
- •Methodical instructions
- •In discipline «Food and Biologically Active Additives »
- •Methodical instructions
- •In discipline «Food and Biologically Active Additives »
- •Content
- •Laboratory work№8. Studying of the main processing behavior of emulsifiers, geleobrazovatel, thickeners definition of their quality and ways of introduction to food
- •Introduction
- •Laboratory work № 1 calculation of the compounding, preparation and analysis natural food dye (caramel colour) e 150 and
- •Determination of extractives
- •Color detection
- •Laboratory work № 3 calculation of the formulation and preparation of protein cream with food additives usage
- •Technology of protein cream preparation
- •Laboratory work № 4 determination of vitamin c content in beverages as a biologically active additives
- •Laboratory work № 5 determination of benzoic acid
- •Quantitative determination of benzoic acid
- •Laboratory work № 6 the calculation of the formulation and preparation of non-alcoholic beverage with the use of food additives
- •Brief information
- •Calculation of the working formulation of non-alcoholic beverage
- •Technology of preparation of beverage
- •Laboratory work № 7 studying of technological properties of dyes and fragrances
- •Control questions
- •Laboratory work № 8 studying of the main processing behavior of emulsifiers, geleobrazovatel, thickeners definition of their quality and ways of introduction to food
- •Control questions:
- •Questions for self-preparation:
- •Laboratory work № 9 studying of the main processing behavior of preservatives, preparation of solution of the given concentration
- •Questions for self-preparation:
- •Laboratory work № 10 reactions of detection of vitamins in food products
- •The list of the recommend literature:
Questions for self-preparation:
1. General characteristic of technological additives.
2. Acidity regulators, chemical nature.
3. Chemical nature of buffer systems.
4. Use of regulators of acidity in production of vegetable juice.
5. Use of regulators of acidity in production of meat products.
6. The anti-making foam agents, application.
7. Defoaming agents, application.
8. Baking powder, general characteristic, application.
9. Carriers, solvents, thinners - a general characteristic, application.
10. Means for capsulation, a general characteristic, application.
11. Ways of microencapsulation.
12. Means for tabletting, a general characteristic, application.
13. Dissolution accelerators, general characteristic, application.
14. Dividers, general characteristic, application.
15. Propellants, general characteristic, application.
16. The moistening agents, a general characteristic, application.
17. Use of regulators of acidity.
18. The substances facilitating filtering.
19. Clarifiers, general characteristic, application.
20. Auxiliary materials, general characteristic, application.
Laboratory work № 10 reactions of detection of vitamins in food products
Materials: test tubes, supports, reactants and raw materials
Now special relevance is acquired by questions of improvement of vitamin security of the population. Inadequate security of an organism with vitamins reduces working capacity and resilience to diseases, aggravates negative impact on an organism of harmful environmental conditions that in general leads to big economic losses.
Experience No. 1. Vitamin A detection by reaction with sulfuric acid
Vitamin A is necessary for perception of light in the course of sight, maintenance and development in a healthy condition of mucous membranes of respiratory organs, digestive tract, secretory, reproductive and genitals, and also immune system. Vitamin A contains only in animal products: liver of cattle, egg yolk, dairy products. Cod-liver oil is especially rich with this vitamin. Vegetable products (tomatoes, carrots, pepper, etc.) contain the carotinoids which are pro-vitamins A.
Experiment technique. In a dry test tube to mix 1 drop of cod-liver oil with 5 drops of chloroform, to add 1 drop the concentrated chamois of acid - mix in the presence of vitamin A is painted in red-brown color.
Observations:
Conclusions:
Experience No. 2. D3anilinovoy vitamin detection breakdown
D3 vitamin participates in exchange of ions of calcium, phosphates. The greatest number of D3 vitamin in butter, a yolk of eggs, cod-liver oil.
Experiment technique. In a dry test tube to mix 1 drop of cod-liver oil with 5 drops of chloroform, to add 1 drop of an aniline reactant (the 15th chaskty aniline and 1 part of the concentrated hydrochloric acid) - the formed emulsion when heating gains red color that demonstrates vitamin D availability.
Observations:
Conclusions:
Experience No. 3. Vitamin detection by Ereaktion with nitric acid
In relation to nonsaturated lipids of a tokoferola inhibitors of process of their oxidation and defining their resistance to the damaging action of peroksidny oxidation. Vitamin E sources – vegetable oils, salad, cabbage, seeds of cereals, butter, an egg yolk.
Experiment technique. In a dry test tube to mix 5 drops of spirit solution of vitamin E and 10 drops of the concentrated nitric acid - solution is painted in red color owing to oxidation of tocopherol to the painted products of a hinoidny row.
Observations:
Conclusions:
Experience No. 4. B1 vitamin detection by dinitriding reaction sulfanilovy acid
B1 vitamin (thiamine) uchastut in exchange of carbohydrates and reactions of power exchange in nervous system and muscular tissue. B1 vitamin is widespread in products of plant origin (a cover of seeds of grain cereals and rice. peas, haricot, soy, etc.), are formed in a liver, kidneys, a cardiac muscle.
Experiment technique. Bring in a test tube on 5 drops 1% of solution of sulfanilovy acid and 5% of solution of nitrate sodium (diazoreactant), to add several kristallik of thiamine and on a wall of the inclined test tube carefully to add 5-7 drops of 10% of solution of bicarbonate of sodium - on border of liquids the orange ring appears.
Observations:
Conclusions:
Experience No. 5. Quantitative definition of vitamin C
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) supports blood vessels, skin and a bone tissue in a healthy state. Stimulates protective forces of an organism, strengthens immune system, promotes neutralization and removal of alien substances and poisons, improves iron digestion. Vitamin C sources - fresh vegetables, fruit, greens. Quantitative definition of ascorbic acid is based on its ability to be oxidized in degidroaskorbinovy acid 2,6 - dikhlorfenolindofenoly with recovery of the last in leykosoyedineiy.
The technique eksperimenta.0,1 or 1 g of needles to pound of a dogrose in a mortar from 9,9 ml (9 ml in a case with needles) 2% of solution of hydrochloric acid and a pinch of quartz sand. Filter contents and for the analysis to take 3 ml of a filtrate in a conic flask. Titrovat 0,001 N solution of sodium salt of a 2,6-dikhlorfenolindofenol before emergence of poorly rokzovy coloring which isn't disappearing during 30 pages.
Calculation:
С(%)=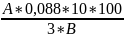 ,
where
,
where
A-number of ml of 0,001 N of solution of sodium salt of a 2,6-dikhlorfenolindofenol,
0,088 – stoichiometric koeffitsit; 10 – total of a water extension from a hinge plate; 100 – recalculation coefficient in %; 3 – amount of the studied liquid taken on titration; In – a hinge plate of a dogrose (needles) in mg.
Conclusions:
Experience No. 6. The restoring properties of ascorbic acid
The Askorbiknovy acid which is contained in many vegetable and animal fabrics has oxidation-reduction properties.
Experiment technique. To add 2 drops of 0,01% of solution of a methylene blue and 2 drops of 3% of solution of carbonic sodium to 1 ml of svezheotzhaty potato or cabbage juice (a source of ascorbic acid). Warm up and watch a test tube change of coloring of a methylene blue.
Observations:
Conclusions:
