
- •Предисловие
- •Content
- •General Practitioner 1
- •Remember
- •Exercises
- •1.7 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart. Heart trouble.
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises.
- •General practitioner 2
- •Exercises
- •2.7 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart.
- •Visiting general practitioner
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises:
- •1.Translatethe following wordcombinations and make up sentences of yourown.
- •2. Put questions to the italicized parts.
- •3.Put the following sentences into Passive Voice.
- •4. Underlinethe correctword or phrasein each sentence.
- •5. Match each of the medical terms with a term which a patient would easily understand.
- •Nurses in the uk
- •Remember
- •Exercises
- •3.7 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart. Helping a patient
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises.
- •1. Explain the meanings of wordshaving almostsimilar spelling.
- •2. Match sentences (1-10)with an explanation (a-j).
- •4. Read the instructions for nurses at their work-place. Try to comment each rule. Why is it so important to follow it?
- •5. Study the meaning of the prefixes:
- •Health professionals in the uk
- •Exercises
- •4.6 Learn questions of an eye specialist and make your own dialogue. Consulting an ophthalmologist.
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises.
- •1. Try to learn or revise linking words and phrases, their definitions are given below, make up sentences of your own.
- •2.Underline the correct word orphrase in each sentence.
- •3.Complete the second sentence so that it has a similar meaning to the first sentence, using the word given. Do not change the word given. The first one hasbeen done foryou.
- •4. Change any part of the sentence by Participle construction.
- •5. Read sentences with Absolute Participle Construction and define the ing-forms.
- •Hospitals in the United Kingdom
- •Introduction to a hospital
- •Inpatients
- •Exercises
- •Information for outpatients
- •5.8 Answer the following questions.
- •5.9 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart. Consulting a traumatologist.
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises:
- •2. Do you know what instruments you use are called in English? Read the descriptions and try to guess. The first has been done as an example for you.
- •3. Substitute the Subordinate clauseby Gerund with prepositions:
- •4.Make up sentences of your own with verbs and expressions demanding Gerund to be followed after them.
- •5. Read, translate into your own language and put sentences in the following order: a) Participle b) Gerund c) Verbal Noun;
- •Primary care
- •Remember
- •Exercises
- •6.7 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart. Quinsy
- •Additionalgrammar and vocabulary exercises.
- •1. Learn prepositions following nouns,make up sentences of your own.
- •3.Complete sentences using Complex Object.
- •4. Paraphrase sentencesusing Complex Object with Participle.
- •5.Make up sentences with Complex Objects with the infinitive.
- •Medical education in the United Kingdom (Part 1)
- •Information froman undergraduate leaflet
- •Vocational Studies and Clinical Skills
- •View of a first year student
- •Exercises
- •7.7 Read, translate and learn a dialogue between an eye doctor and a residency course student.
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises.
- •1. Match a and b columns. Learn word combinations.
- •2. Paraphrase the following sentences using Complex Subject.
- •3. Paraphrase the followingsentences using Complex Object (complex infinitive or participial object).
- •4. Point out theComplex Object and Complex Subject in the following sentences. State their structure.
- •5. Changesentences fromIndirect speech into Direct speech.
- •Medical education in the United Kingdom (Part 2)
- •Exercises
- •8.6 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart. Otitis
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercise:
- •1. In two groups, a and b, check these verbs in a dictionary.
- •2. Change sentences (doctor’s questions)into Indirect Speech.
- •3.Change sentences into Direct speech.
- •4. Paraphraze these sentences into Passive Voice.
- •5. Open the brackets and choose the right Participle.
- •The international doctor
- •Provisional registration
- •Full registration
- •Specialist registration
- •Exercises
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises:
- •1. Put the adverbs and adverbial phrases of frequency according to the frequency scale in the box. Make up sentences of your own.
- •2. Complete sentences with Participle Construction using the information in brackets.
- •3. Learn the following phrases which are always followed by Gerund. Look at the examples, and makeup sentences of your own.
- •4. Use the required Pasttense instead of infinitives in brackets.
- •5. Continue making up sentences of your own looking at the models. Do as many as possible, pronounce them to your partner.
- •Research articles
- •Exercises
- •Addtitional grammar and vocabulary exercises:
- •1. Match the verbs on the left with a group of nouns on the right.
- •3. Put thefollowing sentencesinto the Past tense.
- •4. Complete the following sentences using therequired Oblique Mood.
- •5. Supply necessary forms of the Subjunctive Mood in clauses byas if and as though.
- •How to write an abstract for the research article
- •Exercises
- •11.5 Read, translate and learn a dialogue. Making an Appointment with the Dentist.
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises:
- •1. Work in pairs, learn body language expressions, practise miming and guessing the actions.
- •2. Make a new sentence from the questions in brackets. Look at the example.
- •3. Paraphrase sentences using “I wish”.
- •5. Ask questions to the words in italics. There might be several questions to one sentence.
- •Conference presentations
- •Introduction
- •I'll begin by ...
- •I'll then ...
- •It is well known that...
- •X has established clearlythat ...
- •12.3 Answer a question: What makes a good presentation, in your mind? Think about it.
- •12.5 Read and learn a dialogue by heart. At the doctor’s
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises:
- •1. Put the following expressions in the box under one of three headings.
- •2. Revise or learn the following quantity expressions.
- •3. Which expressions from the ex.3. Are followed by a plural verb and which by a singular verb? Give examples.
- •4. Put the sentencesinto reported speech.
- •Case presentations
- •Exercises
- •13.9 Read, translate and learn a dialogue by heart. Appendicitis
- •Additional grammar and vocabulary exercises.
- •1. Learnexpressions beginning with prepositions. Make up sentences of your own.
- •2. Work in pairs,write sentences using these adverbs.
- •3. Translate sentences into your own language following the rules of Sequences of tences.
- •Appendix II
- •Таble I
- •Plural nouns formation
- •Irregular nouns
- •Remember! Some nouns derived from Greeck and Latin
- •Remember!
- •Таble III Regular and irregular verb form
- •Таble IV Modal verbs
- •Table V
- •Present Simple (Indefinite) Tense Positive form
- •Past Simple (Indefinite) Tense
- •Yes/No form
- •Negative form
- •Future Simple (Indefinite) Tense Positive form
- •Future Simple (Indefinite) Tense in the Past Positive form
- •Тable VII
- •Present Continuous Tense Positive form
- •PastContinuousTense Positive form
- •Future Continuous Tense Positive form
- •Future Continuous Tense in the Past
- •Perfect Tenses
- •Present Perfect Tense Positive form
- •PastPerfectTense Positive form
- •Future Perfect Tense in the Past Positive form
- •Table IX
- •Future Perfect Continuous Tense Positive form
- •Future Perfect Continuous Tense in the Past p ositive form
- •Active and Passive Voices
- •Различие в употреблений страдательного залога в английском и русском языках
- •Table XI Pronouns.
- •Table XII Questions: general, special General questions
- •Table XIII Participle.
- •Numerals. Дробиичасти
- •Таble XVIII Direct and Indirect speech
- •Таble XIX
- •Perfect Conditional
- •Таble XX Gerund and its position in the sentence
- •English-English vocabulary.
- •References
Table IX
PerfectContinuousTenses
Perfect Continuous Tenses |
||
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
|
It expresses an action that has recently stopped or just stopped or it is still happening. |
I have been waiting for you for 4 hours
|
PastPerfectContinuousTense |
It expresses continuous action that had been happening for a period of time before something else happened. |
When I came into the ward the X-ray consultant had already been examining images for half an hour
|
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
|
It expresses continuous action in future. Itwillhavestartedbeforethedefinitemomentinfutureandwillcontinueлось до определенного момента в будущем и будет продолжаться до этого момента, о котором идет речь |
By next week you will have been studying in this class for 4 months
|
Future Perfect Continuous Tense in the Past
|
It is used in subordinate clause if the verb of the main sentence is in the past. |
She said that by the next month her mother would have been working in the hospital for 2 years
|
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Positive form

Yes/No forms
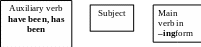
Образование отрицательной формы

Affirmative Form |
Interrogative Form |
Negative Form |
I have been living |
Have I been living? |
I have not been living |
You have been living |
Have you been living? |
You have not been living |
He (she, it) has been living |
Has he (she, it) been living? |
He (she, it) has not been living |
We have been living |
Have we been living? |
We have not been living |
They have been living |
Have they been living? |
They have not been living |
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Positive form

Yes/No questions

Negative forms

Main verb in
–ingform
Affirmative Form |
Interrogative Form |
Negative Form |
I had been working |
Had I been working? |
I had not been working |
You had been working |
Had you been working? |
You had not been working |
He (she, it) had been working |
Had he (she, it) been working? |
He (she, it) had not been working |
We had been working |
Had we been working? |
We had not been working |
They had been working |
Had they been working? |
They had not been working |
