
- •Мета навчання англійської мови на заочному відділенні
- •Вимоги на заліках та екзаменах
- •Мовний матеріал
- •Методичні вказівки
- •Scientific progress
- •Unit II
- •Man and biosphere
- •Unit III
- •Climatic forecast for the 21st century
- •Unit IV
- •Physical and chemical sciences
- •Unit VI
- •The periodic law
- •Unit VII
- •Changes in matter
- •Reference section Phonetical Rules
- •Irregular Verbs
- •Список використаної літератури
Unit VII
Grammar: 1.Countable/Uncountable Nouns
2. Prepositions
a) of time
b) of position and direction
c) other prepositions
3. Word Formation
Pre-reading exercises
Exercise I. Pronounce the following words:
matter /'mxtq/ – речовина
particular /pq 'tIkjVlq/ – певний
neutron /'njHtrPn/ – нейтрон
unique /jH 'nJk/ – єдиний, унікальний
evaporation /I "vxpq 'reISn/ – випаровування
mixture /'mIksCq/ – суміш
charge /CRG/ – заряд
Exercise II. Read the headline of the text. What do you know about three states of matter? What are they? How can we define them?
Reading
Read closely the text; divide it into several logical parts and think of a suitable headline for each part:
Changes in matter
There are three states of matter – solid, liquid, and gas. Each matter has its own distinct physical properties. Changes in the temperature of a particular type of matter can cause matter to change from one state to another. This type of change is called a physical change because only the physical properties of matter have been changed; its composition remains the same. Matter can also be changed chemically. A chemical change converts matter into a new substance. Chemical properties describe how a substance can react to form another substance.
All matters are made up of atoms which consist of a nucleus containing positively charged protons and neutrons that have no electrical charge. Negatively charged electrons travel around the nucleus. The chemical and physical properties of matter can be explained in terms of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Substances containing only one type of atom are called elements. A compound is formed when two or more elements are combined in a chemical reaction. Each compound has its own unique chemical and physical properties. A molecule is made up of two or more atoms. Molecules can be formed by atoms from different elements as well as some atoms from a single element.
Mixtures are composed of two or more substances; and each retains its physical properties. A chemical reaction does not occur when a mixture forms. Mixtures can be separated by physical means, such as evaporation, filtering or magnetism, into their components parts.
Text-based exercises
Exercise III. Give English equivalents for the following words and word combinations:
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
|
……………………… |
Exercise IV. Match the terms with the following definitions. Choose from gas, molecule, liquid, solid, neutron:
One of the three fundamental states of matter, in which matter is hard or firm, is called …………….
One of the constituent particles of every atomic nucleus except ordinary hydrogen is called ……………
Smallest identifiable unit into which a pure substance can be divided and retain its composition and chemical properties is called ………..
One of the three fundamental states of matter, in which matter has no definite shape and is very fluid, is called ……………...
One of the three principal states of matter that flows freely is called …………….
Exercise V. Answer the following questions to check your understanding of the text:
How many states of matter are there?
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
What type of change is called a physical change?
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
What can chemical properties describe?
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
When does a chemical reaction occur?
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
How can we separate mixtures?
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
Grammar exercises
Exercise VI. Which of the following nouns are countable and which are uncountable? Give the plural of the following nouns if possible:
|
|
Exercise VII. Insert the prepositions from the box below and translate the sentences:
Out on x 3 above for at over without from behind |
People walk on the pavements, buses and cars drive ……… the roads.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
They are sitting ……… the table.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
The sun is ……… the clouds.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
They come ……… the institute at three.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
During the break students go ……… of the room.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
The plane was flying ……… the clouds.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
There is a bridge ……… the river.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
I was going to leave home ……… the moment you came in.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
This is ……… you to decide.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
This is a book ……… the life of Newton.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
My friend return from London ……… the 12th of August.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
We cannot read technical texts ……… a dictionary.
…………………………………………………………………..………………….............
Exercise VIII. Form the adjectives using the suffixes – able, – al, – ent, – ive,– ful, –ous, – less, – ly. Translate the words:
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
|
………………………………... |
Speaking task
Exercise IX. Look at the Picture 5 and describe all the types of matter. Use the words below the pictures. Work in pairs, small groups or alone.
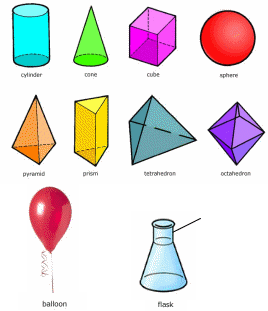
liquid
Picture 5. Different types of matter
