
- •Network Intrusion Detection, Third Edition
- •Table of Contents
- •Copyright
- •About the Authors
- •About the Technical Reviewers
- •Acknowledgments
- •Tell Us What You Think
- •Introduction
- •Chapter 1. IP Concepts
- •Layers
- •Data Flow
- •Packaging (Beyond Paper or Plastic)
- •Bits, Bytes, and Packets
- •Encapsulation Revisited
- •Interpretation of the Layers
- •Addresses
- •Physical Addresses, Media Access Controller Addresses
- •Logical Addresses, IP Addresses
- •Subnet Masks
- •Service Ports
- •IP Protocols
- •Domain Name System
- •Routing: How You Get There from Here
- •Summary
- •Chapter 2. Introduction to TCPdump and TCP
- •TCPdump
- •TCPdump Behavior
- •Filters
- •Binary Collection
- •TCPdump Output
- •Absolute and Relative Sequence Numbers
- •Dumping in Hexadecimal
- •Introduction to TCP
- •Establishing a TCP Connection
- •Server and Client Ports
- •Connection Termination
- •The Graceful Method
- •The Abrupt Method
- •Data Transfer
- •What's the Bottom Line?
- •TCP Gone Awry
- •An ACK Scan
- •A Telnet Scan?
- •TCP Session Hijacking
- •Summary
- •Chapter 3. Fragmentation
- •Theory of Fragmentation
- •All Aboard the Fragment Train
- •The Fragment Dining Car
- •The Fragment Caboose
- •Viewing Fragmentation Using TCPdump
- •Fragmentation and Packet-Filtering Devices
- •The Don't Fragment Flag
- •Malicious Fragmentation
- •TCP Header Fragments
- •Teardrop
- •Summary
- •Chapter 4. ICMP
- •ICMP Theory
- •Why Do You Need ICMP?
- •Where Does ICMP Fit In?
- •Understanding ICMP
- •Summary of ICMP Theory
- •Mapping Techniques
- •Tireless Mapper
- •Efficient Mapper
- •Clever Mapper
- •Cerebral Mapper
- •Summary of Mapping
- •Normal ICMP Activity
- •Host Unreachable
- •Port Unreachable
- •Admin Prohibited
- •Need to Frag
- •Time Exceeded In-Transit
- •Embedded Information in ICMP Error Messages
- •Summary of Normal ICMP
- •Malicious ICMP Activity
- •Smurf Attack
- •Tribe Flood Network
- •WinFreeze
- •Loki
- •Unsolicited ICMP Echo Replies
- •Theory 1: Spoofing
- •Theory 2: TFN
- •Theory 3: Loki
- •Summary of Malicious ICMP Traffic
- •To Block or Not to Block
- •Unrequited ICMP Echo Requests
- •Kiss traceroute Goodbye
- •Silence of the LANs
- •Broken Path MTU Discovery
- •Summary
- •Chapter 5. Stimulus and Response
- •The Expected
- •Request for Comments
- •TCP Stimulus-Response
- •Destination Host Listens on Requested Port
- •Destination Host Not Listening on Requested Port
- •Destination Host Doesn't Exist
- •Destination Port Blocked
- •Destination Port Blocked, Router Doesn't Respond
- •UDP Stimulus-Response
- •Destination Host Listening on Requested Port
- •Destination Host Not Listening on Requested Port
- •Windows tracert
- •TCPdump of tracert
- •Protocol Benders
- •Active FTP
- •Passive FTP
- •UNIX Traceroute
- •Summary of Expected Behavior and Protocol Benders
- •Abnormal Stimuli
- •Evasion Stimulus, Lack of Response
- •Evil Stimulus, Fatal Response
- •No Stimulus, All Response
- •Unconventional Stimulus, Operating System Identifying Response
- •Bogus "Reserved" TCP Flags
- •Anomalous TCP Flag Combinations
- •No TCP Flags
- •Summary of Abnormal Stimuli
- •Summary
- •Chapter 6. DNS
- •Back to Basics: DNS Theory
- •The Structure of DNS
- •Steppin' Out on the Internet
- •DNS Resolution Process
- •TCPdump Output of Resolution
- •Strange TCPdump Notation
- •Caching: Been There, Done That
- •Reverse Lookups
- •Master and Slave Name Servers
- •Zone Transfers
- •Summary of DNS Theory
- •Using DNS for Reconnaissance
- •The nslookup Command
- •Name That Name Server
- •HINFO: Snooping for Details
- •List Zone Map Information
- •Tainting DNS Responses
- •A Weak Link
- •Cache Poisoning
- •Summary
- •Part II: Traffic Analysis
- •Chapter 7. Packet Dissection Using TCPdump
- •Why Learn to Do Packet Dissection?
- •Sidestep DNS Queries
- •Normal Query
- •Evasive Query
- •Introduction to Packet Dissection Using TCPdump
- •Where Does the IP Stop and the Embedded Protocol Begin?
- •Other Length Fields
- •The IP Datagram Length
- •Increasing the Snaplen
- •Dissecting the Whole Packet
- •Freeware Tools for Packet Dissection
- •Ethereal
- •tcpshow
- •Summary
- •Chapter 8. Examining IP Header Fields
- •Insertion and Evasion Attacks
- •Insertion Attacks
- •Evasion Attacks
- •IP Header Fields
- •IP Version Number
- •Protocol Number
- •The Don't Fragment (DF) Flag
- •The More Fragments (MF) Flag
- •Mapping Using Incomplete Fragments
- •IP Numbers
- •IP Identification Number
- •Time to Live (TTL)
- •Looking at the IP ID and TTL Values Together to Discover Spoofing
- •IP Checksums
- •Summary
- •Chapter 9. Examining Embedded Protocol Header Fields
- •Ports
- •TCP Checksums
- •TCP Sequence Numbers
- •Acknowledgement Numbers
- •TCP Flags
- •TCP Corruption
- •ECN Flag Bits
- •Operating System Fingerprinting
- •Retransmissions
- •Using Retransmissions Against a Hostile Host—LaBrea Tarpit Version 1
- •TCP Window Size
- •LaBrea Version 2
- •Ports
- •UDP Port Scanning
- •UDP Length Field
- •ICMP
- •Type and Code
- •Identification and Sequence Numbers
- •Misuse of ICMP Identification and Sequence Numbers
- •Summary
- •Chapter 10. Real-World Analysis
- •You've Been Hacked!
- •Netbus Scan
- •How Slow Can you Go?
- •RingZero Worm
- •Summary
- •Chapter 11. Mystery Traffic
- •The Event in a Nutshell
- •The Traffic
- •DDoS or Scan
- •Source Hosts
- •Destination Hosts
- •Scanning Rates
- •Fingerprinting Participant Hosts
- •Arriving TTL Values
- •TCP Window Size
- •TCP Options
- •TCP Retries
- •Summary
- •Part III: Filters/Rules for Network Monitoring
- •Chapter 12. Writing TCPdump Filters
- •The Mechanics of Writing TCPdump Filters
- •Bit Masking
- •Preserving and Discarding Individual Bits
- •Creating the Mask
- •Putting It All Together
- •TCPdump IP Filters
- •Detecting Traffic to the Broadcast Addresses
- •Detecting Fragmentation
- •TCPdump UDP Filters
- •TCPdump TCP Filters
- •Filters for Examining TCP Flags
- •Detecting Data on SYN Connections
- •Summary
- •Chapter 13. Introduction to Snort and Snort Rules
- •An Overview of Running Snort
- •Snort Rules
- •Snort Rule Anatomy
- •Rule Header Fields
- •The Action Field
- •The Protocol Field
- •The Source and Destination IP Address Fields
- •The Source and Destination Port Field
- •Direction Indicator
- •Summary
- •Chapter 14. Snort Rules - Part II
- •Format of Snort Options
- •Rule Options
- •Msg Option
- •Logto Option
- •Ttl Option
- •Id Option
- •Dsize Option
- •Sequence Option
- •Acknowledgement Option
- •Itype and Icode Options
- •Flags Option
- •Content Option
- •Offset Option
- •Depth Option
- •Nocase Option
- •Regex Option
- •Session Option
- •Resp Option
- •Tag Option
- •Putting It All Together
- •Summary
- •Part IV: Intrusion Infrastructure
- •Chapter 15. Mitnick Attack
- •Exploiting TCP
- •IP Weaknesses
- •SYN Flooding
- •Covering His Tracks
- •Identifying Trust Relationships
- •Examining Network Traces
- •Setting Up the System Compromise?
- •Detecting the Mitnick Attack
- •Trust Relationship
- •Port Scan
- •Host Scan
- •Connections to Dangerous Ports
- •TCP Wrappers
- •Tripwire
- •Preventing the Mitnick Attack
- •Summary
- •Chapter 16. Architectural Issues
- •Events of Interest
- •Limits to Observation
- •Human Factors Limit Detects
- •Limitations Caused by the Analyst
- •Limitations Caused by the CIRTs
- •Severity
- •Criticality
- •Lethality
- •Countermeasures
- •Calculating Severity
- •Scanning for Trojans
- •Analysis
- •Severity
- •Host Scan Against FTP
- •Analysis
- •Severity
- •Sensor Placement
- •Outside Firewall
- •Sensors Inside Firewall
- •Both Inside and Outside Firewall
- •Analyst Console
- •Faster Console
- •False Positive Management
- •Display Filters
- •Mark as Analyzed
- •Drill Down
- •Correlation
- •Better Reporting
- •Event-Detection Reports
- •Weekly/Monthly Summary Reports
- •Summary
- •Chapter 17. Organizational Issues
- •Organizational Security Model
- •Security Policy
- •Industry Practice for Due Care
- •Security Infrastructure
- •Implementing Priority Countermeasures
- •Periodic Reviews
- •Implementing Incident Handling
- •Defining Risk
- •Risk
- •Accepting the Risk
- •Trojan Version
- •Malicious Connections
- •Mitigating or Reducing the Risk
- •Network Attack
- •Snatch and Run
- •Transferring the Risk
- •Defining the Threat
- •Recognition of Uncertainty
- •Risk Management Is Dollar Driven
- •How Risky Is a Risk?
- •Quantitative Risk Assessment
- •Qualitative Risk Assessments
- •Why They Don't Work
- •Summary
- •Chapter 18. Automated and Manual Response
- •Automated Response
- •Architectural Issues
- •Response at the Internet Connection
- •Internal Firewalls
- •Host-Based Defenses
- •Throttling
- •Drop Connection
- •Shun
- •Proactive Shunning
- •Islanding
- •Reset
- •Honeypot
- •Proxy System
- •Empty System
- •Honeypot Summary
- •Manual Response
- •Containment
- •Freeze the Scene
- •Sample Fax Form
- •On-Site Containment
- •Site Survey
- •System Containment
- •Hot Search
- •Eradication
- •Recovery
- •Lessons Learned
- •Summary
- •Chapter 19. Business Case for Intrusion Detection
- •Part One: Management Issues
- •Bang for the Buck
- •The Expenditure Is Finite
- •Technology Used to Destabilize
- •Network Impacts
- •IDS Behavioral Modification
- •The Policy
- •Part of a Larger Strategy
- •Part Two: Threats and Vulnerabilities
- •Threat Assessment and Analysis
- •Threat Vectors
- •Threat Determination
- •Asset Identification
- •Valuation
- •Vulnerability Analysis
- •Risk Evaluation
- •Part Three: Tradeoffs and Recommended Solution
- •Identify What Is in Place
- •Identify Your Recommendations
- •Identify Options for Countermeasures
- •Cost-Benefit Analysis
- •Follow-On Steps
- •Repeat the Executive Summary
- •Summary
- •Chapter 20. Future Directions
- •Increasing Threat
- •Improved Targeting
- •How the Threat Will Be Manifested
- •Defending Against the Threat
- •Skills Versus Tools
- •Analysts Skill Set
- •Improved Tools
- •Defense in Depth
- •Emerging Techniques
- •Virus Industry Revisited
- •Smart Auditors
- •Summary
- •Part V: Appendixes
- •Appendix A. Exploits and Scans to Apply Exploits
- •False Positives
- •All Response, No Stimulus
- •Scan or Response?
- •SYN Floods
- •Valid SYN Flood
- •False Positive SYN Flood
- •Back Orifice?
- •IMAP Exploits
- •10143 Signature Source Port IMAP
- •111 Signature IMAP
- •Source Port 0, SYN and FIN Set
- •Source Port 65535 and SYN FIN Set
- •DNS Zone Followed by 0, SYN FIN Targeting NFS
- •Scans to Apply Exploits
- •mscan
- •Son of mscan
- •Access Builder?
- •Single Exploit, Portmap
- •rexec
- •Targeting SGI Systems?
- •Discard
- •Weird Web Scans
- •IP-Proto-191
- •Summary
- •Appendix B. Denial of Service
- •Brute-Force Denial-of-Service Traces
- •Smurf
- •Directed Broadcast
- •Echo-Chargen
- •Elegant Kills
- •Teardrop
- •Land Attack
- •We're Doomed
- •nmap
- •Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks
- •Intro to DDoS
- •DDoS Software
- •Trinoo
- •Stacheldraht
- •Summary
- •Appendix C. Detection of Intelligence Gathering
- •Network and Host Mapping
- •Host Scan Using UDP Echo Requests
- •Netmask-Based Broadcasts
- •Port Scan
- •Scanning for a Particular Port
- •Complex Script, Possible Compromise
- •"Random" Port Scan
- •Database Correlation Report
- •SNMP/ICMP
- •FTP Bounce
- •NetBIOS-Specific Traces
- •A Visit from a Web Server
- •Null Session
- •Stealth Attacks
- •Explicit Stealth Mapping Techniques
- •FIN Scan
- •Inverse Mapping
- •Answers to Domain Queries
- •Answers to Domain Queries, Part 2
- •Fragments, Just Fragments
- •Measuring Response Time
- •Echo Requests
- •Actual DNS Queries
- •Probe on UDP Port 33434
- •3DNS to TCP Port 53
- •Worms as Information Gatherers
- •Pretty Park Worm
- •RingZero
- •Summary
V |
V |
Pointer 26 |
26 Bytes |
bytes into DNS |
|
Payload |
|
Look at the hex output. You will see the query name (in bold) of evasive mode. The name starts, as before, with a label of 07 followed by the first node of the query. What had previously been all lowercase letters in "version" now is "Version". This would successfully elude any string matching software that does not do uppercase/lowercase conversions.
That is not the entirety of the ruse used here. Look at the next byte: c0. A label has a maximum value of 63 and a hexadecimal c0 is 192 when converted to decimal. Any time that a label has the two high-order bits of the byte set to 1 (a hex c), it is considered a pointer. A pointer is the number of bytes into the DNS message where the next label (or pointer) is to be found. In this case, we see that the pointer is a hexadecimal 1a or a decimal 26. Therefore, we have to count 26 bytes from the beginning of the DNS message to find the next node. The DNS message is delimited between the < > on the left side of the output.
Moving 26 bytes into the DNS message directs us to the string beginning with 0442 494e 4400. The 04 is the label 26 bytes into the DNS message, and as expected, it is followed by 4 bytes that represent the string "BIND". The query then ends when a label of 00 is encountered. It appears that resolution of the query resumes at the next byte after the first pointer in the query name. This brings us back to the string "0010 0003" that represents the query type of TXT and a query class of CHAOS. This query elicits the version of BIND running on the queried DNS server if the DNS server does not prevent queries for the version of BIND.
Sidestep can be found at www.robertgraham.com/tmp/sidestep.html.
Introduction to Packet Dissection Using TCPdump
When you run TCPdump in standard mode, it will dump the most pertinent fields in the packet. More fields will be collected than displayed in the default 68 bytes of capture (14 bytes for Ethernet frame header and the remainder for the IP packet). Yet, all of the fields will not be displayed unless you ask for TCPdump to display the output in hexadecimal mode using the –x command line option. The first thing that you have to do before attempting any kind of packet dissection is arm yourself with the standard layouts of the various kinds of TCP/IP headers such as IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP. There are many sources of these including the RFCs.
Look at the following output to see a sample of hexadecimal output from TCPdump using the –x command line option:
11:55:52.069484 192.168.143.5 > 192.168.143.101: icmp: echo request
4500 0054 064b 0000 4001 bc12 c0a8 8f05 c0a8 8f65 0800 620a 850a 0000 889f 4b39 510f 0100 0809 0a0b 0c0d 0e0f 1011 1213 1415 1617 1819
It looks like a big jumble of garbage at first glance. Let's begin methodically to describe the output. First, each character you see is a hexadecimal character, as you might have astutely intuited from the fact that we are doing hex output. (Okay, enough sarcasm.) Each hex
character can have a value of 0 to 0xf, which corresponds to 0 to 15 decimal. Again, the 0x notation means hexadeci-mal. And, each hex character is 4 bits, also known as a nibble. That means two hex characters are 8 bits or one byte. Finally, each row of hex dumped by TCPdump has 16 bytes or 32 hex characters.
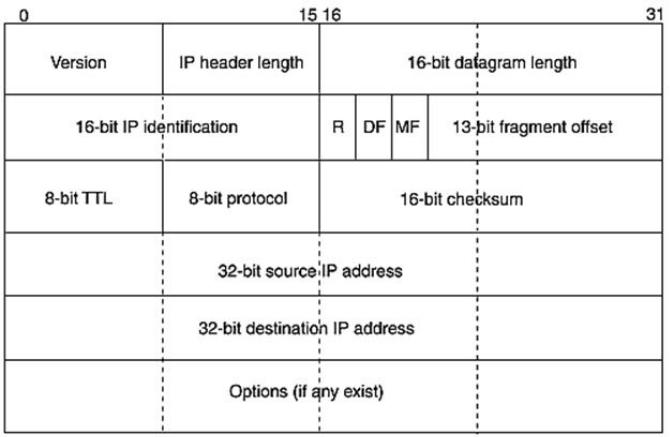
The trick is "superimposing" this hex output over a standard layout of the fields. In this case, we are looking at an IP header followed by some embedded protocol that we will discover as we progress. Take a look at Figure 7.1. It shows the standard IP header layout that we've examined several times before in the book. Let's just make sure we can look at a field or two before we move on. For instance, the first field you see in the IP header layout is the IP version number, which is 4 bits long. If we look at the previous hex dump, we see that the first hex character is a 4. This is the IP version number or IP version 4.
Figure 7.1. IP header layout.
That was fairly simple. Let's try something a little more advanced. Another very important field is the protocol field found in the IP header. This tells us the embedded protocol that follows the IP header. If you look at Figure 7.1, you'll see that the 8-bit protocol field is found in the third row of the IP header. This layout is different from the hex dump because each row contains 32 bits of output or 4 bytes. No matter, we can still find the displacement of the protocol field from the beginning of the IP header (again, another annoying reminder that we start counting at offset 0). So, each row contains 4 bytes, and we find the protocol is located in the 9th byte offset of the IP header. The 9th byte offset found in the hex dump is 01. A value of 01 in this field means that the ICMP protocol follows the IP header. Other common values that we will examine are a value of 06 means TCP follows, and a hex 11 or decimal 17 means that UDP follows the IP header.
