
- •1. Concepts of symptoms and syndromes
- •2. Pulmonology
- •1. Syndrome of compaction of lung tissue (decrease in airiness)
- •2. Syndrome of increased airiness of lung tissue (emphysema)
- •3. Broncho obstructive syndrome
- •4. Lung cavity syndrome
- •5. The syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity
- •6. The syndrome of accumulation of air in the pleural cavity
- •7. Bronchiectasis Syndrome
- •8. Syndrome of lung atelectasis
- •9. Syndrome of dry pleurisy (pleuritis)
- •10. Respiratory failure syndrome
- •11. Pulmonary heart failure (pulmonary heart)
- •12. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
- •3. Cardiology
- •1. Syndromes of coronary insufficiency
- •2. Angina pectoris syndrome (stenocardia)
- •4. Myocardial damage syndrome
- •5. Resorption-necrotic syndrome
- •6. Post-infarction syndrome (Dressler's syndrome).
- •7. Аrterial hypertension Syndrome (ah)
- •8. Arterial hypotension syndrome
- •9. Heart failure syndrome
- •V.Kh. Vasilenko (1935).
- •10. Cardiomegaly syndrome
- •Syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pericardium (hydropericardium) The reasons for the accumulation of exudate:
- •12. Rhythm and conduction disturbances syndromes
- •I. Arrhythmias due to a violation of the automatism of the sinus node:
- •Atrial flutter (irregular and regular forms). Symptoms
- •Ventricular flutter and fibrillation. Symptoms
- •IV. Conductivity disorders - blockade:
- •13. Syndromes of valvular heart disease.
- •14. Mitral valve prolapse
- •15. Syndrome of hypertension of the pulmonary circulation
- •16. The syndrome of acute vascular insufficiency
- •4. Gastroenterology
- •4.1. Syndromes for diseases of the esophagus, stomach and gut
- •1. Dysphagia Syndrome
- •Gastroduodenal pain syndrome
- •3. Gastric hypersecretion syndrome
- •4. Gastric hyposecretion syndrome
- •5. Syndrome of gastric evacuation
- •6. Functional dyspepsia syndrome:
- •Bleeding syndrome from the lower gastrointestinal tract
- •9. The syndrome of "acute abdomen"
- •10. Dyspeptic syndrome (indigestion)
- •11. Irritable bowel syndrome:
- •2. Pain abdominal syndrome:
- •13. Asthenoneurotic syndrome:
- •4.2 Syndromes for diseases of the liver and bilitary ways
- •1. Biliary colic syndrome
- •2. Subhepatic jaundice (mechanical)
- •3. Hepatic jaundice (parenchymal)
- •4. Suprahepatic jaundice (hemolytic)
- •6. Cholestatic syndrome
- •8. Hypersplenism syndrome
- •9. Portal hypertension
- •10. Hepatic failure syndrome
- •12. Cytolysis syndrome (cytolytic syndrome)
- •13. Mesenchymal inflammatory syndrome
- •1. Pancreatic pain syndrome
- •1. The insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function
- •Syndrome of pancreatic incretory function.
- •5. The syndrome of gastric pancreatic dyspepsia:
- •1. Renal colic syndrome
- •2. Urinary Syndrome
- •4. Nephrotic syndrome
- •5. Acute nephritic syndrome (acute glomerulonephritis)
- •Chronic nephritic syndrome (chronic glomerulonephritis)
- •7. Edema syndrome (renal edema)
- •Hypertension Syndrome
- •9. Renal eclampsia syndrome
- •Acute renal failure (arf)
- •11. Chronic renal failure
- •6. Endocrinology
- •1. Syndrome of hypothyroidism:
- •Thyrotoxicosis syndrome (hyperthyroidism):
- •3. The syndrome of insulin deficiency:
- •1. Anemic syndrome
- •2. Sideropenic syndrome (iron deficiency)
- •Iron deficiency anemia
- •Hemolytic anemia
- •6. Hemorrhagic syndrome
- •7. Inflammatory syndrome
- •Neurological syndrome
- •10. Immunodeficiency syndrome
- •Leukemia syndrome (hemoblastosis) 11.1 Acute Leukemia Syndrome
- •11.2 Chronic myeloproliferative syndrome
- •11.3 Chronic lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •2. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
- •Urticaria syndrome
- •2. Quincke's angioedema
- •3. Anaphylactic shock
- •4. Joint syndrome
- •9. The meaning of eponymous terms and syndromes in clinical medicine
3. Cardiology
1. Syndromes of coronary insufficiency
By coronary insufficiency is understood circulatory disorders in the coronary vessels, in which, under physiological conditions, about 5% of all blood discharged into the aorta flows.
In clinical practice, acute and chronic coronary insufficiency are distinguished. Acute coronary insufficiency occurs suddenly or within a few minutes. An important role in its origin is played, first of all, by disturbances in the functional state of the coronary arteries (spasm, dystonia), coronary artery thrombosis, as well as rapidly occurring relative coronary insufficiency.
Chronic coronary insufficiency develops gradually, has a progressive character, it is based on a variety of long-term, recurrent and progressive lesions of the coronary artery, leading to their persistent narrowing, or occlusion.
The most common cause of acute and chronic coronary insufficiency is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, less commonly other diseases: rheumatism, periarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus, infectious endocarditis.
2. Angina pectoris syndrome (stenocardia)
This is a characteristic attack of pain behind the sternum caused by transient myocardial ischemia due to insufficiency of coronary circulation.
BASIC SYMPTOMS:
paroxysmal;
characteristic localization and irradiation of pain;
short duration of the attack (no more than 20-30 minutes);
relief of pain by taking nitroglycerin or stopping the load.
Pain behind the sternum or to the left of it of a different nature: burning, squeezing, compression, heaviness that occurs during physical exertion, under the influence of cold, wind, emotional stress, at rest.
Irradiation of pain: in the left shoulder, left arm, left half of the neck or upper abdomen. Duration of pain from a few seconds to 30 minutes (usually 2-10 minutes). The pain stops when physical activity is stopped, and nitrates are taken.
On the ECG, there may be no changes outside the seizures. During an attack of angina pectoris or tests with physical activity, flattening or inversion of the T wave, depression of the S-T segment, various rhythm and conduction disturbances are possible.
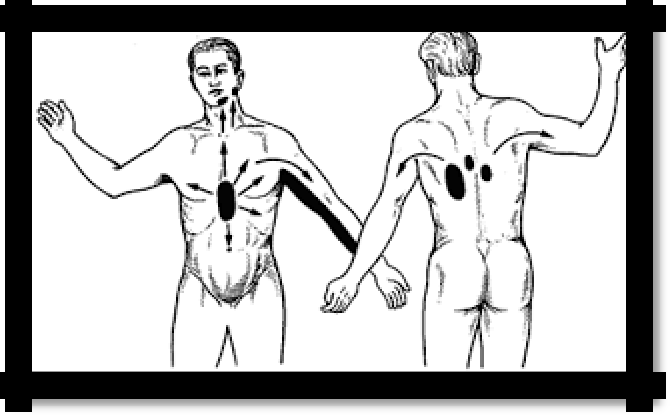
Pic 3.1 Localization and irradiation of pain in angina pectoris
26
3. Myocardial infarction is ischemic necrosis of the area of the heart muscle that occurs as a result of an acute discrepancy between the oxygen demand of the myocardium and its delivery through the coronary arteries.
Depending on the characteristics of the symptoms, 6 main clinical options are distinguished:
painful or anginal (status anginosus);
asthmatic (status astmaticus);
abdominal (status abdominalis, gastralgicus);
arrhythmic;
cerebrovascular;
asymptomatic or low-symptom.
The most common pain variant of myocardial infarction, the main manifestation is pain.
Pain with I.M. in many ways resembles angina pectoris, but differs from it in greater strength, duration and lack of effect after taking nitroglycerin, is accompanied by changes in hemodynamics (drop in blood pressure up to the development of shock, development of arrhythmias, blockade, etc.).
ECG changes are characteristic: ST segment elevation (Pardi plateau), deep Q wave, negative T wave, decreased R wave amplitude.
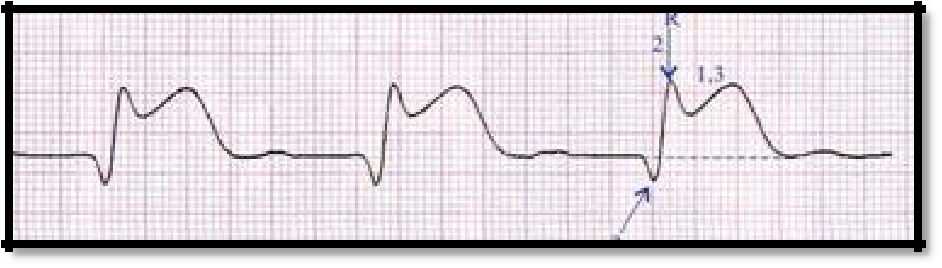
Pic 3.2 ST elevation, deep Q wave, lower R wave amplitude.
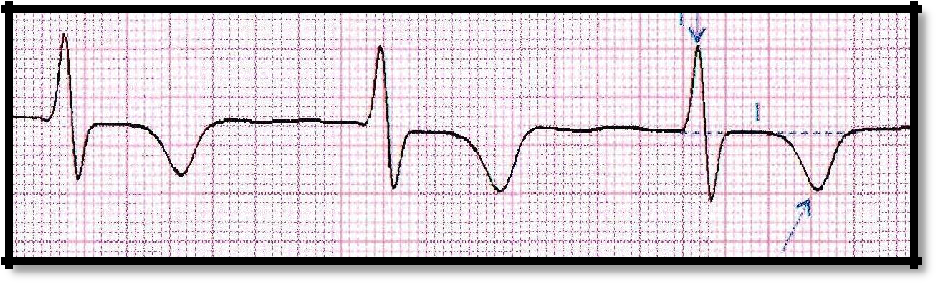
Pic 3.3 Negative T wave
