
- •Internal combustion engine
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Using the English-Russian dictionary translate the following text
- •Into Russian:
- •IV. Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Explain and translate the following definitions of the car body elements:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Be ready to talk and discuss the general structure of a ship
- •Uss Nimitz’s catapult 1
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Inspecting a used car
- •Incandescent lighting - освещение лампами накаливания
- •Answer and translate the following questions:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •IV. Translate the following information into English:
- •Various definitions
- •Decipher and translate the following abbreviations:
- •Answer the following question:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following material into English:
- •I. Translate the following sentences:
- •II. Translate the following information in to Russian:
- •Translate the following advertising material into English:
- •Be ready to talk about the power supply at your home.
- •Introduction to power electronics
- •I. Answer the following questions:
- •Translate into English words in brackets and then the sentences
- •Into Russian:
- •Translate the following text: Conductors
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate into English: Теория цепей
- •Translate into Russian: Current supply
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate and answer the following questions:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate the text and be ready to discuss the general radio design:
- •Translate into English the following material:
- •Translate the following extract: Microphone transmitter.
- •Introduction to radar fundamentals
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Put 10 questions to the text and answer them:
- •Translate into Russian the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Read and translate the list of chemical elements with their symbols and atomic number: (in alphabetical order)
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Put 6 questions to the text and answer them:
- •Translate the following sentences in to Russian:
- •Translate the following text and he ready to discuses properties of elements: Chemical properties of elements
- •Vanderwaals radius
- •Ionic radius
- •Isotopes
- •Translate the following text into English using proper terms given below:
- •Classification by Structural Change
- •Classification by Reaction Type
- •Translate into Russian the following sentences:
- •Translate the follow text into Russian:
- •Translate the classification of hydrocarbons into Russian:
- •Reaction Characteristics
- •Factors that Influence Reactions
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English: Насыщенные углеводороды
- •Translate the following material into Russian:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the words and word combinations in brackets into English.
- •Give equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Be ready to answer questions on the text and talk about the refinery presses.
- •Translate words and word combinations in brackets into English. Translate
- •Give equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate in to English:
- •Interface поверхность раздела; граница
- •Viscosity
- •Translate words and word combinations in brackets into English. Then
- •Translate the following text and be ready to discuss it: crude oil pretreatment (desalting).
- •Electrostatic desalting.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Give eqvivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Improving the quality of petroleum products
- •Give eqvivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian: The Physics of Oil Refineries
- •Discussion of the refinery process. Prepare the brief report on one of the theme topics.
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text in writing:
- •Introduction to nuclear power
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Inside the reactor
- •Put some questions to the text and translate them:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following material into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following word combination into Russian:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following extract into English:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Give equivalents to the terms on the fig.2 using technical dictionaries.
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into English: Устройство энергетических ядерных реакторов.
- •Put several questions to the text above and answer them:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following extract into Russian:
- •To check yourself try to translate the following text at sight:
- •Introduction to the almr/prism
- •Translate the following information into English: хранение ядерного топлива
- •Work area
- •Electrical safety
- •Power tool use and care
- •Service
- •Рабочее место
- •Поддерживайте чистоту и порядок на Вашем рабочем месте.
- •Меры безопасности при подключении к электросети.
- •Указания по безопасности
- •Использование инструмента и уход за ним.
- •Important safety instructions
- •Translate into English:
- •Устройство и принцип работы р ис. 1. Внешний вид аппарата.
- •6 Claims, 5 Drawing Figures exhaust gas recirculation apparatus for engine with turbocharger
- •Read the patent given above, identify its parts and be ready to comment on peculiarities of their translation. 2. Translate the following extract into English:
- •Beltline: The horizontal area of the body along the door just below the side-window glass.
- •Abstract
- •Description
T
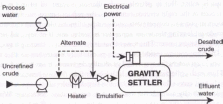
Electrostatic desalting.
he feedstock crude oil is heated to between 150° and 350°F to reduce viscosity and surface tension for easier mixing and separation of the water. The temperature is limited by the vapor pressure of the crude-oil feedstock. In both methods other chemicals may be added. Ammonia is often used to reduce corrosion. Caustic or acid may be added to adjust the pH of the water wash. Wastewater and contaminants are discharged from the bottom of the settling tank to the wastewater treatment facility. The desalted crude is continuously drawn from the top of the settling tanks and sent to the crude distillation (fractionating) tower.
LESSON# 4
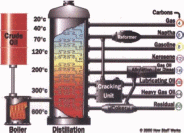
CRUDE OIL DISTILLING
Once water and salts have been removed from the crude oil, the refinery is ready to begin sorting its molecules. The principal sorting technique is distillation. Distillation is described in the supplement on water purification, but here the job is somewhat different. In water purification, the goal is to separate a volatile chemical (water) from a non-volatile chemical (salt) and the only molecule that becomes a gas at reasonable temperatures is water. But in petroleum distillation, almost all of the molecules can become gaseous in the right circumstances. So the refinery must carefully adjust those circumstances in order to collect particular groups of molecules from the mixture.
The crude oil leaving the water separator is heated and then injected near the bottom of a tall distillation tower. This tower contains a series of collecting trays, one above the other. The temperature inside the tower is carefully controlled so that it’s highest where the crude oil enters the tower and gradually decreases from the bottom to the top of tower. Thus each collecting tray is a little cooler than the one beneath it.
As the hot oil enters the tower, all but the largest molecules evaporate and become gas. This gas gradually ascends the tower and its temperature decreases. With each decrease in temperature, the molecules in the gas find it more difficult to stay apart. The larger molecules in the gas begin to stick to one another and form liquid in the tower’s trays. Some of this liquid drips down from each tray to the tray below. Overall, gas moves up the tower from below and liquid drips down the tower from above.
Each tray tends to accumulate those molecules that can be either gas or liquid at the tray’s temperature of the tower. Any molecules that tend to be gaseous at that temperature will move up the tower to the trays above. Any molecules that tend to be liquid at that temperature will drip down the tower to the trays beneath. Thus each tray concentrates a particular group of molecules.
However this concentrating process doesn’t produce pure chemicals. The liquid in a particular tray still contains a number of different molecules. While one range of sizes is most likely to accumulate in that tray, it will also contain some smaller and larger molecules that manage to find their way into the liquid. In general, nature always tries to maximize the randomness of a liquid. The same statistical rules that govern the flow of heat and are responsible for the laws of thermodynamics also make it very difficult to purify chemicals completely.
Unlike oil and water, these hydrocarbon molecules mix easily with one another. They all stick together with van der Waals forces, regardless of how large their molecules are. Chemical such as these that dissolve freely in one another are said to be
miscible. While the smaller molecules will tend to evaporate from the liquid more easily than the larger molecules, they are all pretty much equal in the liquid itself.
Crude oil’s first trip through a distillation tower separates it into several parts, including diesel oil, kerosene, and raw gasoline. The diesel oil and kerosene are basically ready for consumer products, but the raw gasoline is not. It has a very low octane number and must be reformed and blended before it’s ready for automobiles. Molecules that are too small to become liquid even at room temperature reach the top of the tower and are processed into propane and LP gases.
The largest molecules that enter the distillation tower rarely become gaseous below 300 °C and drip as a liquid to the bottom tray. It might seem reasonable to heat this residual liquid to a higher temperature to separate its molecules from one another. Unfortunately, temperatures above about 360 °C cause hydrocarbon molecules to decompose into fragments, a phenomenon called cracking. These fragments can then recombine to form gums that plug up the distillation equipment. To avoid cracking, the distillation columns must avoid excessive temperatures.
While the molecules in the residual liquid can still be separated by distillation, that distillation must be performed at very low pressures in a vacuum distillation tower. The residual liquid from an atmospheric pressure tower is reheated to 350 °C and fed into a vacuum tower near its base. Gases move upward while liquid moves downward and each tray accumulates those molecules that can be either gaseous or liquid at its particular temperature.
Because the pressure and density of the gas are reduced in the vacuum tower, molecules don’t have to be very volatile to become a gas. Since forming a thin, low pressure gas of lubricating oil molecules is much easier than forming a dense, high pressure gas of those same molecules, it occurs at a much lower temperature. Thus the vacuum distillation column is able to separate various lubricating oils and waxes from molecules that simply aren’t volatile. The residual liquid leaving the bottom of the vacuum column is asphalt.
T
as liquid. Trays near the bottom of the high pressure tower accumulate liquid butane, those near the middle of the tower accumulate liquid propane, and ethane and methane drift to the top of the tower.
The temperature in a distillation tower decreases from the crude oil inlet to the top of the tower. Liquid extracted from trays at various heights and temperatures contain different mixtures of molecules, and are appropriate for different petroleum products.
Inside a distillation tower is a series of trays, each one cooler than one below it. Gaseous oil molecules bubble up through each tray from below. As they do, the larger molecules condense into liquid. The liquid in each tray is different, with lower trays containing larger molecules than upper trays.
In a vacuum distillation tower, the reduced pressure allows even relatively nonvolatile lubricating oils to become gaseous.
WORDLIST:
Crude oil distillation
(preliminary distillation) первичная перегонка нефти
volatile chemical легкоиспаряющееся хим. вещество
water separator водоотделитель
collecting tray сборная тарелка
miscible смешиваемый
raw низкосортный (неочищенный) бензин
liquid petrol gas газойль
residual liquid отстой
vacuum distillation вакуумная перегонка
hydrotreating гидроочистка
EXERCISE:
