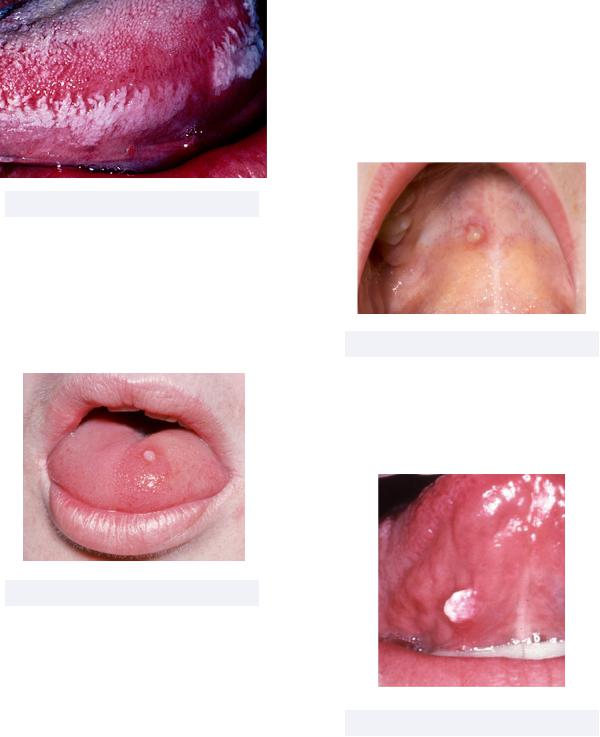
•Oral Hairy Leukoplakia - a condition triggered by Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) causing white hairy-appearing patches on the tongue that do not wipe off
Must know: This is an opportunistic infection associated with HIV and
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES |
13 |
Burkett’s lymphoma |
- Recurrent: When the virus is triggered |
|
again by stress, sunlight, |
|
immunosuppression; leads to shingles |
|
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: a herpes |
|
zoster reactivation in geniculate |
|
ganglion impacting CN VII and VIII |
|
leading to facial paralysis, vertigo, |
|
and deafness |
|
Treatment: Acyclovir |
Figure 2.16 Oral hairy leukoplakia
•Papilloma - benign noncancerous exophytic growths caused by several strains of HPV
Must know: Papillomas have pedunculate (ballooning) or sessile (mound shaped) proliferation on skin or mucosa
Figure 2.17 Papilloma
•Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV) - a herpes virus infection causing itchy, blister-like rashes on the skin
Must know: Similar to HSV, VZV has two manifestations = primary and recurrent
-Primary: When you contract the virus for the first time; is self-limiting and occurs during childhood. Upon healing, the virus becomes latent in trigeminal ganglion
Figure 2.18 Chickenpox lesion in mouth
•Verruca Vulgaris - a type of papilloma caused by several strains of HPV
Must know: A common skin wart; can auto inoculate
Figure 2.19 Oral verruca vulgaris
Bacterial Infections (uncommon due to preventative effects of saliva!)
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM

INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
•Actinomycosis - an infection caused by filamentous bacteria Actinomyces israelii — do not confuse this with a fungal infection!
Must know: This is an opportunistic, chronic, and granulomatous infection with two main types = periapical and cervicofacial
-Periapical: jaw infection
-Cervicofacial: head and neck infection
-The most common characteristic of actinomycosis is the presence of sulfur granules in the purulent exudate
Treatment: Long-term high-dose penicillin
Figure 2.20 Actinomycosis
•Gonorrhea - infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae that usually impacts urethra, rectum, or throat
Must know: Oral manifestations of gonorrhea are extremely rare
Figure 2.21 Throat gonorrhea
14
•Syphilis - a bacterial infection caused by contact with Treponema pallidum
(spirochete) and usually spread by sexual contact that starts as a painless sore on genitals, rectum, or mouth, but can become a systemic condition
Must know: There are three different types of lesions = primary, secondary, and tertiary
-Primary lesion: chancre, a painless genital ulcer, forms
-Secondary lesion: oral mucous patch, condyloma latum, or maculopapular rash are observed
-Tertiary lesion: gumma, or a soft tumorlike growth, forms; CNS and cardiovascular systems become involved
-Congenital syphilis: a mother with syphilis can give birth to a baby with congenital syphilis, and the condition follows Hutchinson’s triad pattern of presentation:
Teeth abnormalities (notched incisors, mulberry molars), deafness, and ocular keratitis (think: hear no evil = deafness, see no evil = ocular keratitis, speak no evil = teeth abnormalities)
Figure 2.22 Oral syphilis
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
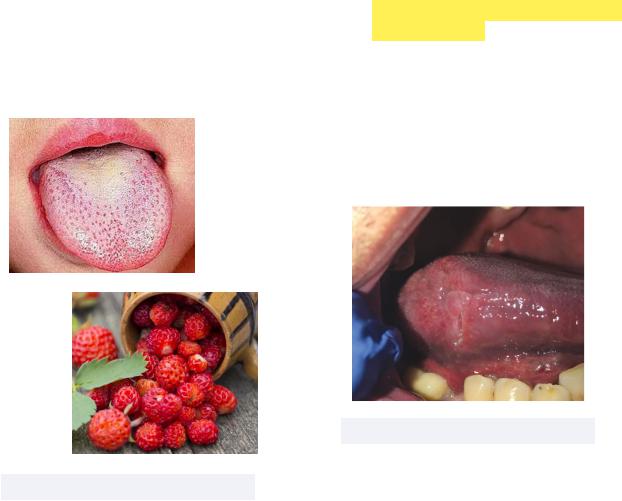
•Scarlet Fever - a bacterial infection caused by Group A Strep (such as streptococcus pyrogenes) that develops when strep throat becomes a systemic infection
Must know: Strawberry tongue is a characteristic oral manifestation, and appears as a white-coated tongue with inflamed red fungiform papillae — not to be confused with hairy tongue where filiform papillae is impacted
Treatment: Penicillin
15
-in a granuloma that undergoes caseating necrosis (type of cell death with cheese-like appearance). In addition, the hilar lymph node (located at the root of the lung) draining the first lesion becomes infected
The inhaled bacteria is “gone” in the “Ghon complex”
-Secondary infection: The lung infection becomes more widespread, and pulmonary cavitation is observed
-Miliary infection: Systemic spread of tuberculosis
Treatment: Multi-drug therapy involving isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol
Figure 2.23 Strawberry tongue
•Tuberculosis - infection caused by inhalation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that results in oral non-healing chronic ulcers that follow the characteristic tuberculosis lung infection
Must know: has three different types of infections = primary, secondary, and miliary
-Primary infection: Involves formation of the Ghon complex, which forms when inhaled bacteria becomes surrounded
Figure 2.24 Oral tuberculosis
Fungal Infections
•Candidiasis - a fungal infection caused by Candida
Must know: Also known as thrush, this infection has several different types
-Angular cheilitis: inflammation of corners of the mouth
-Atrophic: a red plaque on oral mucosa that may form due to a poorly fitting denture or prosthetic device, or poorly cleaned prosthetic device
-Median rhomboid glossitis: loss of lingual papillae resulting in a “bald
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
-spot” on the tongue
-Pseudomembranous: a white plaque that does wipe off
Treatment: An anti fungal such as Clotrimazole or Nystatin
•Deep fungal infections - common infections with their characteristic US locations
Must know: the 4 major regions of the US have higher prevalence (albeit overall low) of the following fungal infections
-Blastomycosis: Northeast; usually occurs due to inhalation of spores after a big rain
-Coccidioidomycosis: Southwest; fungus lives in soil and causes “Valley Fever”
-Cryptococcosis: West; inhalation of soil contaminated with Cryptococcus fungus
-Histoplasmosis: Midwest; fungus found in soil that contains large amounts of bird or bat droppings
Figure 2.25 Atrophic candidiasis
Figure 2.26 Median rhomboid glossitis
16
Figure 2.27 Pseudomembranous candidiasis
Figure 2.28 Map of US fungal disease
Mucosal Immunologic Diseases
Continuing through our study of mucosal lesions, we now turn our attention to immunologic diseases of the oral cavity. These diseases may be autoimmune, when the immune system attacks itself, or hyperimmune, when the immune response is overexaggerated.
•Angioedema - an allergic reaction in response to contact to food or drugs causing diffuse swelling on face, neck, and/ or lips
Must know: allergic reactions, in general, are mediated by the mast cell release of IgE and histamines
-This can also occur due to side effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Treatment: antihistamines
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM

INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
Figure 2.29 Angioedema
•Aphthous Ulcer - the most common immunologic mucosal condition commonly known as a “canker sore"
Must know: this condition impacts nonkeratinized tissues (includes lining mucosa such as alveolar, buccal, labial mucosa; the soft palate; and ventral surface of the tongue)
-While this condition may superficially look similar to HSV, the two differ in that HSV impacts only keratinized tissues
-Can have two different types: minor ulcers, which heal without scarring, and major ulcers (Sutton Disease), that heal with scarring
-Behcet’s Syndrome is a multi system vasculitis condition that causes aphthous ulcers in the oral cavity and genitals, as well as inflammation of the eyes
Treatment: only necessary for serious cases; corticosteroids are perfect due to their anti-inflammatory properties
Figure 2.30 Aphthous Ulcer
17
•Erythema Multiforme - an acute selflimiting condition causing oral and skin lesions that present as flat, round, bullseye, target lesions, as well as hemorrhagic crusting of the lips
Must know: can have minor or major conditions
-Minor: related to herpes simplex hypersensitivity
-Major: related to drug sensitivity; also known as Stevens Johnson Syndrome
Figure 2.31 Erythema Multiforme
•Lichen Planus - a skin or oral mucosa inflammatory condition in which T lymphocytes target and destroy basal keratinocytes resulting in a burning or itching rash
Must know: secondary to the destruction of basal keratinocytes are basal zone vacuolization and sawtooth rete pegs, both of which are observed histologically
-Two forms of the condition: reticular and erosive
Reticular: characterized by Wickham striae, lacy ribbon-like stripes on affected area
Erosive: also has Wickham striae, as well as red ulceration
Treatment: No treatment for asymptomatic reticular conditions; corticosteroids for symptomatic erosive conditions
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES |
18 |
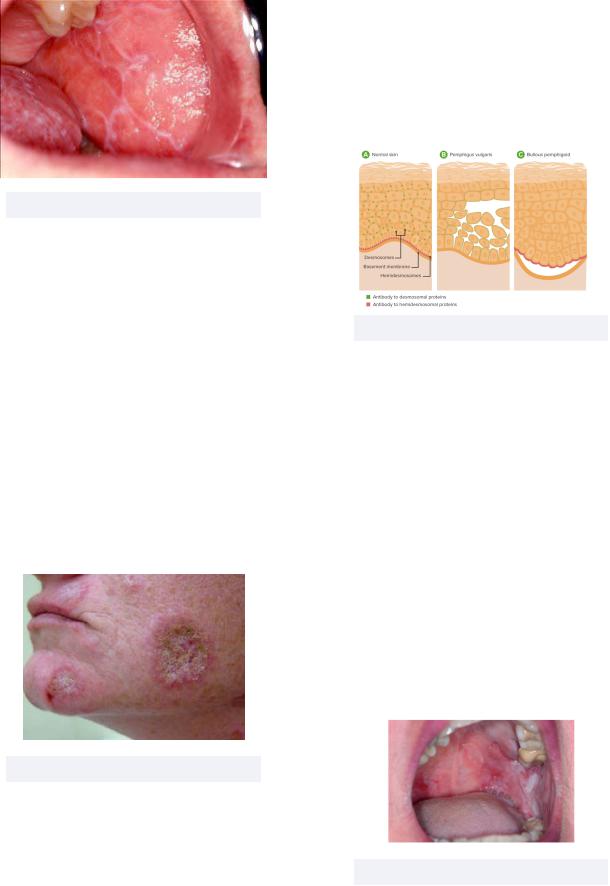
Must know: a sub-basilar condition in which the body creates autoantibodies against the basement membrane
- Other than this difference, MMP is the same as pemphigus vulgaris
Treatment: corticosteroids
Figure 2.32 Lichen Planus
•Lupus Erythematosus - an autoimmune disease that causes widespread inflammation and tissue damage in affected organs
Must know: there are two main forms of lupus
-Systemic acute: a type III hypersensitivity reaction with involvement of multiple organs; presence of butterfly rash along the bridge of nose; detected via presence of autoantibodies using the ANA test
-Discoid chronic: disc-shaped lesions on face; oral lesions look similar to erosive lichen planus
Treatment: corticosteroids
Figure 2.34 MMP vs PV
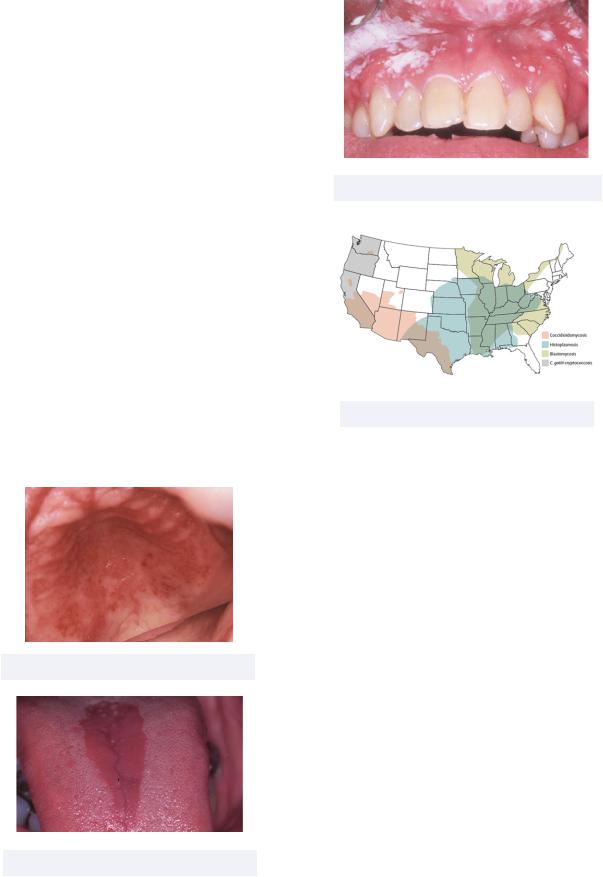
•Pemphigus Vulgaris - an autoimmune disorder involving blistering and erosion of skin and mucosal membranes
Must know: a suprabasilar condition in which the body creates autoantibodies against desmosomes, adhesive proteins that maintain structural integrity of tissues
-The primary lesion of the condition is a soft blister filled with clear fluid “bullae” followed by multiple painful ulcers
-Detected by a positive Nikolsky’s sign in which slight rubbing of affected skin or mucosa results in exfoliation of the outermost layer
Treatment: corticosteroids
Figure 2.33 Discoid lesions
•Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid - an autoimmune disease characterized by blistering lesions on mucous membranes
Figure 2.35 Pemphigus Vulgaris
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES
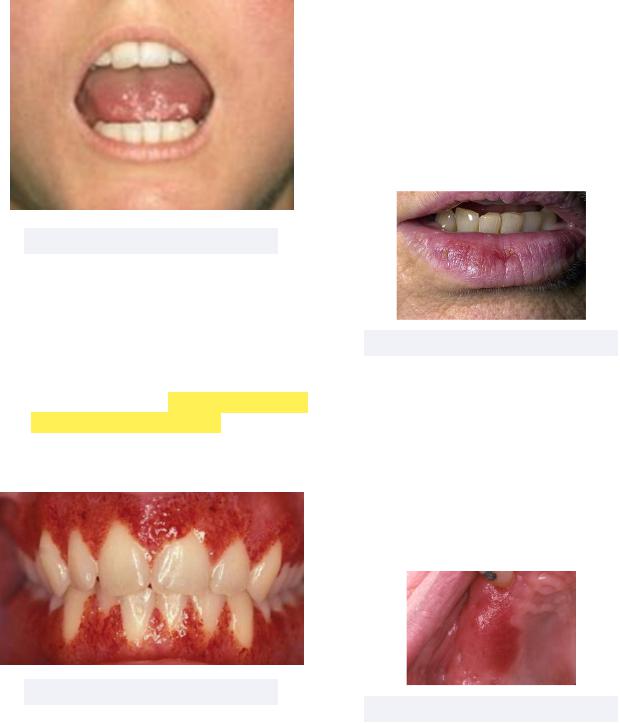
•Scleroderma - a condition involving the hardening of skin and connective tissue
Must know: relating to dentistry, scleroderma can make it more difficult to open the mouth
-Uniform widening of the PDL space is also observed
19
Premalignant Mucosal Lesions
Let us now delve into premalignant, or precancerous, mucosal lesions! High risk areas in mouth for developing cancer include floor of mouth, lateral and ventral tongue, and palate. The risk of premalignant lesions and oral cancers increases with tobacco and alcohol consumption.
•Actinic Cheilitis - inflammation of lip due to prolonged sun exposure
Must know: “actinic” = solar, “cheilitis” = reaction to long term sun damage caused primarily by UVB rays
Treatment: surgical excision, or laser ablation for severe cases
Figure 2.36 Scleroderma
•Wegener’s Granulomatosis (new name: granulamatosis polyangiitis, GPA) - an allergic reaction to inhaled antigens, NOT direct contact like angioedema
Must know: the characteristic oral manifestation of this condition is strawberry gingivitis (“chewing strawberry gum gives you a high GPA”)
Treatment: corticosteroids (prednisone) and cyclophosphamide
Figure 2.38 Actinic Cheilitis
•Erythroplakia - red patch on inside surface of mouth
Must know: this is a clinical description and not a diagnosis
-Almost all true erythroplakias are histologically diagnosed as significant epithelial dysplasia or carcinomas
Treatment: mandatory biopsy for histology
Figure 2.37 GPA
Figure 2.39 Erythroplakia
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
INBDE ORAL PATHOLOGY NOTES |
20 |
•Leukoplakia - white patch inside mouth that does not wipe/rub off
Must know: clinical description and not a diagnosis. Once diagnosis is determined, we no longer refer to this as leukoplakia
Treatment: mandatory biopsy for histology
•Smokeless Tobacco Associated Lesions - lesions from prolonged smokeless tobacco use
Must know: smokeless tobacco & its additives drive white mucosal change in vestibule
Treatment: ranges from basic biopsy to surgical excision depending on severity; early and late stage lifestyle interventions
Figure 2.40 Leukoplakia
•Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia (PVL)
-still a white patch that does not rub off, but is now spreading and has a warty appearance
Must know: PVL is believed to be associated with HPV strains 16 and 18, which are the same strains that are highest risk for development of cervical cancer
-PVL has a high risk of malignant transformation to verrucous carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma
Treatment: surgical resection
Figure 2.41 PVL
Figure 2.42 White Mucosal Change
Malignant Mucosal Lesions
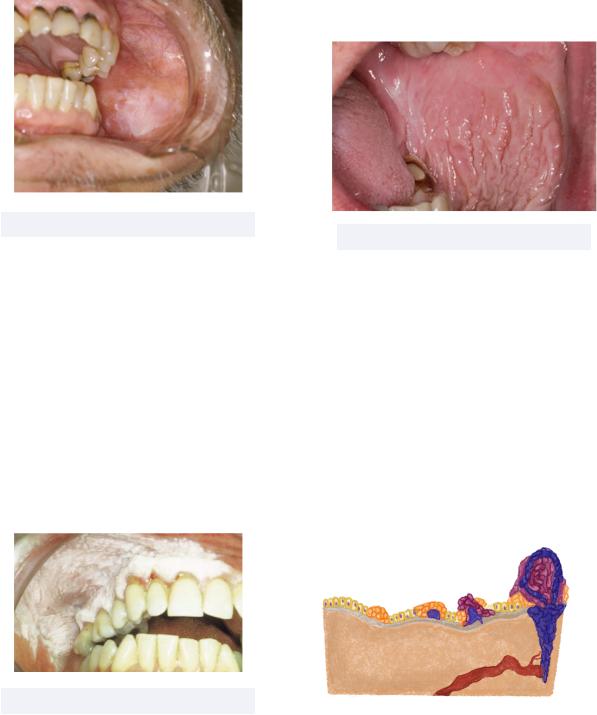
We wrap up our discussion of mucosal lesions by learning about malignant conditions. When cells of mucosal lesions do become cancerous, they are now malignant, and follow the progression of cancer development as is seen throughout the body. The following graphic shows four overarching stages of cancer development:
Invasive
cancer
In situ cancer
Hyperplasia
Dysplasia
INBDE Booster | Booster PrepTM
