
- •Пояснительная записка к программе курса «Деловой английский»
- •Тематический план
- •1. Etiquette. “nice to meet you!”
- •Practice the dialogues in pairs. Imagine you come from different countries. Take turns to be the host and the visitor.
- •Read what Sandee usually does on Mondays. Look at Sandee’s agenda for yesterday. Compare the information. Tell what she usually does on Mondays and what she did yesterday.
- •Fill in the blanks with the verbs in brackets in the past simple. Cat comes home!
- •In pairs, ask and answer questions about what you did yesterday.
- •2. Talking of the phone. Taking messages
- •Work in pars and discuss the questions.
- •Read these two calls and complete the notes.
- •Look at the phrases from the two phone calls. Does the person answering the call (a) or the person making the call (b) say them? Write a or b in the boxes. Translate the phrases in italics.
- •Work in pairs. Read the phone calls in Exercise 2 aloud. Take turns to be a and b.
- •Complete the phrases
- •3. Making arrangements by telephone
- •1. Work in pairs and discuss the questions
- •3. Read the call again. Find and and underline one or more pha phrases which:
- •5. Complete the expressions.
- •Write the time expressions in the calendar.
- •7. Give your answers to the following phrases.
- •8. Work in different pairs. Practise making arrangements on the phone. Use the diagram to help you. Take turns to be a and b.
- •4. Writing a business e-mail
- •8. Look up in a dictionary:
- •9. Complete the sentences with the following words.
- •10. A) Correct the sentences if they are wrong.
- •Put the verb into the correct form, present continuous or present simple.
- •5. Jobs in organization
- •1. Think about the people who work in your college/university, e.G. The teachers, the administrators. What are they responsible for? Who are they responsible to?
- •2. Read the text about some of the people in a film crew. Complete the diagram. The diagram is called an organization chart (or family tree). It shows the chain of command in an organization.
- •3. L ook at these phrases from the text. Use a dictionary to check any words you don’t know. Then write them in your language.
- •4. Complete the sentences (1-8) with a phrase from Exercise 3. Use each phrase only once.
- •Rockbridge International Corporate Organization
- •9. Work in pairs. Draw an arganigram of an organization you know, e.G. Your college or university. Explain it to another pair.
- •10. A) Ask Mark questions. Look at the answers before you write the questions.
- •3. In the text the articles and the verb to be are missing. Write a few similar sentences using the table.
- •5. Find the following information in the text about different forms of business organisation:
- •Vertical differentiation
- •6. Read the case study carefully, and answer the questions that follow. Power and influence
- •8. Use your dictionary to complete the chart to show the different forms of each word.
- •9. Writing.
- •10. Look at the examples and explain the differences between the sentences.
- •11. Underline the verbs in the Passive Voice; read and translate the sentences.
- •12. Complete the text with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •7. Parts of a company
- •1. Someone is giving a visitor a tour of a company. Read the text and underline the names of all the departments.
- •2. Match the names of the departments (1-9) with the phrases (a-I) to make a short description for each department.
- •8. Choose the right modal verb.
- •9. Read the rules about traveling by plane. Fill in the blanks. Use the words below.
- •10. Each company possesses its own regulations. Match the jobs with the company regulations.
- •13. The sales manager of a small plastics company has some problems.
- •Indonesia
- •Management
- •1) Read the article. What are the good traits of a manager?
- •6. Before a meeting a manager should write a memo informing about the staff about the main points of the meeting. Read the information about what a memorandum is.
- •7. Here are some rules of things to do before a meeting. Read the rules and the memo below. Tick the rules that the memo follows.
- •8. Match the words and phrases from the e-mail (1-7) with the definitions (a-g).
- •9. Write a memo to tell the class about the meeting. Include the following information:
- •9. Translate the following sentences. What are the words in bold?
- •9 . Live to work or work to live?
- •5. Which of the jobs in Ex. 2 would you most like to have? Which would you least like to have? Why?
- •6. Match each job with its description.
- •8. What are the prepositions or other words used with the following expressions?
- •9. Write about a job you would like , or would not like to have.
- •10. Complete the dialogues.
- •11. Use modal verbs or their equivalents.
- •12. Make questions with have to do smth
- •Read the table and complete the sentences with the verbs from the box.
- •10. Applying for a job
- •8. What is expected of the Sales Manager/ Personnel Manager/ Marketing Manager? List all the requirements to the person holding this position.
- •9. This draft letter of application is not suitable. Rewrite it using some of the expressions from the box, and making any other necessary changes.
- •10. Read the passage below about how to prepare for a job interview.
- •11. You want to apply for the job in the advertisement below. Make a list of your personal qualities. Invent experience that would be useful for the job. Write a letter applying for the job.
- •12. Match two parts of the sentences and translate them.
- •13. Complete and read out the dialogues.
- •14. Match these sentence halves.
- •15. Rewrite if the sentences are not correct (remember about the “state verbs”!).
- •16. Put the verbs in brackets in the correct past tense. Anita Roddick: a Businesswoman with a Vision
- •11. Writing a carriculum vitae.
- •1 . When applying for a job, applicants are required to produce a resume. List tree things you need to include in it.
- •2. Read the sections of a cv (a-h) and match them with the headings (1-8).
- •3. Complete (1-5) with the highlighted words.
- •4. Tick (√) the items you would state in your cv.
- •7. Read and translate the letter.
- •8. Here are the questions most often asked by employers during interviews when hiring college graduates. Answer them to produce a favorable impression.
- •9. You are the Human Resources Manager. Take an interview from an applicant. Would you hire him/her? Why?
- •10. Open the brackets using the verbs in Present Perfect.
- •11. Complete the dialogues.
- •12. Three business people were asked about their experiences. Look at the table; then answer the questions.
- •13. Now read about other people's experiences, and make questions for the answers.
- •14. The phrases below all include the word career. Match them to their correct meanings.
- •15. Complete the sentences with the verbs form the box.
- •16. Look at the groups of words below. Cross out the noun or noun phrase which doesn't go with the verb in each group.
- •12. What is marketing?
- •1. What is marketing? Why is it important?
- •2. “The four Ps” form the basis of the marketing mix. If you want to market a product successfully, you need to get this mix right. Match “Ps” (1-4) to the definitions (a-d).
- •3. Read this article about marketing. Match the questions (1-16) with the paragraphs (a-f).
- •4. Match the highlighted words and phrases in the text with the definitions (1-8)
- •7. Choose a well-known product for each of these product categories.
- •14. Put the words in the questions in the correct order.
- •15. Use the verbs in Present Perfect Continuous.
- •16. Use the verbs in Past Perfect Continuous.
- •13. International trade
- •1. Think of things that you have in your home or school, e.G. A fridge, a tv, a computer. What are the names of the companies that made them?
- •2. Read the text and correct the statements below.
- •3. Match the highlighted words and phrases in the taxt with the definitions (1-8).
- •12. Complete the text with the best word. The life cycle of a product
- •13. Match the following sentence halves. Underline the passive forms.
- •14. Make the sentences passive.
- •14. Advertising and promotion
- •1. There are different ways of advertising: newspaper/magazine ad direct mail, tv, website ad, posters. Answer the questions:
- •2. Which way (or ways) of advertising do you think is most suitable for these situations?
- •3. Read the business advice information. Match the questions (1-4) with the paragraphs (a-d).
- •4. Find the words or phrases in the advertisements which match the definitions below.
- •Is so user-friendly
- •Ideal for the
- •Is compact and
- •9. Make the adjectives negative by adding the correct prefix from the box.
- •10. Complete each sentence with the negative form of one of the three adjectives.
- •11. Open the brackets, read and translate the sentences.
- •12. Match the sentence halves.
- •13. Complete the sentences with 'll, 'd, won't or wouldn't.
- •14. Complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •15. Brands
- •1. What famous brands do you know and what do they sell?
- •2. Read Parts a and b quickly. Does the text come from an e-mail, a newspaper article or an advertisement?
- •3. Read the text again and answer the questions.
- •4. Match the words or phrases from the article (1-6) with the definitions (a-f). Then write the words and phrases in your language.
- •5. Read the text below about launching a new product. In each line there is one wrong word. For each line, write the correct word in the space provided.
- •11. Put the words in order to make the sentences of a reported dialogue.
- •12. Check your answers to ex. 9 Then complete the sentences with the actual words spoken.
- •13. Find and correct the mistakes in three of these sentences.
- •14. Look at these examples. Then report the other four questions in the same way.
- •Самостоятельная подготовка к занятиям курса
- •Примерные вопросы к зачету.
- •Библиография
- •Increased Efficiency of Trading Globally
- •Top 4 Mistakes That Cause Futures Traders To Fail
- •Stress management
- •Why "Blink" Matters: The Power of First Impressions
- •Spice Up Your Company Meeting: Ten Tips for Planning and Success
3. In the text the articles and the verb to be are missing. Write a few similar sentences using the table.
e.g. A company is an organization operating to make profit.
4. Point out the sentences with the construction there is/there are and the verbs in the Passive Voice. Translate them.
5. Find the following information in the text about different forms of business organisation:
a) What do business organizations consist of?
b) Tell about 2 ways that a company can organize itself. Give examples.
c) What is the difference between a “tall” and a “flat” company? What kind is easier to manage? What company are senior managers more likely to experience job satisfaction in? What about junior managers?
There are many forms of business organisation. Some businesses consist of just one person. While others employ thousands of people. Some businesses make products, while others are involved in providing services. Despite these differences, all business organisations consist of:
A group of people who form a structure
The structure has rules and authority
It follows a set of objectives
It uses economic resources
Companies can be differentiated in two ways: there is horizontal differentiation and vertical one.
Horizontal differentiation refers to the way in which a company’s activities are divided into distinct units. These are the most popular forms of horizontal differentiation:
O

 rganisation
by function. e.g. the top management
of a computer company decide that the company should be structured
according to the functions it performs – research and development,
manufacturing, marketing, and finance:
rganisation
by function. e.g. the top management
of a computer company decide that the company should be structured
according to the functions it performs – research and development,
manufacturing, marketing, and finance:
Research and Finance Manufacturing Marketing
development
O rganisation by product. e.g. The computer company makes two kinds of products, hardware and software. Top management thinks that these products are so different to each other that it is better to organize the company on the basis of the different products it makes.

Hardware Software
Organisation by location. An alternative to structure the company on the basis of location. e.g. The headquarters are in London, but the company has offices around the world.
Organisation by customer. e.g. The company sells its products to business users and consumers.
Vertical differentiation
This term refers to the number of management levels in a company. A company with many levels is known as a “tall” company. There are many levels in the hierarchy, because there are many different production processes, like in government bureaucracies and military organizations. This kind of organization is difficult to control, and the lower levels usually have to obey very precise rules, rather than plan their own work. A company with very few management levels is known as a “flat” organization. A company like this usually has a Chief Executive, one management level, and a number of supervisors in charge of ordinary employees.
Vertical differentiation
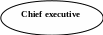
Finance director Marketing director Production director
Senior management Senior management Senior management
Finance department Sales department Production department
manager manager manager
Junior managers Area sales managers Junior managers
Finance department Sales force Production work force
Vocabulary
Consist of – состоять из
(be) involved in – быть вовлеченным в
Provide - обеспечивать
Authority - власть
Follow - следовать
Objective - цель
Differentiation – различение, различие
Refer to – относиться к (чему-л)
Divide into – делиться на
Unit - часть
Perform - выполнять
According to – в соответствии с
Research - исследование
Location – положение, местоположение
Headquarter – штаб-квартира, головной офис
Level - уровень
Obey rules – соблюдать правила
Employ (v) нанимать
Employee – служащий, работающий по найму
