
- •Internal combustion engine
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Using the English-Russian dictionary translate the following text
- •Into Russian:
- •IV. Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Explain and translate the following definitions of the car body elements:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Be ready to talk and discuss the general structure of a ship
- •Uss Nimitz’s catapult 1
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Inspecting a used car
- •Incandescent lighting - освещение лампами накаливания
- •Answer and translate the following questions:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •IV. Translate the following information into English:
- •Various definitions
- •Decipher and translate the following abbreviations:
- •Answer the following question:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following material into English:
- •I. Translate the following sentences:
- •II. Translate the following information in to Russian:
- •Translate the following advertising material into English:
- •Be ready to talk about the power supply at your home.
- •Introduction to power electronics
- •I. Answer the following questions:
- •Translate into English words in brackets and then the sentences
- •Into Russian:
- •Translate the following text: Conductors
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate into English: Теория цепей
- •Translate into Russian: Current supply
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate and answer the following questions:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate the text and be ready to discuss the general radio design:
- •Translate into English the following material:
- •Translate the following extract: Microphone transmitter.
- •Introduction to radar fundamentals
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Put 10 questions to the text and answer them:
- •Translate into Russian the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Read and translate the list of chemical elements with their symbols and atomic number: (in alphabetical order)
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Put 6 questions to the text and answer them:
- •Translate the following sentences in to Russian:
- •Translate the following text and he ready to discuses properties of elements: Chemical properties of elements
- •Vanderwaals radius
- •Ionic radius
- •Isotopes
- •Translate the following text into English using proper terms given below:
- •Classification by Structural Change
- •Classification by Reaction Type
- •Translate into Russian the following sentences:
- •Translate the follow text into Russian:
- •Translate the classification of hydrocarbons into Russian:
- •Reaction Characteristics
- •Factors that Influence Reactions
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English: Насыщенные углеводороды
- •Translate the following material into Russian:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the words and word combinations in brackets into English.
- •Give equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Be ready to answer questions on the text and talk about the refinery presses.
- •Translate words and word combinations in brackets into English. Translate
- •Give equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate in to English:
- •Interface поверхность раздела; граница
- •Viscosity
- •Translate words and word combinations in brackets into English. Then
- •Translate the following text and be ready to discuss it: crude oil pretreatment (desalting).
- •Electrostatic desalting.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Give eqvivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Improving the quality of petroleum products
- •Give eqvivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian: The Physics of Oil Refineries
- •Discussion of the refinery process. Prepare the brief report on one of the theme topics.
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text in writing:
- •Introduction to nuclear power
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Inside the reactor
- •Put some questions to the text and translate them:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following material into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following word combination into Russian:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following extract into English:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Give equivalents to the terms on the fig.2 using technical dictionaries.
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into English: Устройство энергетических ядерных реакторов.
- •Put several questions to the text above and answer them:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following extract into Russian:
- •To check yourself try to translate the following text at sight:
- •Introduction to the almr/prism
- •Translate the following information into English: хранение ядерного топлива
- •Work area
- •Electrical safety
- •Power tool use and care
- •Service
- •Рабочее место
- •Поддерживайте чистоту и порядок на Вашем рабочем месте.
- •Меры безопасности при подключении к электросети.
- •Указания по безопасности
- •Использование инструмента и уход за ним.
- •Important safety instructions
- •Translate into English:
- •Устройство и принцип работы р ис. 1. Внешний вид аппарата.
- •6 Claims, 5 Drawing Figures exhaust gas recirculation apparatus for engine with turbocharger
- •Read the patent given above, identify its parts and be ready to comment on peculiarities of their translation. 2. Translate the following extract into English:
- •Beltline: The horizontal area of the body along the door just below the side-window glass.
- •Abstract
- •Description
Improving the quality of petroleum products
Catalysts also help individual hydrocarbon molecules to change their structures, processes called isomerization and reforming. Long unbranched paraffin molecules and cycloparaffins aren’t useful in gasoline because they cause knocking. Isomeriz- ing catalysts, usually platinum, help the unbranched molecules to rearrange into highly branched molecules (Fig. 1). Reforming catalysts, usually platinum and rhenium, assist in converting cycloparaffins into aromatics. In both cases, the octane numbers increase substantially. Much of the low octane, raw gasoline obtained from the first distillation tower is subsequently sent through catalytic isomerizing and reforming facilities to increase its octane number.
The goal of isomerization is to add more branches to a paraffin molecule by interchanging hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms. On the isomerizing catalyst’s surface, one carbon atom and one hydrogen temporarily let go of the hydrocarbon molecule and exchange places. Several such interchanges turn the molecule into highly branched paraffin with a high octane number.
Without a catalyst, this isomerizing process requires a great deal of energy. Two separate covalent bonds must break completely so that the pieces become free radicals. The carbon and hydrogen atoms must then exchange places and reattach to the main portion of the molecule. This complicated process is unlikely to happen, even at high temperatures.
The isomerizing catalyst facilitates the process by binding temporarily to the molecule and its fragments. The various pieces never become free radicals. Instead, they migrate along the surface of the catalyst and eventually reattach to one another without ever being completely free. The catalyst even helps the fragments stay close enough together to exchange places. What would otherwise be an almost impossible event becomes rather likely.
A reforming catalyst helps cycloparaffin molecules get rid of hydrogen atoms and become aromatics (Fig. 2). Aromatics have higher octane numbers than cycloparaffins, so this reforming is important for gasoline. Although catalysts ease the removal of the hydrogen atoms as hydrogen molecules, the final product molecules have more chemical potential energy than the original molecules. Because this reaction converts a significant amount of thermal energy into chemical potential energy, heat must be added to keep it going.
In addition to isomerization and reforming, oil refineries also use catalysts to attach smaller molecules together to form larger molecules. Catalytic alkylation and polymer
ization are used to form gasoline molecules from smaller molecules that would otherwise be difficult to use. Both processes start with olefin molecules produced in thermal or catalytic cracking. The olefin molecules have reactive double bonds, and catalysts encourage them to stick to one another or to other molecules. These reactions produce highly branched, high octane gasoline.
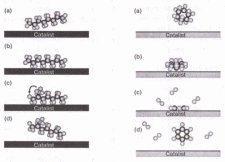
Fig. 1 - An unbranched paraffin molecule (a) attaches to the surface of an isomerizing catalyst (b). This catalyst helps a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom exchange places (c) by stabilizing the pieces during the exchange. The branched paraffin molecule leaves and the catalyst is left unchanged (d).
Fig. 2 - A cycloparaffin (a) attached to the surface of a reforming catalyst (b). This catalyst helps in the removal of hydrogen molecules from the ring (c) and creates an aromatic molecule. This molecule leaves the surface and the catalyst is left unchanged (d).
WORDLIST
Isomerization изомеризация
branched paraffin предельный парафин
rhenium рений
covalent bond ковалентная связь
to reattach восстановить (соединение)
original molecule исходная молекула
reactive double bond химически активная двойная связь
catalytic alkylation каталитическое алкилирование
absorption column абсорбционная колонна
scrubber газопромыватель
GLOSSARY
aromatic ring A ring of six carbon atoms in which each carbon atom is bound to its neighbor with one and a half covalent bonds. The first bond is a typical covalent bond, with a pair of electrons located between the atoms, but the half bond involves electrons that circulate above and below the ring of atoms.
aromatics Hydrocarbon molecules containing one or more aromatic rings, cracking The separation of a large hydrocarbon molecule into two or more smaller hydrocarbon molecules.
cycloparaffins Ring-like hydrocarbon molecules based on closed chains of carbon atoms. These rings contain only single covalent bonds.
immiscible Two or more materials that cannot dissolve in one another and remain as two separate phases when they are mixed.
isomerization A rearrangement of the atoms in a molecule that leaves it with a different spatial structure than it had originally.
isomers Two or more molecules containing exactly the same number of atoms but having different and inequivalent spatial structures.
nonpolar molecule A molecule that has no electrical dipole. A nonpolar molecule has no positive or negative end because its charge is symmetrically arranged about its center.
olefins Chain-like or ring-like hydrocarbon molecules based on chains of carbon atoms. Olefin molecules include one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
paraffins Chain-like hydrocarbon molecules based open chains of carbon atoms. Paraffins contain only single covalent bonds and may have branches.
reforming Removal of hydrogen atoms from a cycloparaffin to create an aromatic hydrocarbon.
residual liquid The liquid that falls to the bottom of a distillation tower because it contains molecules that rarely become gaseous at the temperatures of the tower.
volatile A material that easily becomes gaseous because its molecules are not strongly attached to one another.
EXERCISES
