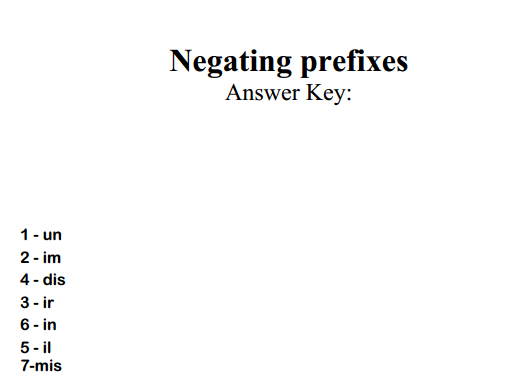- •1.The content of foreign language teaching Components assigned to the teaching of foreign languages in primary schools
- •2. The aims of foreign language teaching;
- •3. Resources for Foreign Language teaching
- •4. The principals of Foreign Language Teaching
- •5. Methods and techniques in Foreign Language Teaching
- •6. The content of teaching phonetics. Teaching phonetics
- •Techniques for teaching phonetics
- •7. Requirements for selection of phonetic material:
- •Types of drill:
- •Types of reproduction exercises:
- •11. Board game
- •10. Methods of teaching vocabulary: translation, synonyms, antonyms.
- •Syns and Ants
- •11. Methods of teaching vocabulary: the use of visibility, word formation.
- •Teaching with flashcards
- •Flash cards are images on cards, used to help to remember new vocabulary in a new language.
- •The benefits of flashcards:
- •Types of
- •12. Methods of teaching vocabulary: a description of a word in English language, context.
- •13. Types of exercises in teaching vocabulary.
- •The learners have to match words/pictures with definitions.
- •The importance of grammar in teaching a foreign language
- •Student's difficulties in learning English grammar
- •1. Word order.
- •Methods of teaching grammar
- •Principles of teaching English grammar
- •Types of exercise for learning English grammar
- •The content of teaching listening. The most common difficulties in listening comprehension
- •Reasons for listening:
- •To get the gist.
- •Purposes for teaching listening:
- •The processes of listening comprehension: bottom-up and top-down
- •Types of listening:
- •Principles of teaching listening:
- •Difficulties in listening comprehension
- •Resources for teaching listening
- •Live speech (teacher’s speech (another teacher or guest’s speech), face–to-face interaction of learners in interviews, dialogues, etc.) Teacher should:
- •3. Video materials:
- •Methods of teaching listening
- •Types of exercises in teaching listening
- •Interviews
- •To train learners’ oral speech:
- •2. To stimulate learners to master English language and culture
- •3. To stimulate learners to think in English.
- •Learners’ difficulties with speaking:
- •Methods of teaching speaking
- •Types of exercises in teaching speaking
- •Problems with speaking activities
- •The content of teaching reading
- •Reasons for reading:
- •Kinds of reading:
- •Types of texts for reading:
- •Reading skills:
- •Reading principals:
- •Difficulties in reading:
- •Ways of reading:
- •Methods of teaching reading
- •There are three stages of the Communicative method in teaching reading:
- •Types of exercises in teaching reading The aims of reading exercises:
- •Types of exercises in teaching reading
- •Some examples of tasks:
- •The content of teaching writing
- •Reasons for writing:
- •The purposes for teaching writing:
- •Learners need to develop writing skills:
- •Writing involves subskills: accuracy and fluency.
- •Problems:
- •Connected penmanship of small letters.
- •Principles of teaching writing:
- •Methods of teaching writing
- •Teaching penmanship and spelling has some stages:
- •Writing compositions have three stages:
- •3. Post writing stage:
- •Types of exercises in teaching writing
- •Skill building exercises: The aims:
- •1. Copying.
- •2. Exercises on penmanship, spelling and punctuation.
- •Guided and Free writing exercises: The aims:
- •A descriptive paragraph about a text, or a number of texts on a certain subject.
- •An annotation on the text read.
- •In testing learners’ skills in writing the teacher should:
- •Tasks of thematic-calendar planning:
- •Lesson planning
- •The reasons of lesson planning: For teachers
- •For learners
- •Problems
- •The content of lesson planning The content of lesson planning includes the solution of the following tasks:
- •Requirements for lesson planning
- •1. Stages of the lesson
- •1. Preparation
- •2. Presentation/Modeling
- •3. Practice
- •4. Evaluation
- •5. Expansion
- •2.Ways to organize English lessons
- •3. How To Prepare a "Successful" Lesson!
- •5. The Plan of analysis of a lesson
- •6. The plan of self-analysis of a lesson.
- •7. The content (содержание) of teaching of primary school pupils
- •8. The content of teaching of preschoolers
- •1 . Sequence.(последовательность) The teacher doesn’t have to hurry to train the child in of spelling and grammar.
- •2 . Naturalness (естественность). The child doesn’t have to feel any excess loading (лишний груз).
- •3 . Persistence (настойчивость). The teacher has to interrupt studies for a while, and then to continue training, but already with other material.
- •1. The content of Foreign Language Teaching.
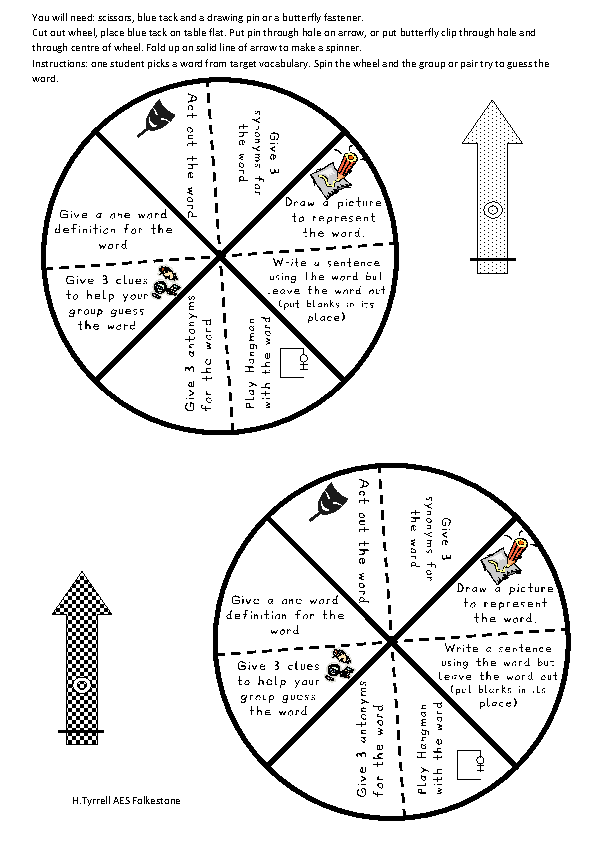
11. Board game
Board games are used for teaching pronunciation in pairs or small groups. They teach not only pronunciation but also learner interaction.
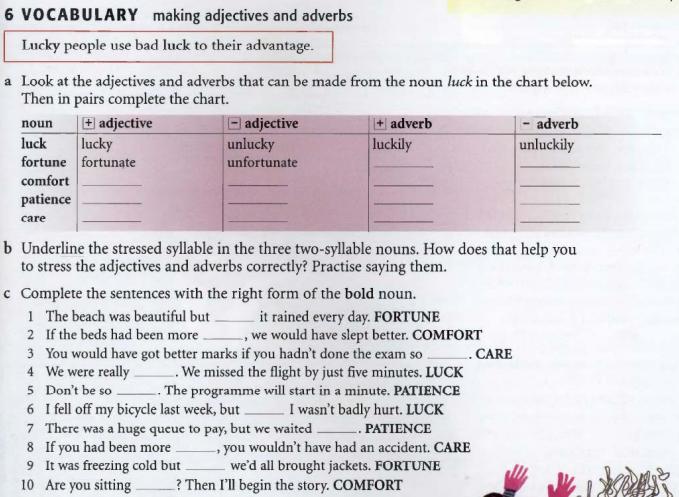
9. The content of teaching vocabulary

1. Grammar
2. Lexis
3. Phonology
5. Reading
6. Writing
7. Listening
8. Speaking






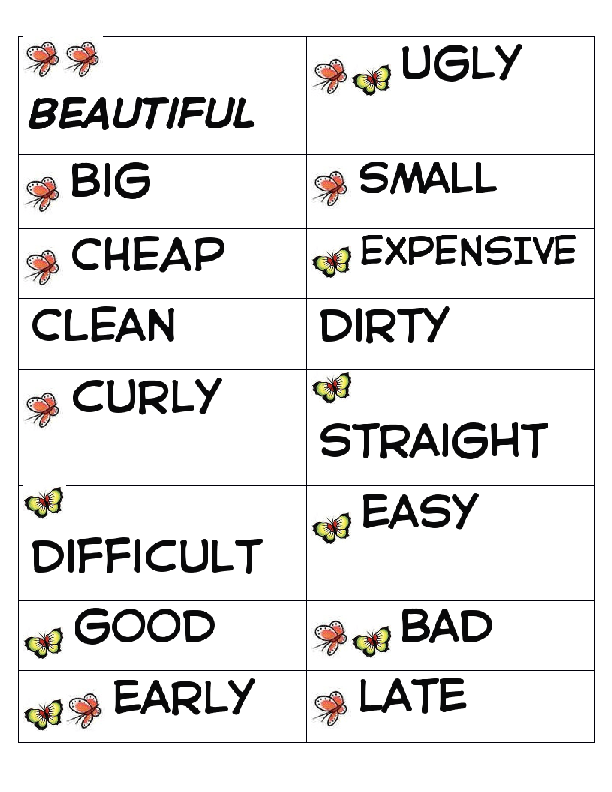
10. Methods of teaching vocabulary: translation, synonyms, antonyms.



![]()
Syns and Ants
By Mark Tuohy Age Range: 7 to 11
A teacher prepares about 20 cards beforehand each having a headword followed by a list of between 5 to 8 synonyms or antonyms in order of difficulty (1 easy, 5 harder, etc).
Children are split into teams and then the teacher writes the headword on the board and tells them to give a synonym or an antonym. Each group has a guess and if their guess is one of the words on the card they get the point value of that word.
The team at the end of the game with most points wins.



11. Methods of teaching vocabulary: the use of visibility, word formation.
Teaching with flashcards
Flash cards are images on cards, used to help to remember new vocabulary in a new language.
The benefits of flashcards:
- bring images of reality
- interesting and funny activity
- helps SS to remember new vocabulary in a new language instead of simply reading the definition in a dictionary, as the student can SEE what the word means.
- motivate and draw learners’ attention
- involve SS producing and revising vocabulary quickly
- useful for various types of activities (drilling, comparing, etc.)
- develop speaking, writing and other skills
- flexibility ( flashcards are easily kept)
-- come in a variety of formats and styles. When the collection of pictures is once made, it can serve for a long time.
- It is important to combine them with other techniques and different types of stimuli (movement, verbal stimuli, sound, etc). Moreover, pictures used for demonstration of the meaning should be repeatedly connected with the spoken and subsequently also written form of the word.
- The presentation of vocabulary with flashcards can be done in lots of
various ways, for example in telling a story or just simply based on
a set of vocabulary for a particular topic.
The presentation of vocabulary with flashcards can be done in lots of
various ways, for example in telling a story or just simply based on
a set of vocabulary for a particular topic.
Types of
Large: useful for whole-class work
Small: useful for group-work, games and other group-work activities
A new word flashcard
- A single picture
- several pictures if students don’t get the correct idea about what aspect of the picture the teacher had in mind. (E.g. to teach the phrase ‘to be horrified’, the teacher could show three pictures of people horrified by different things).
Big flashcards
- suitable for vocabulary practice and testing. The teacher just flashes the cards quickly and students guess or describe what they saw.
W ord
flashcards
ord
flashcards
- typically used in teaching reading and writing
- used in teaching vocabulary too (in teaching the spelling of newly learnt words)
Small picture flashcards
-used in reviewing and practicing vocabulary (one-side-only cards, both-sided ones and sets of pairs (antonyms or synonyms, a picture and the corresponding word or phrase) or sets of cards connected e.g. by their meaning)
- used in games (“domino”)
- used in matching activities
- used in creating story
- used for asking each other questions
- used in individual practice of vocabulary, e.g. looking at a picture and guessing the meaning written on the other side.

Drawing