
40_semantic syntax
.docx
Semantic syntax (or generative semantics)
This method was put forward by the American scholars: Van Deik, Fillmore.
It studies the sentence as a means of communication, that is how the sentence is organized as a semantic unite.
Every sentence is built around a predicative element which is usually accompanied by one or more nominal elements.
Semantic unites (participants of the situation are called semantic roles or semantic cases (падежи).
Fillmore calls them arguments
Semantic roles are:
-
agent - denotes an animate object who performs the action expressed by the verb. It is expressed either by a subject or by an object.
Ex. I read the note. ( I – an agent (participant) that performs an action)
The note was written by me. (Me – an agent)
-
patient – denotes an object affected by the action, the agent does smth to smth/smb
Ex. The dog bit his hand. ( dog – agent, hand – patient)
-
benefactive – denotes an animate object for whom the action is performed.
Ex. I gave John the book. (I – agent, John – benefactive, book – patient)
-
factitive – denotes the result of the action.
Ex. The boy dug a hole. ( boy – agent, hole – factitive)
-
insrument – denotes the object, used by the agent to perform the action.
Ex. John broke the window with a stone. (John – agent, stone – instrument)
-
locative – denotes some special (пространственные) meanings.
Ex. He stayed in Moscow. (Moscow – locative)
-
temperative – denotes temporal relations.
Ex. They met in the evening. (evening – temperative)
Semantic configuration (proposition of the sentence is a set of semantic roles + the meaning of the verb)
It may be of three types:
-
agent
patient
instrument
Ex. The glazier cuts glass with a diamond. (glazier – agent, glass – patient, diamond – instrument)
-
agent
patient
Ex. The glazier cuts glass. (glazier – agent, glass – patient)
-
instrument
patient
Ex. A diamond cuts glass. (diamond – instrument, glass – patient)
Types of predicates:
-
states
-
actions
-
process
-
action-process
Semantic Syntax is based on DICTUM and MODUS
Dictum – objective modality, deals with the situation – the place of a thing or event in the situation..the centre of the utterance; the main idea of the sentence.
EX.
John is a student
If only John were a student
I wish John were a student different structural communicative force but they have so
John was a student me meaning in common (dictum) – john a student
Modus ( о вещи)
In Semantic syntax by dictum we mean verbs of physical mental perception (to think, believe) v. of saying, v. which can be followed by complex obj-t, modal words.
Ex.
I think that peter is ill.
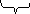
Dictum Modus
intention
