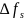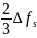- •Telecommunication Systems Department course project
- •050903 – «Telecommunications»
- •Input data
- •Introduction
- •1 Branch line on the basis of pdh dts
- •1.1 Characteristic of the pdh dts transmission line
- •2 Communication organization in the sdh ring
- •2.1 Levels of the synchronous transport modules in sdh ring
- •2.2 Types of sdh modules in the ring
- •2.4 Synchronization of communication network
- •3. Branch line on basis of rrts
- •3.1 Parameters of frequency plan.
- •3.2 Terminal radio relay station (trs)
- •3.3 Terminal radio relay station (trs)
- •3.4 Intermediate radio relay station (irs)
- •5.1 The multiplex plan structure for dwdm dts
- •Choice of multiplexing equipment type
- •5.5 Efficiency of dwdm technology usage
- •Conclusions
- •Bibliography
3. Branch line on basis of rrts
3.1 Parameters of frequency plan.
Modern radio-relay systems are multi-trunk systems, which allow increasing economic efficiency of the system using one and the same antenna pylon, technical building, and system of power supply organization with several trunks. The method of frequency division is used for building of multi-trunk radio-relay systems, because the SHF signals with different frequency bands are used for signals transmission of different trunks (table 3.1).
Table 3.1 – RRTS classes
Class № |
Modulation type |
|
1 |
FM-2 |
2 |
2 |
QAM-4 |
|
3 |
PM-8 |
|
4 |
QAM-16 |
|
5 |
QAM-64 |
|
6 |
QAM-256 |
|
From the input data:
B=622,08 Mbit/s = 0,62208 Gbit/s.
For RZ code
 (GHz)
(GHz)
As
the equipment class in RRTS-1 so the modulation type is FM-2 for
which


F=1,246 (GHz)
Upper boundary frequency plan is calculated by the following formula:
 ,
,
where
 - is lower boundary of frequency band; 2F – is the interval between
carriers of neighboring trunks;
- is lower boundary of frequency band; 2F – is the interval between
carriers of neighboring trunks;
 - is the separation (protection) band between carriers of adjacent
trunks with the opposite transmission directions;
- is the separation (protection) band between carriers of adjacent
trunks with the opposite transmission directions;
 - is the number of trunks. The carrier frequencies of lower group of
frequency plan are calculated by the formulas:
- is the number of trunks. The carrier frequencies of lower group of
frequency plan are calculated by the formulas:
 ,
GHz ;
,
GHz ;
 ,
GHz ;
,
GHz ;
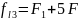 ,
GHz ;
,
GHz ;
 ,
GHz ;
,
GHz ;
 ,
GHz .
,
GHz .
The carrier frequencies of upper group of frequency plan are calculated by the formula:
 ,
GHz.
,
GHz.
The slip frequency (the interval between carriers of lower and upper group of the same trunk in the RRTS frequency plan):
 ,
GHz.
,
GHz.
Central frequency of the used frequency bandwidth is calculated by the formula:

The corresponding wavelength is:

Let us perform the calculation by using these formulas:
 )
)
 (GHz)
;
(GHz)
;
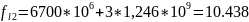 (GHz)
;
(GHz)
;
 (GHz)
;
(GHz)
;
 (GHz)
;
(GHz)
;
 (GHz);
(GHz);
 (GHz);
(GHz);
 (GHz);
(GHz);
 (GHz);
(GHz);
 (GHz);
(GHz);
 (GHz);
(GHz);
 ;
;
 (MHz)
= 0,020406 (GHz);
(MHz)
= 0,020406 (GHz);
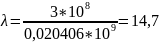 (m).
(m).
3.2 Terminal radio relay station (trs)
In section 3.2 it is necessary to describe RRTS frequency plan parameters. The spectral diagram of frequency plan is shown in fig. 3.1.
The two-frequency distribution of operating frequencies for one high-frequency trunk is used at duplex communications through radio relay links. The high-frequency trunkis the chain of radio relay stations, and on each of them one set of the same type high-frequency transmitter-receiver equipment and separation band pass filters are installed. In case of two-frequency distribution of operating frequencies, at each intermediate station transmitters operate with one frequency, and receivers –with the other.
The transmitter has no interfering effect on the receiver, as transmission and reception of radio signals is performed in different radio frequencies. Frequency separation is performed by separation band pass filters. The frequency changing is performed at intermediate station in order to eliminate communication between the transmitter and receiver, which operate in different directions.
In multi-channel RRL with two-frequency distribution of operating frequencies, transmission and receiving frequencies of each trunk differ in the same value.