
- •1. Concepts of symptoms and syndromes
- •2. Pulmonology
- •1. Syndrome of compaction of lung tissue (decrease in airiness)
- •2. Syndrome of increased airiness of lung tissue (emphysema)
- •3. Broncho obstructive syndrome
- •4. Lung cavity syndrome
- •5. The syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity
- •6. The syndrome of accumulation of air in the pleural cavity
- •7. Bronchiectasis Syndrome
- •8. Syndrome of lung atelectasis
- •9. Syndrome of dry pleurisy (pleuritis)
- •10. Respiratory failure syndrome
- •11. Pulmonary heart failure (pulmonary heart)
- •12. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
- •3. Cardiology
- •1. Syndromes of coronary insufficiency
- •2. Angina pectoris syndrome (stenocardia)
- •4. Myocardial damage syndrome
- •5. Resorption-necrotic syndrome
- •6. Post-infarction syndrome (Dressler's syndrome).
- •7. Аrterial hypertension Syndrome (ah)
- •8. Arterial hypotension syndrome
- •9. Heart failure syndrome
- •V.Kh. Vasilenko (1935).
- •10. Cardiomegaly syndrome
- •Syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pericardium (hydropericardium) The reasons for the accumulation of exudate:
- •12. Rhythm and conduction disturbances syndromes
- •I. Arrhythmias due to a violation of the automatism of the sinus node:
- •Atrial flutter (irregular and regular forms). Symptoms
- •Ventricular flutter and fibrillation. Symptoms
- •IV. Conductivity disorders - blockade:
- •13. Syndromes of valvular heart disease.
- •14. Mitral valve prolapse
- •15. Syndrome of hypertension of the pulmonary circulation
- •16. The syndrome of acute vascular insufficiency
- •4. Gastroenterology
- •4.1. Syndromes for diseases of the esophagus, stomach and gut
- •1. Dysphagia Syndrome
- •Gastroduodenal pain syndrome
- •3. Gastric hypersecretion syndrome
- •4. Gastric hyposecretion syndrome
- •5. Syndrome of gastric evacuation
- •6. Functional dyspepsia syndrome:
- •Bleeding syndrome from the lower gastrointestinal tract
- •9. The syndrome of "acute abdomen"
- •10. Dyspeptic syndrome (indigestion)
- •11. Irritable bowel syndrome:
- •2. Pain abdominal syndrome:
- •13. Asthenoneurotic syndrome:
- •4.2 Syndromes for diseases of the liver and bilitary ways
- •1. Biliary colic syndrome
- •2. Subhepatic jaundice (mechanical)
- •3. Hepatic jaundice (parenchymal)
- •4. Suprahepatic jaundice (hemolytic)
- •6. Cholestatic syndrome
- •8. Hypersplenism syndrome
- •9. Portal hypertension
- •10. Hepatic failure syndrome
- •12. Cytolysis syndrome (cytolytic syndrome)
- •13. Mesenchymal inflammatory syndrome
- •1. Pancreatic pain syndrome
- •1. The insufficiency of exocrine pancreatic function
- •Syndrome of pancreatic incretory function.
- •5. The syndrome of gastric pancreatic dyspepsia:
- •1. Renal colic syndrome
- •2. Urinary Syndrome
- •4. Nephrotic syndrome
- •5. Acute nephritic syndrome (acute glomerulonephritis)
- •Chronic nephritic syndrome (chronic glomerulonephritis)
- •7. Edema syndrome (renal edema)
- •Hypertension Syndrome
- •9. Renal eclampsia syndrome
- •Acute renal failure (arf)
- •11. Chronic renal failure
- •6. Endocrinology
- •1. Syndrome of hypothyroidism:
- •Thyrotoxicosis syndrome (hyperthyroidism):
- •3. The syndrome of insulin deficiency:
- •1. Anemic syndrome
- •2. Sideropenic syndrome (iron deficiency)
- •Iron deficiency anemia
- •Hemolytic anemia
- •6. Hemorrhagic syndrome
- •7. Inflammatory syndrome
- •Neurological syndrome
- •10. Immunodeficiency syndrome
- •Leukemia syndrome (hemoblastosis) 11.1 Acute Leukemia Syndrome
- •11.2 Chronic myeloproliferative syndrome
- •11.3 Chronic lymphoproliferative syndrome
- •2. Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome
- •Urticaria syndrome
- •2. Quincke's angioedema
- •3. Anaphylactic shock
- •4. Joint syndrome
- •9. The meaning of eponymous terms and syndromes in clinical medicine
4. Lung cavity syndrome
REASONS: The formation of a cavity in the lung is usually preceded by compaction of the lung tissue. Most often, this is inflammatory infiltration (abscesses, lung gangrene, staphylococcal destruction of the lungs, pneumonia, tuberculosis), tumor decay, pulmonary infarction. SYMPTOMS:
Shortness of breath, often a productive cough, possibly hemoptysis;
Lag in the act of breathing of the affected half of the chest;
Strengthening of voice trembling and bronchophony;
Percussion: a blunt-tympanic sound is determined. With a large cavity located on the periphery, tympanic sound is observed;
Auscultatory: bronchial, and sometimes amphoric breathing, sonorous medium and large bubble rales are revealed.
It should be emphasized that all these signs are determined in the presence of a smooth-walled cavity of at least 4 cm in diameter, located close enough to the surface of the chest containing air, connecting to the bronchus and surrounded by a densified lung tissue. In the absence of these conditions, the cavity in the lung remains "dumb" and is detected only during x-ray examination.
X-ray (linear tomography, CT) signs of a cavity syndrome in the lung are limited enlightenment of a round or oval shape, usually against a background of blackout. A horizontal level of fluid in the cavity is characteristic if it communicates with the bronchus and contains exudate and air.

Pic 2.2 Linear tomography
5. The syndrome of fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity
REASONS: As a rule, a complication of another disease.
The causes of transudate are heart failure, kidney disease - nephrotic syndrome, hypo- and dysproteinemia.
The causes of exudate are inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy) of various etiologies (infectious exudate in pneumonia, abscess, tuberculosis; non-infectious exudate in malignant tumors, autoimmune diseases, uremia), wounds, trauma (hemothorax), chylous exudate (x). SYMPTOMS:
9
respiratory dyspnea;
On examination - protrusion and limitation of mobility of the corresponding side, smoothing of intercostal spaces;
Palpation - increased resistance of intercostal spaces, weakening or absence of voice trembling;
Percussion - dullness or absolute dullness over a liquid; directly above its level - a blunt-tympanic sound; the appearance of a dull sound on the healthy side due to displacement of the mediastinal organs (with large effusions); downward hepatic dullness. (Damuaso Line, Rauchfus-Grocco and Garland Triangles).
Auscultatory - the presence of fluid suggests the absence or weakening of breathing and bronchophony, and above the fluid level in the Garland triangle - a bronchial shade of breathing (on the effusion side).
X-ray homogeneous dimming is determined in the lower part of the pulmonary field with a characteristic oblique upper border for exudate and a more horizontal upper border for transudate. In the latter case, the process is often two-way. There is a shift in the mediastinal organs to a healthy side.
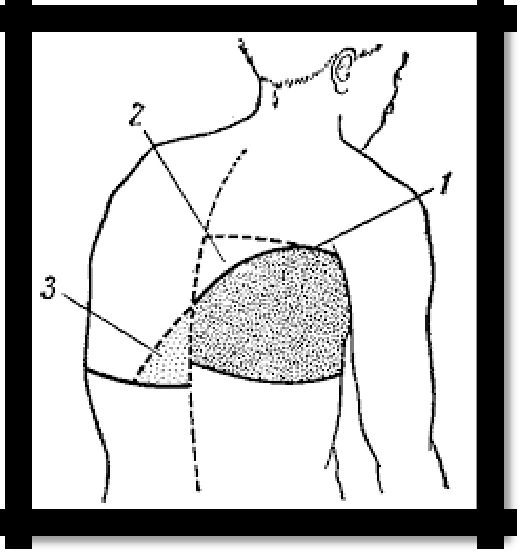
Pic 2.4 The line of Damoiso-Ellis-Sokolov (1); The Garland Triangle (2)
and the Rauchfus-Grocco Triangle (3) with exudative pleurisy.
Pic 2.5 Left-
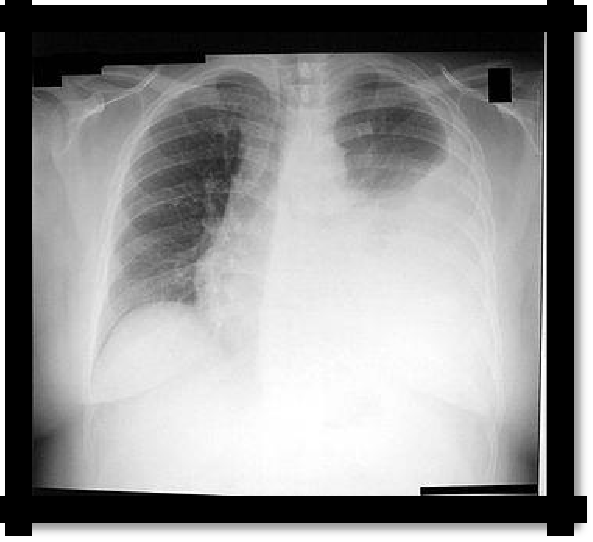
sided exudative pleuritis
10
Table 2.1 Differential diagnostic signs of exudates and transudates.
-
Type of effusion
Transudate
Exudate
Relative density
Usually
below
1.015;
rarely
Not
lower
than
1.015;
(with
compression of
large
usually 1.018
vessels by a tumor) - above
1.013-1.025
Coagulation
-
+
Color
and
Almost
transparent;
lemon
Serous
exudates
in
transparency
yellow or light yellow
appearance
do not
differ
from
transudates;
other
types
of
exudates
are
cloudy;цвет различен
Rivalt's reaction
-
+
Содержание белка
<30 g / l, usually 5-25 g / l
> 30 g / l, usually 30-50 g / l,
in purulent - up to 80 g / l
Cytological
There are few cellular elements;
There
are
more cellular
study
common
elements
than
in
mesothelial cells, red blood cells,
transudates. The number of
sometimes
lymphocytes
cellular elements,
their
predominate;
types and condition depend
after
repeated
punctures
on the etiology and phase
sometimes - eosinophils
of
the
inflammatory,
oncological processes
