
- •Foreword
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •1 Introduction to Nonlinear Acoustics
- •1.1 Introduction
- •1.2 Constitutive Equations
- •1.3 Phenomena in Nonlinear Acoustics
- •References
- •2 Nonlinear Acoustic Wave Equations for Sound Propagation in Fluids and in Solids
- •2.1 Nonlinear Acoustic Wave Equations in Fluids
- •2.1.1 The Westervelt Equation [1]
- •2.1.2 The Burgers’ Equation [2]
- •2.1.3 KZK Equation
- •2.1.4 Nonlinear Acoustic Wave Equations for Sound Propagation in Solids
- •References
- •3 Statistical Mechanics Approach to Nonlinear Acoustics
- •3.1 Introduction
- •3.2 Statistical Energy Analysis is Transport Theory
- •3.3 Statistical Energy Analysis
- •3.4 Transport Theory Approach to Phase Transition
- •References
- •4 Curvilinear Spacetime Applied to Nonlinear Acoustics
- •4.1 Introduction and Meaning of Curvilinear Spacetime
- •4.2 Principle of General Covariance
- •4.3 Contravariant and Covariant Four-Vectors
- •4.4 Contravariant Tensors and Covariant Tensors
- •4.5 The Covariant Fundamental Tensor gμν
- •4.6 Equation of Motion of a Material Point in the Gravitational Field
- •4.8 The Euler Equation of Fluids in the Presence of the Gravitational Field
- •4.9 Acoustic Equation of Motion for an Elastic Solid in the Presence of Gravitational Force
- •Reference
- •5 Gauge Invariance Approach to Nonlinear Acoustical Imaging
- •5.1 Introduction
- •5.3 Illustration by a Unidirectional Example
- •5.4 Quantization of the Gauge Theory
- •5.5 Coupling of Elastic Deformation with Spin Currents
- •References
- •6.1 Introduction
- •6.2 The Thermodynamic Method
- •6.2.1 Theory
- •6.2.2 Experiment
- •6.3 The Finite Amplitude Method
- •6.3.1 The Wave Shape Method
- •6.3.2 Second Harmonic Measuements
- •6.3.3 Measurement from the Fundamental Component
- •6.4 B/A Nonlinear Parameter Acoustical Imaging
- •6.4.1 Theory
- •6.4.2 Simulation
- •6.4.3 Experiment [17]
- •6.4.4 Image Reconstruction with Computed Tomography
- •References
- •7 Ultrasound Harmonic Imaging
- •7.1 Theory of Ultrasound Harmonic Imaging
- •7.2 Methods Used to Isolate the Second Harmonic Signal Component
- •7.3 Advantages of Harmonic Imaging
- •7.4 Disadvantages of Harmonic Imaging
- •7.5 Experimental Techniques in Nonlinear Acoustics
- •7.6 Application of Ultrasound Harmonic Imaging to Tissue Imaging
- •7.7 Applications of Ultrasonic Harmonic Imaging to Nondestructive Testing
- •7.8 Application of Ultrasound Harmonic Imaging to Underwater Acoustics
- •References
- •8 Application of Chaos Theory to Acoustical Imaging
- •8.1 Nonlinear Problem Encountered in Diffraction Tomography
- •8.4 The Link Between Chaos and Fractals
- •8.5 The Fractal Nature of Breast Cancer
- •8.6 Types of Fractals
- •8.6.1 Nonrandom Fractals
- •8.6.2 Random Fractals
- •8.7 Fractal Approximations
- •8.8 Diffusion Limited Aggregation
- •8.9 Growth Site Probability Distribution
- •8.10 Approximating of the Scattered Field Using GSPD
- •8.11 Discrete Helmholtz Wave Equation
- •8.12 Kaczmarz Algorithm
- •8.14 Applying GSPD into Kaczmarz Algorithm
- •8.15 Fractal Algorithm using Frequency Domain Interpretation
- •8.16 Derivation of Fractal Algorithm’s Final Equation Using Frequency Domain Interpolation
- •8.17 Simulation Results
- •8.18 Comparison Between Born and Fractal Approximation
- •References
- •9.1 Introduction
- •9.2 Mechanisms of Harmonic Generation Via Contact Acoustic Nonlinearity (CAN)
- •9.2.1 Clapping Mechanism
- •9.2.2 Nonlinear Friction Mechanism
- •9.3 Nonlinear Resonance Modes
- •9.4 Experimental Studies on Nonclassical CAN Spectra
- •9.4.1 CAN Application for Nonlinear Acoustical Imaging and NDE
- •9.5 Conclusions
- •References
- •10.1 Introduction
- •10.2 Principles of Modulation Acoustic Method
- •10.3 The Modulation Mode of Method of Crack Location
- •10.4 Experimental Procedure of the Modulation Method for NDT
- •10.5 Experimental Procedures for the Modulation Mode System
- •10.6 Conclusions
- •References
- •11.1 Introduction
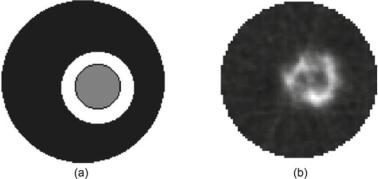
6.4 B/A Nonlinear Parameter Acoustical Imaging |
47 |
Fig. 6.4 a Model of the imaged media: porcine liver surrounded with porcine fat, submerged in water. b The acquired reflection-mode tomographic image, utilizing the finite amplitude insertsubstitution method (After Panfilova [4])
References
1.Law, W., et al. 1985. Determination of the nonlinearity parameter B/A of biological media.
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 11 (2): 307–318.
2.Errabolu, R.L., et al. 1988. Measurement of ultrasonic nonlinear parameter in excised fat tissues. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 14 (2): 137–147.
3.Beyer, R.T. 1960. Parameter of nonlinearity in fluids. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 32: 719–721.
4.Panfilova, A., R.J.G. van Slovun, H. Wijkstra, O.A. Sapozhnikov, and M. Mischi. 2021. A review on B/A measurement methods with a clinical perspective. The Journal of the Acoustical Society America 149 (4): 2200–2237.
5.Greenspan, M., and C.E. Tschiegg. 1957. Speed of sound in water by a direct method. Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards 59 (4): 249–254.
6.Wilson, W.D. 1959. Speed of sound in distilled water as a function of temperature and pressure.
Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 31: 1067–1072.
7.Law, W.K., L.A. Frizzell, and F. Dunn. 1985. Determination of the nonlinearity parameter B/A of biological media. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology 11 (2): 307–318.
8.Fubini, G.E. 1935. Anomalie nella propagazione di onde acustiche di grande ampiezza. Industrie Grafiche Italiane Stucchi.
9.Cobb, W.N. 1983. Finiteamplitude method for the determination of the acoustic nonlinearity parameter B/A. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 73(5): 1525–1531.
10.Zhu, Z., et al. 1983. Determination of the acoustic nonlinearity parameter B/A from phase measurements. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 74 (5): 1518–1621.
11.Sehgal, C., et al. 1986. Measurement and use of acoustic nonlinearity and sound speed to estimate composition of excised livers. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 12 (11): 865–874.
12.Hamilton, M.A., and D.T. Blackstock. 1988. On the coefficient of nonlinearity β in nonlinear acoustics. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 83 (1): 74–77.
13.Dunn, F., W.K. Law, and L.A. Frizzell. 1982. Nonlinear ultrasonic propagation in biological media. British Journal of Cancer Supplementary 45: 55.
14.Fox, F.E., and G.D. Rock. 1941. Ultrasonic absorption in water. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 12: 505–510.
15.Fox, F.E., and W.A. Wallace. 1954. Absorption of finite amplitude sound waves. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 26: 994–1006.
48 |
6 B/A Nonlinear Parameter Acoustical Imaging |
16.Hikata, A., H. Kwun, and C. Elbaum. 1980. Finite amplitude wave propagation in solid and liquid He 4. Physical Review B 21 (9): 3932–3939.
17.Byra, M., J. Wojcik,˙ and A. Nowicki. 2017. Ultrasound nonlinearity parameter assessment using plane wave imaging. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washongton, D.C., 1511–1516, September 6–9, 2017.
18.Varray, F., O. Basset, P. Tortoli, and C. Cachard. 2011. Extensions of nonlinear B/A parameter imaging methods for echo mode. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectgrics, and Frequency Control 58 (6): 1232–1244.
19.Zabolotskaya, E., and R. Khokhlov. 1969. Quasi-plane waves in the nonlinear acoustics of confined beams. Soviet Physics Acoustics 15: 35–40.
20.Kuznesov, V. 1970. Equation of nonlinear acoustics. Soviet Physics 16: 749–768.
21.Zhang, D., and X. Gong. 1999. Experimental investigation of the acoustic nonlinearity parameter tomography for excised pathological biological tissue. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 25: 593–599.
22.Law, W.K., L.A. Frizzell, and F. Dunn, Ultrasonic determination of the nonlinearity parameter B/A for biological media. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 69: 1210–121.
23.Gong, X., R. Feng, C. Zhu, and T. Shi. 1984. Ultrasonic investigation of the nonlinearity parameter B/A in biological media. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 76: 949–950.
24.Wallace, K.D., C.W. Lloyd, M.R. Holland, and J. Miller. 2007. Finite amplitude measurements of the nonlinear parameter B/A for liquid mixtures spanning a range relevant to tissue harmonic mode. Ultasound in Medicine & Biology 33: 620–629.
25.Lee, Y.S., and M.F. Hamilton. 1995. Time-domain modelling of pulsed finite-amplitude sound beam. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 97: 906–917.
26.Gong, X., D. Zhang, J. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Yan, and X. Xu. 2004. Study of acoustic nonlinearity parameter imaging methods in reflection mode for biological tissues. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 116 (3): 1819–1825.
