
- •Unit 1 the profession of an electrician
- •1. Learn the words
- •2. Make the word combinations.
- •3. Answer the questions.
- •4. What is electricity?
- •5. Did you know?..
- •6. Read the text, translate the words in bold.
- •Unit 2 electrical safety rules
- •1. Learn the words
- •2. Make the word combinations. 3. Find the odd word in each line.
- •4. Learn the safety rules.
- •5. Continue the safety rule.
- •6. Find the English equivalents in b to the Russian words in a.
- •7. Translate into English.
- •8. Read the text and translate it.
- •9. Answer the questions.
- •10. Write a memory card with safety rules for beginners who start working with electricity. Unit 3 electrical measuring instruments
- •1. Do you know
- •3. Make the word combinations.
- •4. Make the sentences out of the given words.
- •5. Learn the following information.
- •6. Answer the questions.
- •7 . Read the text. Translate the words in bold.
- •8. What are the rules of using the following measuring instruments?
- •Match the circuit symbols unit 4 electricity basics
- •Learn the following information.
- •Compare the series circuit and the parallel circuit.
- •Which ammeter correctly measures the current flowing through r1? r2?
- •Which ammeter correctly measures the total current?
- •If the Voltmeter reads 20 V and the ammeter reads 1a solve for the equivalent resistance Req.
- •Read the text.
- •Compare the two types of current.
- •L ook at the pictures and describe them.
- •Draw the scheme of distribution and delivery of electrical current to consumers.
- •Read the text eectrical generator
- •Unit 6 electrical installation work
- •1. Make up the word combinations. B)
- •2. Group the words.
- •3. Read and translate the text.
- •4. Learn the words. Top 12 Electrical Tools
- •5.Read the text and fill in the table. Tools Needed By Electricians
- •6. What work is an electrician doing in the pictures? What tools does he use?
- •7. Translate into English and make up the sentences with these words.
Compare the two types of current.
Voltage
In houses
Battery appliance
Need of high voltage
Direct Current
Alternating Current
L ook at the pictures and describe them.
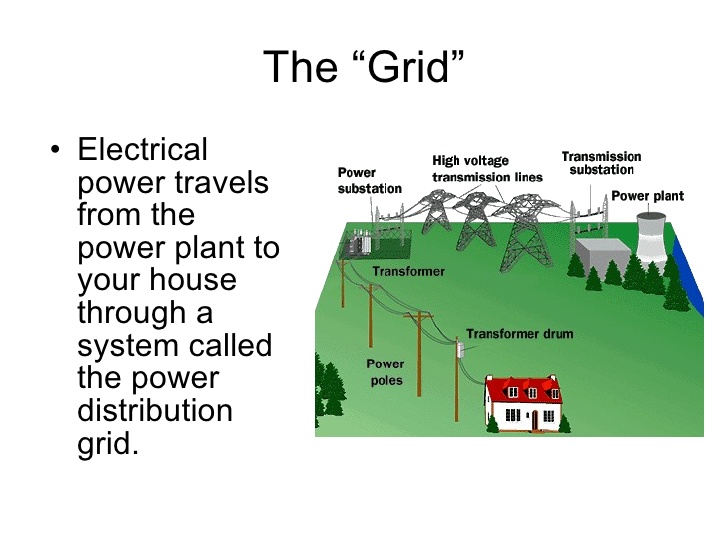
Power
station
Steps
up the voltage to 345 000 V
So
it can be transferred through power line
Area
Substation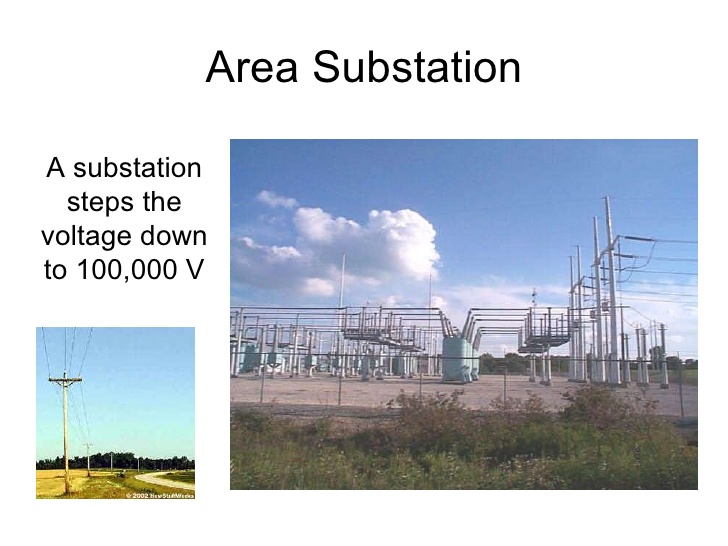
Why
not transfer electricity at a billion volts? 1)
Air is not a perfect insulator; 2)
At very high voltages arcs of “lightning” would shoot between
power lines and the ground; 3)
Safety. (Note: birds can land on a bare wire because they don’t
create a closed circuit)
Steps
the voltage down to 100 000 V
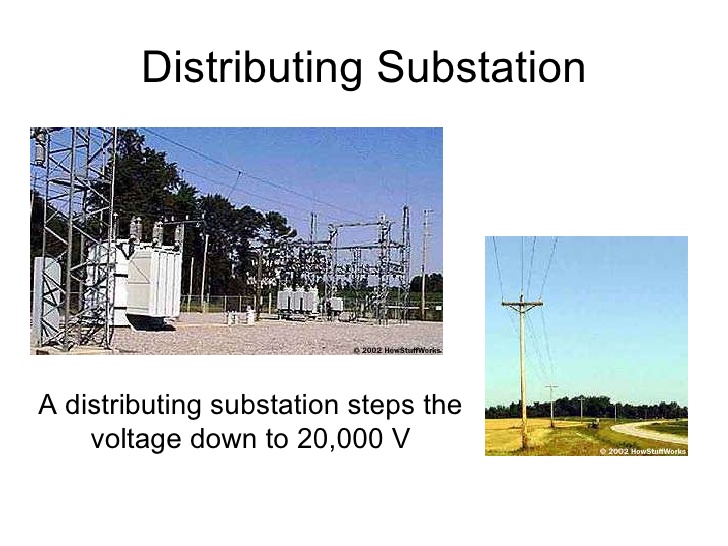
Steps
the voltage down to 20 000 V
Distibuting
Substation


Draw the scheme of distribution and delivery of electrical current to consumers.
Read the text eectrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy usually via electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction works by forcibly moving a loop of wire (a rotor) around a stationary bar (a stator) that provides an electric field, either through a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. By Faraday's law, this induces a current in the rotor, which can be used to power machinery or charge batteries. A generator forces electric current to flow through an external circuit. The source of mechanical energy may be a reciprocating or turbine steam engine, water falling through a turbine or waterwheel, an internal combustion engine, a wind turbine, a hand crank, compressed air, or any other source of mechanical energy. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.
The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and generators have many similarities. Many motors can be mechanically driven to generate electricity and frequently make acceptable generators.
The electrical generator was first invented by the Hungarian inventor and engineer Anyos Jedlik between 1827 and 1830. Jedlik invented the generator, a simple dynamo, at least six years before Warner von Siemens in Germany and Charles Wheatstone in Britain, whose names are usually associated with the device's invention. Though the electrical generator was invented around 1830, it wouldn't be until Nikola Tesla's pioneering work on rotating magnetic fields around 1882 that generators would become suitable for industrial use.
An electric generator or electric motor that uses field coils rather than permanent magnets requires a current to be present in the field coils for the device to be able to work. If the field coils are not powered, the rotor in a generator can spin without producing any usable electrical energy, while the rotor of a motor may not spin at all.
The field coils are connected in series or parallel with the armature winding. When the generator first starts to turn, the small amount of remanent magnetism present in the iron core provides a magnetic field to get it started, generating a small current in the armature. This flows through the field coils, creating a larger magnetic field which generates a larger armature current.
Very large power station generators often utilize a separate smaller generator to excite the field coils of the larger.
Three
Gorges Dam in China

a) Find in the text the English equivalents for Russian words.
1. поступательно-вращательный 8. подходящий 15. сокращать
2. горение твёрдого топлива 9. сходство 16. природоохранный
3. установленный 10. заставлять 17. возбуждать
4. вращаюшееся магнитное поле 11. рукоятка 18. вращаться
5. энергия солнца и ветра 12. сети 19. корпус
6. устройство 13. ядерный 20. железный стержень
7. превращать 14. возобновляемый 21. катушка магнитного
поля
b) Make up the sentences out of the given words.
1. electrical, mechanical, converts, energy, into, energy, A generator.
2. principles, on, generators, electrostatic, First, operated.
3. Michael, In, discovered, 1832, Faraday, of, the principle, generators, electromagnetic.
4. hydraulic, Hydro- generator, turbine, is, by, a, driven.
5. fuels, Today, mainly, generated, is, from, burning, electricity.
c) Translate the word conbinations.
Генератор постоянного тока, возбуждение постоянными магнитами, магнитное поле, преобразовать в электрическую энергию, три подвижных магнита и шесть катушек, для увеличения мощности, возобновляемые источники энергии, неподвижный корпус, заряжать батарею, установить генератор переменного тока, заставить железный стержень вращаться, ядерная электростанция, понижающая и повышающая подстанции, очень высокое напряжение, распределение и потребление энергии.
 d)
Answer the questions.
d)
Answer the questions.
1) What will happen if one bulb burns out in a series circuit? Why?
2) What are the main safety rules when you want to repair a socket?
3) What is necessary to force the generator to produce electrical current?
4) What is the difference between AC and DC?
5) How electrical current is delivered to consumers?
6) What are the two main types of circuit connections?
7) What electrical measuring instruments are used to work with electricity?
 8)
What causes the electrical shock?
8)
What causes the electrical shock?
e) The engineer is in the lab. Describe his duties at work using the following word combinations.
To work with, to test, to measure, to connect, to watch the indications, to check the type of the current, to turn on a switcher, insulated.
