
- •Методичні рекомендації
- •Вступ до методичних рекомендацій
- •Unit 1 meeting a business partner
- •I. Language
- •Illustrative Dialogues
- •Translate the Ukrainian phrases into English.
- •Continue the dialogue:
- •II Reading.
- •In the office
- •III. Speaking.
- •IV. Listening.
- •V. Discussion.
- •Unit 2 oranazing a business meeting. Telephoning
- •I. Language
- •I llustrative Dialogues
- •II Reading.
- •III Speaking
- •IV Reading
- •Different ways of business communication
- •Ahbsc@cuatvm.Cuat.Edu
- •V. Writing
- •VI. Listening
- •Telephone techniques
- •VII. Discussion
- •Unit 3 my speciality
- •I. Language
- •II. Reading and comprehension.
- •My speciality
- •III. Language.
- •IV. Comprehension.
- •V. Speaking.
- •VI. Reading and comprehension.
- •Patents
- •VII. Language.
- •VIII. Comprehension.
- •IX. Speaking.
- •X. Listening.
- •Vocabulary:
- •Fiber Selection for fabric and Garment Design
- •Unit 4 standardization
- •I. Language
- •II. Reading and comprehension.
- •Standardization
- •III. Language.
- •IV. Comprehension.
- •V. Speaking.
- •VI. Reading and comprehension.
- •Open standard
- •VII. Language.
- •VIII. Comprehension.
- •IX. Speaking.
- •X. Writing.
- •De facto standard
- •Unit 5 certification
- •I. Language
- •II. Reading and comprehension.
- •Certification
- •III. Language.
- •IV. Comprehension.
- •V. Speaking.
- •VI. Reading and comprehension.
- •Product certification
- •VII. Language.
- •VIII. Comprehension.
- •IX. Speaking.
- •X. Writing.
- •Certification mark
- •Unit 6 business correspondence
- •Language
- •II Reading.
- •Business correspondence
- •The main parts of a business letter are:
- •Addressing an envelope
- •V. Writing.
- •Additional phrases Opening Phrases
- •Binding phrases
- •Closing phrases
- •Unit 7 quality control
- •I. Language
- •II. Reading and comprehension.
- •Quality control
- •III. Speaking.
- •IV. Reading and comprehension.
- •Total quality control
- •IV. Listening.
- •Silk means elegance
- •Unit 8 basic principles of metrology
- •I. Language
- •II. Reading and comprehension.
- •Metrology
- •III. Speaking.
- •IV. Reading and comprehension.
- •Historical Development of Metrology Standards
- •IV. Writing.
- •Industry-specific metrology standards
- •Unit 9 job hunting
- •II Reading
- •Job Hunting
- •III Language
- •IV Oral Practice
- •V. Reading and Comprehension
- •VI. Reading
- •VII. Oral Practice
- •VIII. Discussion
- •IX. Writing
- •Пример анкеты
- •Резюме (Resume)
- •Жизнеописание (Curriculum vitae (cv))
- •Unit 10 company structure
- •I. Language
- •II. Reading
- •Company structure
- •I nternational business styles
- •A department in charge of finding new ideas
- •A person in charge of a company
- •Список рекомендованої літератури:
II. Reading
Exercise 5. Read the text “Company structure”

Company structure
In business organization structure means the relationship between positions and people who hold the positions. Organization structure is very important because it provides an efficient work system as well as a system of communication.
Most companies are made up of three groups of people: the shareholders (who provide the capital), the management and the workforce.
The management structure of a typical company is shown in this organization chart.
At the top of the company hierarchy is the Board of Directors, headed by the Chairperson or President. The Board is responsible for policy decisions and strategy. It will usually appoint a Managing Director or Chief Executive Officer, who has to overall responsibility for the running of the business. Senior managers or company officers head the various departments or functions within the company, which may include the following:
Marketing
Sales
Public Relations
Information Technology or IT
Personnel or Human Resources
Finance
Production
Research and Development or R&D
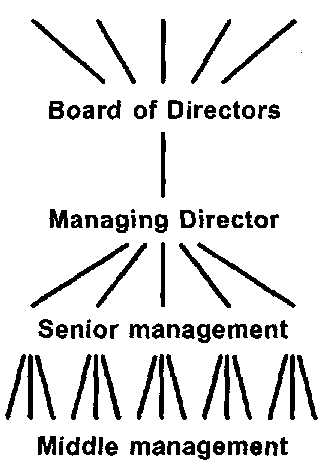
Historically, line structure is the oldest type of organization structure. The main idea of it is direct vertical relationship between the positions and tasks of each level, and the positions and tasks above and below each level. For example, a sales manager may be in a line position between a vice-president of marketing and a salesman. Thus a vice-president of marketing has direct authority over a salesman. This chain of command simplifies the problems of giving and taking orders.
W hen
a business grows in size and becomes more complex, there is a need
for specialists. In such a case administrators may organize staff
departments and add staff specialists
to do specific work. These
people are usually busy with services, they are not tied in with the
company product. The activities
of the staff departments include an accounting, personnel, credit and
advertising. Generally, they do not
give orders to other departments. Here
is an
example
of the organizational chart of the company:
hen
a business grows in size and becomes more complex, there is a need
for specialists. In such a case administrators may organize staff
departments and add staff specialists
to do specific work. These
people are usually busy with services, they are not tied in with the
company product. The activities
of the staff departments include an accounting, personnel, credit and
advertising. Generally, they do not
give orders to other departments. Here
is an
example
of the organizational chart of the company:
I nternational business styles
The characteristics of management often vary according to national culture, which can determine how managers are trained, how they lead people and how they approach their jobs.
The amount of responsibility of any individual in a company depends on the position that he or she occupies in its hierarchy. Managers, for example, are responsible for leading the people directly under them, who are called subordinates. To do this successfully, they must use their authority, which is the right to take decisions and give orders. Managers often delegate authority. This means that employees at lower levels in the company hierarchy can use their initiative that is make decisions without asking their manager.
Exercise 6. Say if the following statements are true or false:
1. Organization structure means the relationship between positions and people who hold the positions.
2. Most companies are made up of four groups of people.
3. The Board of Directors is at the top of the company hierarchy.
4. Managing Director has to overall responsibility for the running of the business.
5. Line structure is comparatively new type of organization structure.
6. Managers never delegate authority.
Exercise 7. Answer the questions:
Why is organization structure very important?
What is the Board responsible for?
What departments does usually a company include?
What is the main idea of the line structure?
What is a staff department?
What are managers responsible for?
Exercise 8. Describe the structure of the company according to the chart:



Exercise 9. Read the text describing company structure. Then choose the correct answer to the questions.
SBS stands for Siemens Business Services. It is a division of the famous German company Siemens. It is only about five years old but is already responsible for a considerable part of Siemens' turnover. How? Siemens had the idea in 1995.
A whole department of Siemens was at the time responsible for the information and communication activities of Siemens. The idea was to offer this service not only inside the company but outside too. SBS is now one of the world's leading providers in the area of electronic business solutions and services.
Friedrich Froeschi is the CEO and SBS is now an independent division with 33,000 employees in 88 countries and turnover of €5.8 billion. One of its largest customers is the British government.
SBS organizes and manages the passports and national savings accounts for Britain. In Europe its main competitors are IBM, Cap Gemini, and EDS. With growth in this marker of at least 15% the future looks bright for this German service company.
I.
1. What is the activity of SBS?
electronic engineering
printing
database management
2. Which company does Friedrich Froeschi manage?
Siemens Business Services
Siemens
IBM
3. One of its largest customers is:
a) EDS
b) SBS
c) the British government
4. €5.8 billion represents:
Siemens turnover
SBS's turnover
SBS's profit
5. SBS manages electronic services for:
IBM
British passports
88 countries
6. SBS is:
a branch of Siemens
a department of Siemens
a division of Siemens.
II.
Look at this list of words. Match pairs of words, as in the examples, to make the expressions defined below.
sales annual company development
office human research marketing
stock market resources managing
head parent director production
site public relations turnover
Example:
