
- •Internal combustion engine
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Using the English-Russian dictionary translate the following text
- •Into Russian:
- •IV. Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Explain and translate the following definitions of the car body elements:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Be ready to talk and discuss the general structure of a ship
- •Uss Nimitz’s catapult 1
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Inspecting a used car
- •Incandescent lighting - освещение лампами накаливания
- •Answer and translate the following questions:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •IV. Translate the following information into English:
- •Various definitions
- •Decipher and translate the following abbreviations:
- •Answer the following question:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following material into English:
- •I. Translate the following sentences:
- •II. Translate the following information in to Russian:
- •Translate the following advertising material into English:
- •Be ready to talk about the power supply at your home.
- •Introduction to power electronics
- •I. Answer the following questions:
- •Translate into English words in brackets and then the sentences
- •Into Russian:
- •Translate the following text: Conductors
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate into English: Теория цепей
- •Translate into Russian: Current supply
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Translate and answer the following questions:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate the text and be ready to discuss the general radio design:
- •Translate into English the following material:
- •Translate the following extract: Microphone transmitter.
- •Introduction to radar fundamentals
- •Give equivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Put 10 questions to the text and answer them:
- •Translate into Russian the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Read and translate the list of chemical elements with their symbols and atomic number: (in alphabetical order)
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Put 6 questions to the text and answer them:
- •Translate the following sentences in to Russian:
- •Translate the following text and he ready to discuses properties of elements: Chemical properties of elements
- •Vanderwaals radius
- •Ionic radius
- •Isotopes
- •Translate the following text into English using proper terms given below:
- •Classification by Structural Change
- •Classification by Reaction Type
- •Translate into Russian the following sentences:
- •Translate the follow text into Russian:
- •Translate the classification of hydrocarbons into Russian:
- •Reaction Characteristics
- •Factors that Influence Reactions
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English: Насыщенные углеводороды
- •Translate the following material into Russian:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the words and word combinations in brackets into English.
- •Give equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Be ready to answer questions on the text and talk about the refinery presses.
- •Translate words and word combinations in brackets into English. Translate
- •Give equivalents to the following word combinations:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate in to English:
- •Interface поверхность раздела; граница
- •Viscosity
- •Translate words and word combinations in brackets into English. Then
- •Translate the following text and be ready to discuss it: crude oil pretreatment (desalting).
- •Electrostatic desalting.
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Give eqvivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following text:
- •Translate into English:
- •Improving the quality of petroleum products
- •Give eqvivalents to the following words and word combinations:
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into English:
- •Translate into Russian: The Physics of Oil Refineries
- •Discussion of the refinery process. Prepare the brief report on one of the theme topics.
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following text in writing:
- •Introduction to nuclear power
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Inside the reactor
- •Put some questions to the text and translate them:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following material into English:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following word combination into Russian:
- •Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following text into English:
- •Translate the following extract into English:
- •Translate the following sentences:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Translate the following information into English:
- •Give equivalents to the terms on the fig.2 using technical dictionaries.
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate into Russian:
- •Translate the following information into Russian:
- •Translate into English: Устройство энергетических ядерных реакторов.
- •Put several questions to the text above and answer them:
- •Translate the following text into Russian:
- •Translate the following extract into Russian:
- •To check yourself try to translate the following text at sight:
- •Introduction to the almr/prism
- •Translate the following information into English: хранение ядерного топлива
- •Work area
- •Electrical safety
- •Power tool use and care
- •Service
- •Рабочее место
- •Поддерживайте чистоту и порядок на Вашем рабочем месте.
- •Меры безопасности при подключении к электросети.
- •Указания по безопасности
- •Использование инструмента и уход за ним.
- •Important safety instructions
- •Translate into English:
- •Устройство и принцип работы р ис. 1. Внешний вид аппарата.
- •6 Claims, 5 Drawing Figures exhaust gas recirculation apparatus for engine with turbocharger
- •Read the patent given above, identify its parts and be ready to comment on peculiarities of their translation. 2. Translate the following extract into English:
- •Beltline: The horizontal area of the body along the door just below the side-window glass.
- •Abstract
- •Description
IV. Translate the following information into English:
Машины постоянного тока.
К машинам постоянного тока относятся генераторы и электрические двигатели. Машина постоянного тока состоит из двух основных частей: а) неподвижной части (статор), предназначенной для создания магнитного потока, б) вращающейся части (ротора), которая называется якорем и в которой происходит процесс преобразования механической энергии в электрическую (электрический генератор); или обратно - электрической энергии в механическую (электродвигатель). Небольшой зазор отделяет статор от ротора.
Статор машины постоянного тока состоит из: а) основных полюсов - для создания магнитного потока; б) добавочных полюсов (interpoles), установленных между основными для обеспечения безыскровой работы щеток коллектора и станины.
Якорь - это цилиндрическое тело, вращающееся в пространстве между полюсами, и состоит из: а) зубчатого цилиндрического якоря; б) обмотки, уложенной на нём; в) коллектора; г) щеточного устройства.
LESSON # 2 DIRECT CURRENT
Direct current (DC or “continuous current”) is the constant flow of electric charge from high to low potential. This is typically in a conductor such as a wire, but can also be through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. In direct current, the electric charges flow in the same direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC).
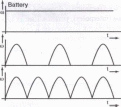
Types of direct current
The first commercial electric power transmission (developed in the late nineteenth century) used direct current. Because alternating current is more convenient than direct current for electric power distribution and transmission, today nearly all electric power transmission uses alternating current.
Various definitions
Within Electrical Engineering, the term DC is a synonym for constant. For example, the voltage across a DC voltage source is constant as is the current through a DC current source. The DC solution of an electric circuit is the solution where all voltages and currents are constant. It can be shown that any voltage or current waveform can be decomposed into a sum of a DC component and a time-varying component. The DC component is defined to be the average value of the voltage or current over all time. The average value of the time-varying component is zero.
Although DC stands for “Direct Current”, DC sometimes refers to “constant polarity.” With this definition, DC voltages can vary in time, such as the raw output of a rectifier.
Some forms of DC (such as that produced by a voltage regulator) have almost no variations in voltage, but may still have variations in output power and current.
Applications
Direct current installations usually have different types of sockets, switches, and fixtures, mostly due to the low voltages used, from those suitable for alternating current. It is usually important with a direct current appliance to not reverse polarity unless the device has a diode bridge to correct for this. (Most battery-powered devices don’t.)
High voltage direct current is used for long-distance point-to-point power transmission and for submarine cables, with voltages from a few kilovolts to approximately one megavolt.
DC is commonly found in many low-voltage applications, especially where these are powered by batteries, which can produce only DC, or solar power systems, since solar cells can produce only DC. Most automotive applications use DC, although the generator is an AC device which uses a rectifier to produce DC. Most electronic circuits require a DC power supply.
Power supplies Audio Amplifier
Power-line operated power supplies are based on transformers, diodes, transistors, and capacitors. Transformers enable these supplies to exchange voltage for current to obtain the large currents and low voltages needed by audio amplifiers and other household electronic devices. Diodes prevent currents from flowing backward through these supplies so that, like batteries, they always pump currents from their negative terminals to their positive ones. Transistors help to control the voltage of the current delivered by a power supply-they cause the output current to experience an adjustable and carefully controlled voltage drop so that the current leaves the supply at a regulated voltage. And capacitors in the supply store separated electric charge and energy for delivery during the times when the supply isn’t receiving any power from the alternating current source.
A basic power supply, without any transistor regulation, connects the primary of its transformer to the electric outlet and the secondary of that transformer to a set of diodes. These diodes act as electronic switches, directing current always in one direction through the circuit that the power supply operates. To stop the current from fluctuating so much, capacitors are often attached to the two output wires of the power supply. These capacitors store separated charge during times when the AC power line is delivering more than enough current and release some of that charge with the power line isn’t delivering enough.
In more sophisticated modem power supplies, often called “switching power supplies,” current from the electric outlet is sent through diodes and into capacitors, where it is stored as separated charge. Several transistors then act as electronic
switches to produce a high-frequency alternating current from this stored separated charge. With a frequency of tens of thousands of cycles per second, this current passes through the primary of a small transformer. Only a small transformer is needed because the short duration of a cycle reduces the amount of energy that the transformer needs to store in its magnetic field during one cycle. Power passes to a current in the transformer’s secondary coil. This secondary coil current is rectified (made DC) by passing it through more diodes. The DC current is filtered with more capacitors and a final transistor stage controls the delivery voltage. But the main delivery voltage control comes from turning on or off the high-frequency AC that is synthesized and delivered to the transformer’s primary coil. By starting or stopping this AC current, the power supply can control the flow of power through the transformer and efficiently limit the voltage of its overall output.
WORDLIST:
Semiconductor - полупроводник
insulator - изолятор
ion beams - ионные лучи
electric power transmission - передача электроэнергии
electrical engineering - электротехника
installations - (зд.) аппаратура, оборудование
fixtures - контактирующие приспособления
diode bridge - диодный мост
point-to-point -двухточечная (сквозная) передача
power transmission электроэнергии
submarine cable - подводный кабель
audio amplifier - звуковой усилитель
capacitor - конденсатор
electronic switch - электронный выключатель
(коммутатор)
EXERSICES:
