
- •6. Fiscal policy affecting is_lm model
- •7. Monetary policy affecting is_lm model
- •9.Aggregate Demand
- •36. Measuring economic growth
- •37 Factorsaffectingeconomicgrowth
- •1.Capital
- •2.Technological Progress
- •3.Investment
- •4.Health
- •39 Theneoclassicalmodel
- •40 Endogenousgrowththeory
- •41 Unifiedgrowththeory
- •36. Measuring economic growth
- •40 Endogenous growth theory
- •41 Unified growth theory
- •37 Factors affecting economic growth
- •1.Capital
- •2.Technological Progress
- •3.Investment
- •4.Health
- •4.Health
- •39 The neoclassical model
- •15. Foreign exchange rate
- •16. Arbitrage
- •17. Nominal exchange Rate
- •19. Fixed exchange rate
- •20. Floating/flexible exchange rate
- •Managed exchange rate
- •22. Determinants of foreign exchange rate
- •23. Theory of Purchasing Power Parity(ppp)
- •Theory of Interest Rate Parity
- •25. Coveredinterestrateparity
- •26. The Balance of Payment Theory
- •27. ForecastingExchangeRates
- •In short term
- •In Medium and Long-term
- •29.The Flow of Goods: Exports, Imports, Net Exports
- •30.The Flow of Financial Resources: Net Capital Outflow, Saving, Investment, and Their Relationship to the International Flows
- •31.Mundell–Fleming model
- •32. Monetary policy at the fixed exchange rate
- •33.Fiscal policy at the fixed exchange rate
- •1. General theory of is-lm model
- •2.A Short Run Model of a Closed Economy: the is-lm model
- •3.The construction of the is curve (downward curve, shifting, describing)
- •Shifting the is Curve
- •4. The construction of the lm curve (upward curve, shifting, describing)
6. Fiscal policy affecting is_lm model
Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the IS curve to the right
Contractionary fiscal policy shifts the IS curve to the left
Fiscal contraction: a fiscal policy that reduces the budget deficit.
Reducing G or increasing T
Fiscal expansion:increasing the budget deficit.
Increasing G or decreasing T
Taxes (T) and government expenditures (G) affect the IS curve, not the LM curve.
7. Monetary policy affecting is_lm model
Expansionary monetary policy shifts the LM curve to the right
Contractionary monetary policy shifts the LM curve to the left
Monetary contraction (tightening) refers to a decrease in the money supply.
An increase in the money supply is called monetary expansion.
Monetary policy affects only the LM curve, not the IS curve.
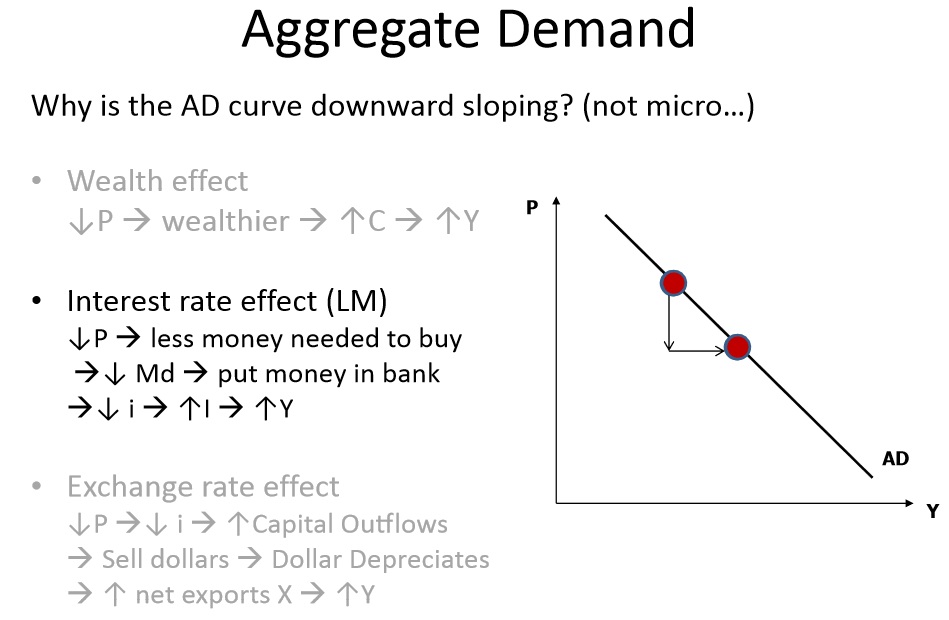
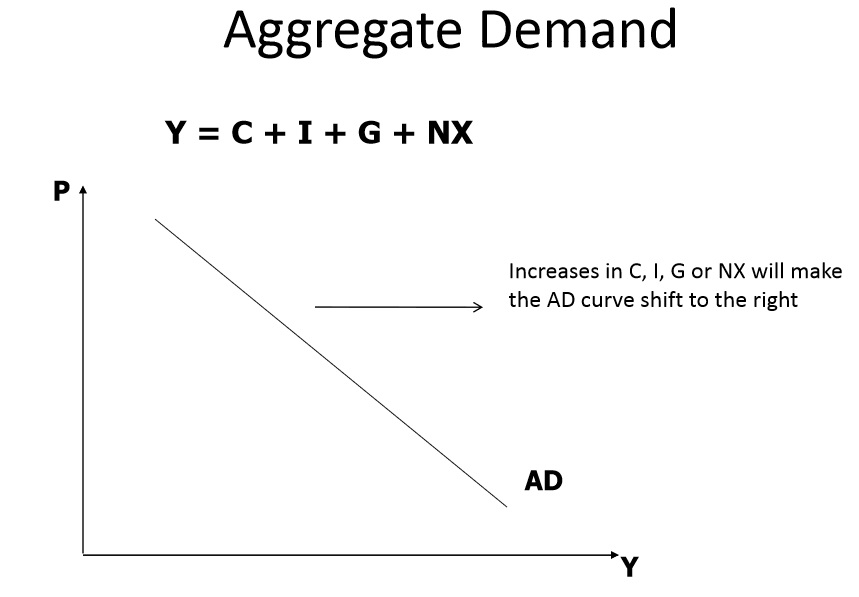
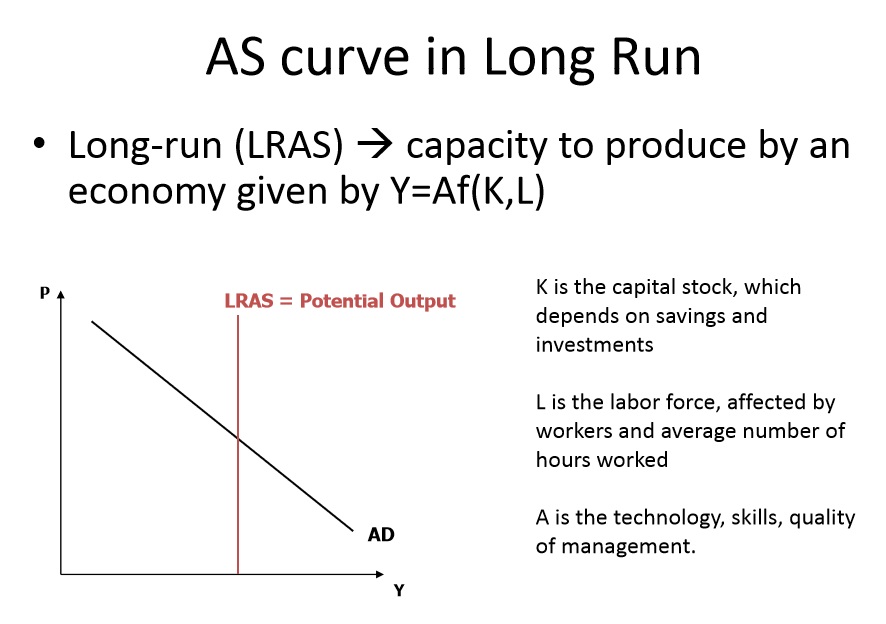
9.Aggregate Demand





36. Measuring economic growth
The U.S. Commerce Department's Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides economic statistics, including GDP. The BEA website conatins links to various documents that explain the concepts and methodology of national income and products accounts and GDP as well as historical tables.
Economic growth is measured by two main indicators: growth rates of real GNP in absolute expression and growth rates of its volume per capita for a certain term.
Growth rate = GNP1/GNP0 * 100%
GNP1 - gross national product of this year
GNP0 - gross national product of the base year – year with which comparison becomes
if average annual rate of a gain of GNP (ga) is known, that, knowing the GDP initial level (Y0) and using a formula of "difficult percent", it is possible to calculate size GDP through t of years (Yt):
Yt = Y0 (1 + ga)t
For the description of interrelation between quantity of the resources used in economy (expenses of factors of production), and volume of release the concept of production function which has an appearance is used:
Y = AF (L, K, H, N),
where Y – output;
F (...) – the function defining dependence of volume of production on values of expenses of factors of production; A – the variable depending on efficiency of production technologies and characterizing technological progress;
L – number of work;
K – quantity of the physical capital;
H – quantity of the human capital;
N – quantity of natural resources.
37 Factorsaffectingeconomicgrowth
1.Capital
The amount of labor and equipment is an indicator of the country’s supply of capital. The amount of capital in the economy is one factor that determines its rate of economic growth. For example, Belize is limited in its economic growth because of the country’s small population, whereas China’s large population enables a larger economic output by virtue of its sheer size. The standard hours in the work week also affects output: Populations that value long work weeks, such as the United States, tend to yield a greater output than nations with fewer hours in the work week, such as France.
