- •What is the uml?
- •2. What are ways of using uml
- •Describe uml diagrams.
- •4. How to fit the uml into development process?
- •Notes and comments, constraint rules, keywords on uml diagrams: definitions, description, examples.
- •6. Main elements of class diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •7. Attributes and operations on class diagram: definitions,
- •Visibility name (parameter-list) : return-type {property-string}
- •8. Relationships between classes: definitions, description, examples.
- •9. Interfaces and abstract classes on class diagram:
- •10. Main elements of sequence diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •11. Creating and deleting participants, synchronous and asynchronous calls on sequence diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •12. Loops and conditionals on sequence diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •13. Main elements of object diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •14. Main elements of package diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •15. How to show aspects on package diagram: definition, description, example.
- •16. Main elements of deployment diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •17. Main elements of use case diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •18. Levels of use cases on use case diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •19. Relationships between use cases: definitions, description, examples.
- •20. Main elements of state machine diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •21. Internal activities, activity states, superstates, concurrent states: definitions, description, examples.
- •22. Main elements of activity diagram: definitions, des, examples.
- •23. Decomposing an action on activity diagram: definition, description, example.
- •24. Partitions, expansion regions, flow final, join specifications: definitions, description, examples
- •25. Main elements of communication diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •26. Composite structures: definition, description, example.
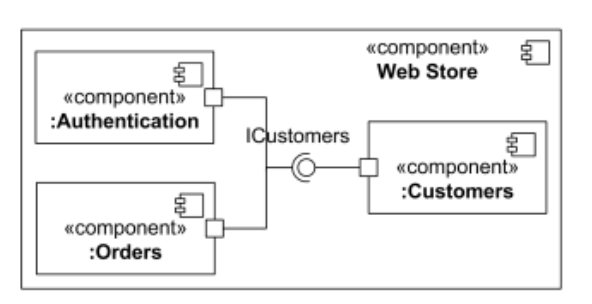
- •27. Main elements of component diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •28. Collaborations: definition, description, example.
- •29. Main elements of interaction overview diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •30. Main elements of timing diagram: definitions, description, examples.
- •Uml: Exam questions
- •What is the uml?
25. Main elements of communication diagram: definitions, description, examples.
Communication diagrams, a kind of interaction diagram, emphasize the data links between the various participants in the interaction. Instead of drawing each participant as a lifeline and showing the sequence of messages by vertical direction as the sequence diagrams does, the communication diagram allows free placement of participants, allows you to draw links to show how the participants connect, and use numbering to show the sequence of messages.
Figure 1 shows a communication diagram for the same centralized control interaction as in Figure 2. With a communication diagram, we can show how the participants are linked together.
As well as showing links that are instances of associations, we can also show transient links, which arise only the context of the interaction. In this case, the «local» link from Order to Product is a local variable; other transient links are «parameter» and «global».
Figure
1. Communication diagram for centralized control
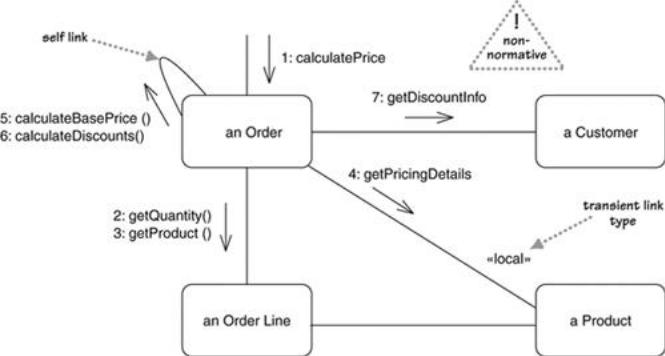
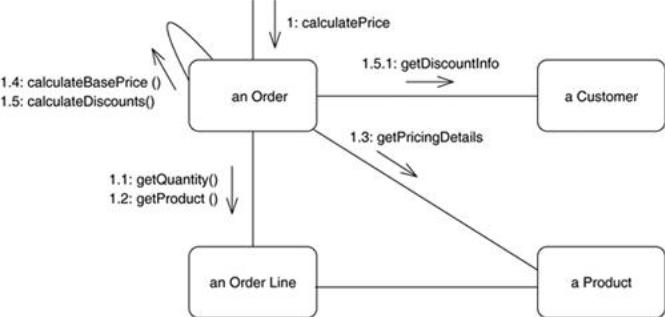
Figure 2. Communication diagram with nested decimal numbering
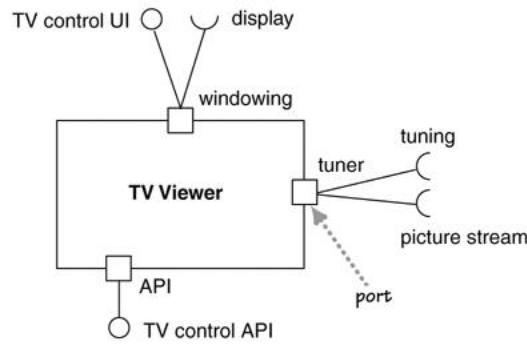
26. Composite structures: definition, description, example.
Def: Composite structure diagram visualizes the internal structure of a class or collaboration. It is a kind of component diagram mainly used in modeling a
system at micro point-of-view.
Descr: We can use the composite structure diagram to show the internal details of a classifier and to describe the objects and roles that work together to perform the behavior of the containing classifier.
We can add ports to the external structure. Ports allow you to group the required and
provided interfaces into logical interactions that a component has with the outside world
Parts In composite structure diagrams, a part is a diagram element that represents a set of one or more instances that a containing structured classifier owns. A part describes the role of an instance in a classifier. You can create parts in the structure compartment of a classifier, and in several UML diagrams such as composite structure, class, object, component, deployment, and package diagrams.
Ports In composite structure diagrams, a port defines the interaction point between a classifier instance and its environment or between the behavior of the classifier and its internal parts.
Example:
27. Main elements of component diagram: definitions, description, examples.
Def: Component diagram shows the physical aspect of an object-oriented software system. It illustrates the architectures of the software components and
dependencies between them.
Des:
Components are connected through implemented and required interfaces.
The important point is that components represent pieces that are independently purchasable and upgradeable. As a result, dividing a system into components is as much a marketing decision as it is a technical decision, for which is an excellent guide.
Use component diagrams when you are dividing your system into components and want to show their interrelationships through interfaces or the breakdown of components into a lower-level structure.
Example: