
- •In this lesson you learn
- •1. Read and translate the text. Text a
- •2. Answer the questions to the text.
- •3. Find the stem-words in the text to the given ones.
- •5. Complete the sentences using the vocabulary from the text.
- •6. Find terms in the text to the following definitions.
- •7. Answer the questions:
- •8. Communicative situation.
- •Look through text a, underline the verbs used in passive. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •Put the verbs in brackets into the correct passive form.
- •L ook at the information and write sentences as in the example.
- •1. Read and translate the text. Pay attention to the following words and word combinations. Text b
- •Various types of goods
- •2. Translate the following words and word combinations into Ukrainian.
- •3. A. Complete the sentences with the right expression from the text.
- •In this lesson you learn
- •1. Read and translate the text. Text a Packaging
- •2. Answer the questions to the text
- •3. Find in the text synonyms to the following words and word combinations.
- •4. Complete the sentences with a necessary word from the essential vocabulary.
- •5. Find in the text the terms described by following definitions.
- •6. A) Match each picture with the corresponding expression.
- •7. Translate the following types of containers into Ukrainian and match the following definitions with the right type of container.
- •8. Give the abbreviations for the following word combinations.
- •Part 2 Text b
- •1. Using essential vocabulary read and translate the text.
- •Insurance
- •6. Match the term with its definition.
- •7. Answer the questions to the text.
- •9. Comment on the following situation.
- •10. Speak about:
- •11. Annotate the text.
Look through text a, underline the verbs used in passive. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
Put the verbs in brackets into the correct passive form.
Making paper from trees
First, logs are cut (cut) into small pieces. Apart from trees, old paper … (may/use).
Then water and chemicals … (put) with the logs.
The materials … (mix) together.
Next, the mixture travels down a wire screen so that the water … (can/remove).
After that, the mixture … (flatten) by large rollers.
Finally, it … (dry). At last, the paper is ready … (use).
L ook at the information and write sentences as in the example.
Located: Edinburgh, Scotland
Known as: Holyrood Palace
Founded by: David I of Scotland
Founded in: 1128
Completed in: the 15th century
Made of: stone
Used as: the official residence of the Monarch of the United Kingdom in Scotland
Number of visitors: many thousand tourists every year
The Palace of Holyroodhouse is located in Edinburgh, Scotland. It …
PART 2
1. Read and translate the text. Pay attention to the following words and word combinations. Text b
Various types of goods
International exchanges involve the transport of a large variety of goods whose nature varies according to the economies of their countries of origin. Roughly speaking less developed countries (L.D.C.s) mostly export their produces and raw materials, while a large part of industrialized countries’ exports is made up of their products and manufactured goods – or “processed goods”.
Examples of the first categories of goods would be timber (construction wood) and logs (tree trunks) from African ports (which can even be carried to these ports from landlocked countries – without any coastline), ore, livestock (live animals, cattle), not to mention oil products – or – “petroleum products” – (mainly crude oil although refined oil represents a significant part of the traffic), and perishable goods such as bananas and tropical fruits.
Developed countries more readily export the output of their industries and agricultures: grain and in a more general way foodstuff – possibly processed –, chemicals (incl. NDC’s – Non Dangerous Chemicals), valuables of all sorts …
These goods are often classified in the shipping trade as “general cargo” – or “mixed cargo”, “break bulk cargo”.
A large part is even carried as dry cargo – or “bulk cargo” (not to be mistaken with “bulky” – or cumbersome - cargo) – when not packaged into units.
2. Translate the following words and word combinations into Ukrainian.
Cargo, to process, to carry, bulky cargo, bulk cargo, general cargo, output, industries, goods, perishable goods, valuables, traffic, to make up, trade, shipping trade, agriculture, to export, to package.
3. A. Complete the sentences with the right expression from the text.
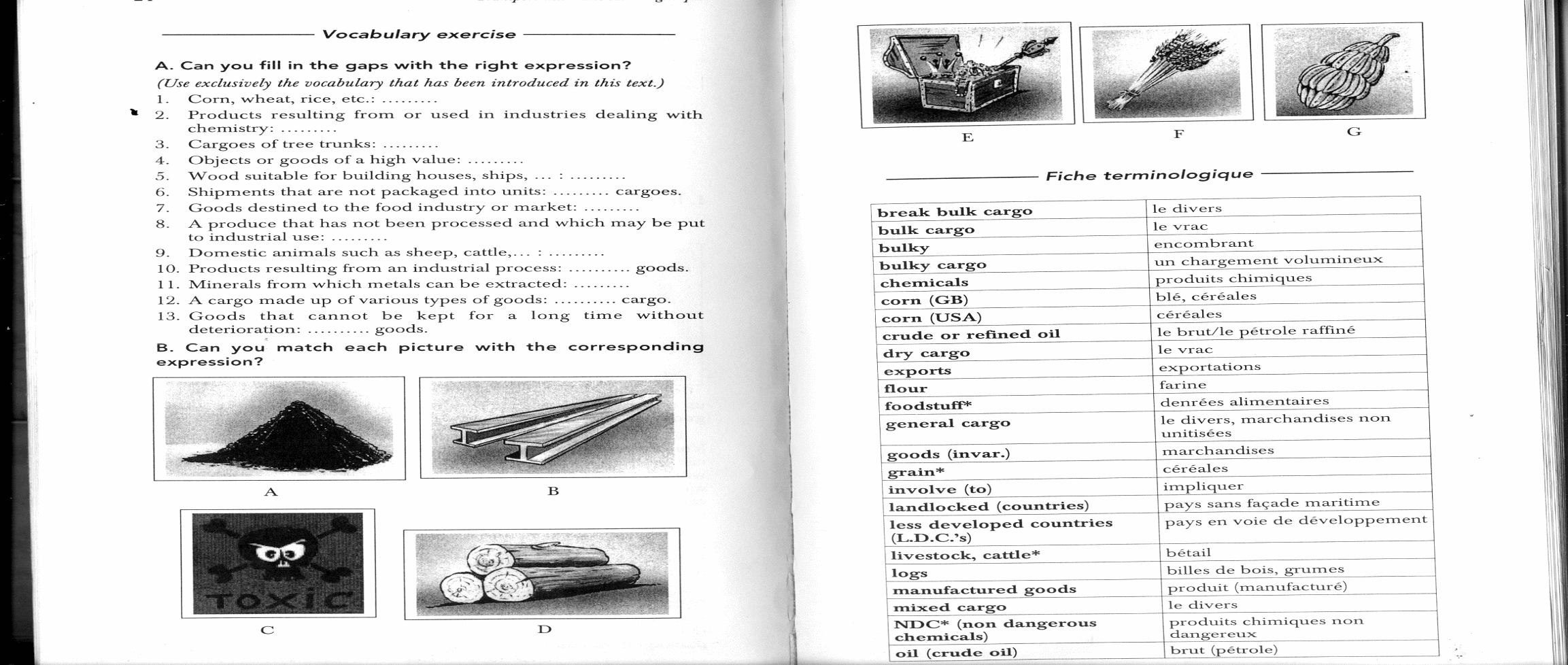
1. Corn, wheat, rice, etc.: …
2. Products resulting from or used in industries dealing with chemistry: …
3. Cargoes of tree trunks: …
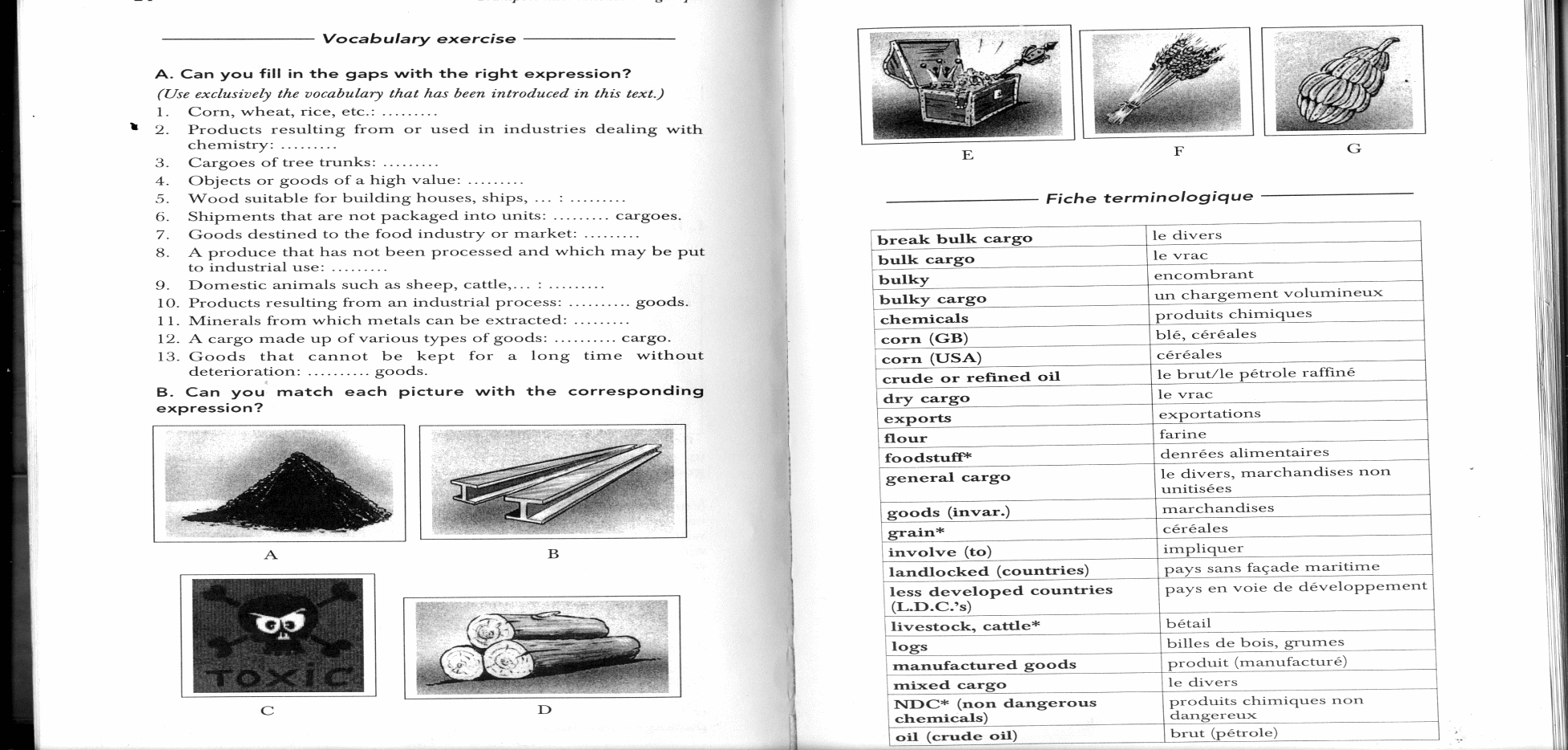
4. Objects or goods of a high value: …
5. Wood suitable for building house, ships, …: …
6. Shipments that are not packaged into units: … cargoes.
7. Goods destined to the food industry or market: …
8. A produce that has not been processed and which may be put to an industrial use: …
9. Domestic animals such as sheep, cattle, …: …
10. Products resulting from an industrial process: … goods.
11. Minerals from which metals can be extracted: …
12. A cargo made up of various types of goods: … cargo.
13. Goods that cannot be kept for a long time without deterioration: … goods.
B. Match the picture with the corresponding expression.
4. Define the following terms.
Cargo, bulky cargo, bulk cargo, general cargo, output, goods, perishable goods, valuables, traffic, trade
5. Answer the questions to the text.
1. What does the international trade involve?
2. What is L.D.C.s?
3. What do the L.D.C.s export?
4. What does the export of industrialized countries consist of?
5. Give the examples of produces.
6. How are called the goods to be transported?
7. Give the examples of perishable goods.
8. Give the examples of valuables.
6. Divide the text into logical parts and name each part.
7. Summarize the text in the possibly shortest way.
8. Write an annotation of the text.
Project work
Using the information provided in texts A, B and using the additional information speak about the transportation as a significant part of one of the stages of industry.
LESSON 2
