
- •1. Concepts of symptoms and syndromes
- •2. Pulmonology
- •1. Syndrome of compaction of lung tissue (decrease in airiness)
- •2. Syndrome of increased airiness of lung tissue (emphysema)
- •3. Broncho obstructive syndrome
- •4. Lung cavity syndrome
- •5. The syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity
- •6. The syndrome of accumulation of air in the pleural cavity
- •7. Bronchiectasis Syndrome
- •8. Syndrome of lung atelectasis
- •9. Syndrome of dry pleurisy (pleuritis)
- •10. Respiratory failure syndrome
- •11. Pulmonary heart failure (pulmonary heart)
- •12. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
- •3. Cardiology
- •1. Syndromes of coronary insufficiency
- •2. Angina pectoris syndrome (stenocardia)
- •4. Myocardial damage syndrome
- •5. Resorption-necrotic syndrome
- •6. Post-infarction syndrome (Dressler's syndrome).
- •7. Аrterial hypertension Syndrome (ah)
- •8. Arterial hypotension syndrome
- •9. Heart failure syndrome
- •V.Kh. Vasilenko (1935).
- •10. Cardiomegaly syndrome
- •Syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pericardium (hydropericardium) The reasons for the accumulation of exudate:
- •12. Rhythm and conduction disturbances syndromes
- •I. Arrhythmias due to a violation of the automatism of the sinus node:
- •Atrial flutter (irregular and regular forms). Symptoms
- •Ventricular flutter and fibrillation. Symptoms
- •IV. Conductivity disorders - blockade:
- •13. Syndromes of valvular heart disease.
- •14. Mitral valve prolapse
- •15. Syndrome of hypertension of the pulmonary circulation
- •16. The syndrome of acute vascular insufficiency
- •4. Gastroenterology
- •4.1. Syndromes for diseases of the esophagus, stomach and gut
- •1. Dysphagia Syndrome
- •Gastroduodenal pain syndrome
- •3. Gastric hypersecretion syndrome
- •4. Gastric hyposecretion syndrome
- •5. Syndrome of gastric evacuation
- •6. Functional dyspepsia syndrome:
- •Bleeding syndrome from the lower gastrointestinal tract
- •9. The syndrome of "acute abdomen"
- •10. Dyspeptic syndrome (indigestion)
- •11. Irritable bowel syndrome:
- •2. Pain abdominal syndrome:
- •13. Asthenoneurotic syndrome:
- •4.2 Syndromes for diseases of the liver and bilitary ways
- •1. Biliary colic syndrome
- •2. Subhepatic jaundice (mechanical)
- •3. Hepatic jaundice (parenchymal)
- •4. Suprahepatic jaundice (hemolytic)
- •6. Cholestatic syndrome
- •8. Hypersplenism syndrome
- •9. Portal hypertension
- •10. Hepatic failure syndrome
- •12. Cytolysis syndrome (cytolytic syndrome)
- •13. Mesenchymal inflammatory syndrome
- •1. Pancreatic pain syndrome
- •1. The insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function
- •Syndrome of pancreatic incretory function.
- •5. The syndrome of gastric pancreatic dyspepsia:
- •1. Renal colic syndrome
- •2. Urinary Syndrome
- •4. Nephrotic syndrome
- •5. Acute nephritic syndrome (acute glomerulonephritis)
- •Chronic nephritic syndrome (chronic glomerulonephritis)
- •7. Edema syndrome (renal edema)
- •Hypertension Syndrome
- •9. Renal eclampsia syndrome
- •Acute renal failure (arf)
- •11. Chronic renal failure
- •6. Endocrinology
- •1. Syndrome of hypothyroidism:
- •Thyrotoxicosis syndrome (hyperthyroidism):
- •3. The syndrome of insulin deficiency:
- •1. Anemic syndrome
- •2. Sideropenic syndrome (iron deficiency)
- •Iron deficiency anemia
- •Hemolytic anemia
- •6. Hemorrhagic syndrome
- •7. Inflammatory syndrome
- •Neurological syndrome
- •10. Immunodeficiency syndrome
- •Leukemia syndrome (hemoblastosis) 11.1 Acute Leukemia Syndrome
- •11.2 Chronic myeloproliferative syndrome
- •11.3 Chronic lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •2. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
- •Urticaria syndrome
- •2. Quincke's angioedema
- •3. Anaphylactic shock
- •4. Joint syndrome
- •9. The meaning of eponymous terms and syndromes in clinical medicine
1. Anemic syndrome
REASONS: anemia of any genesis, including anemia with hemoblastosis
Symptoms common to any anemia:
muscle weakness, reduced ability to work
dizziness, "flies" before the eyes
fainting
shortness of breath and palpitations when walking (decreased exercise tolerance)
pallor (alabaster with blood loss, greenish with iron deficiency (chlorosis), slightly icteric with B-12, folio-deficient anemia, with a lemon-yellow tint with hemolytic anemia) of the skin and sclera, mucous membranes.
tachycardia, systolic functional noise above the apex, pulmonary trunk. Veins: the noise of the top on vv.juqularis, etc.
a decrease in the content of red blood cells, hemoglobin, reticulocytes, the appearance of altered forms of red blood cells (micro-, macrocytes, poikilocytes, hypo-hyperchromia, etc.).
2. Sideropenic syndrome (iron deficiency)
REASONS: repeated blood loss, insufficient intake of iron with food, malabsorption, increased consumption, redistribution, hemoglobinopathies. SYMPTOMS:
complaints of difficulty swallowing dry and solid foods (sideropenic dysphagia), pain and burning of the tongue, impaired taste and appetite (the need to eat chalk, clay, coal, earth, minced meat), a perversion of smell (addiction to the smell of kerosene, acetone, etc. )
fetid rhinitis
trophic changes in the skin, mucous membranes, hair and nails: the skin is dry, slightly peeling, tans poorly, the hair is split off, it turns gray early and falls out, the nails flatten, lose their luster, have transverse striation, they break easily, spoon-like deformations of nails (koilonychia) form, ulcerations and cracks appear in the corners of the mouth, angular stomatitis, pain and burning in the tongue (glossitis)
urinary incontinence with coughing, laughing
erythrocyte hypochromia, microcytosis
decreases the level of serum iron and the total iron binding capacity of the plasma (normal 30.6
84.6 mmol / l) and increases the latent iron binding capacity (normal 16 - 44 μmol / l)
Iron deficiency anemia
CAUSES.
Inadequate intake of iron with food (strict diet, lack of fruits, meat).
Violation of iron absorption in the intestines and stomach (gastritis, enterocolitis).
Increased consumption, redistribution of iron (children, girl, pregnant, lactating women, severe inflammatory processes)).
Repeated blood loss: nasal, gastric, rectal, renal, pulmonary, uterine bleeding, in closed cavities and tissues.
Iron is not absorbed by red blood cells (hemoglobinopathies).
anemic
sideropenic.
Blood:
106
Red blood cells: less than normal. Micro, poikilo, aniso, schizocytes.
HB is below normal, a decrease in the number of reticulocytes.
Red blood cell hypochromia - color indicator (MCH) - below normal,
The content of serum iron, ferritin is reduced to less than 30 μg / l, the percentage of transferrin saturation with iron is less than 25%.
Bone marrow:
Sideroblasts <20%
B-12, folic deficiency anemia
CAUSES.
- malnutrition (lack of B-12)
- atrophic gastritis, gasterectomy
- enteritis, enterectomy (B-12, F.K. is not absorbed)
- increased consumption of B-12 and F.K. (pregnancy) - inferiority of erythroblasts (do not digest B-12, F.K.) Symptoms
Leading syndromes: - anemic;
- neurological - only with B-12 dependent anemia (gait unsteadiness, muscle weakness, pleurisy, polyneuropathy, due to the development of funicular myelosis;
- damage to the gastrointestinal tract - atrophic, inflammatory processes, resection of the stomach, small intestine, glossitis (papillae are erased, the surface is smooth, bright pink - ―varnish‖, ―raspberry‖ tongue), hepatomegaly, splenomegaly.
Blood.
- Red blood cells. Macrocytosis, megaloblasts, aniso- and poikilocytosis. - Nv. below normal, decreased reticulocyte count.
- Hyperchromia of red blood cells - raising color index (MCH). - Polysegmentation of neutrophil nuclei.
- Jolie Taurus, Kebot rings (the remains of the nucleus in red blood cells). - Indirect bilirubin over 34 μmol / L
- Raw iron> normal. The content of Vit B-12 and folic acid is reduced. Bone marrow.
- Megaloblasts.
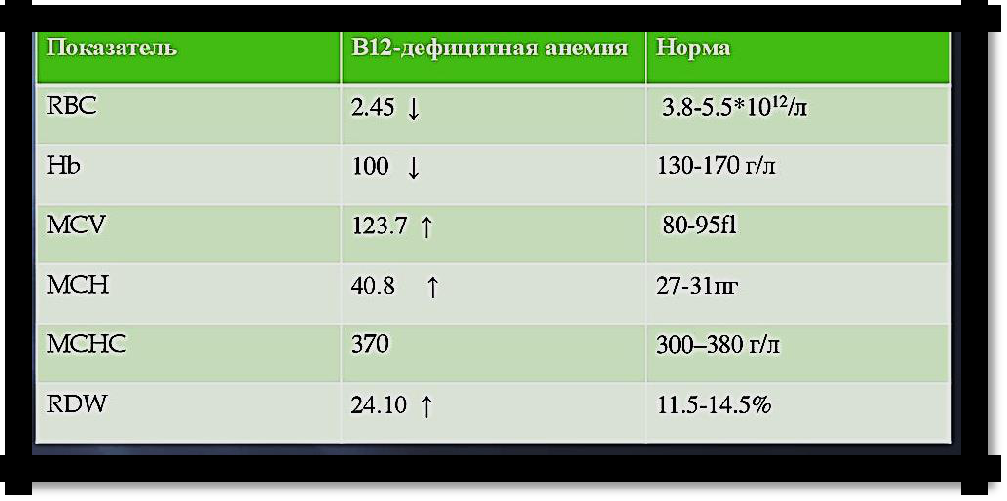
Pic 7.1 Anemia blood rates
107
