- •Physical properties Scandium subgroup
- •Titanium subgroup
- •Vanadium subgroup
- •Scandium subgroup
- •Vanadium Subgroup
- •Preparation
- •Vanadium Subgroup
- •Chemical Properties Scandium subgroup elements, iiib
- •Compounds
- •Titanium subgroup elements, ivb
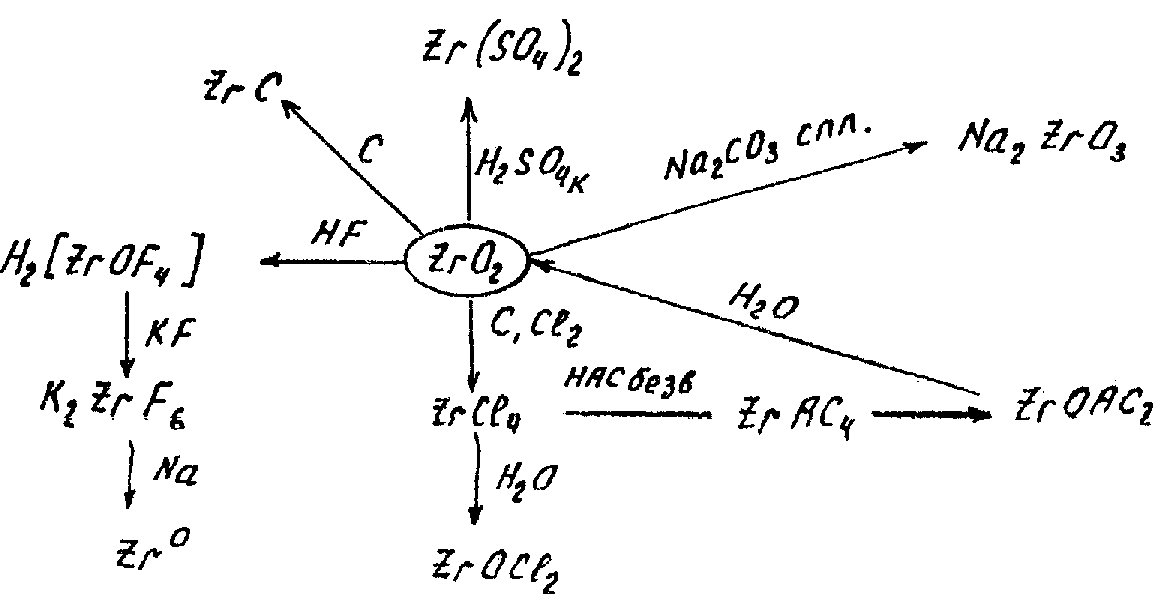
- •In the series TiO2—ZrO2— HfO2 acid properties are weakened and basic properties are increased.
- •Themes for home preparation
- •Carbides and nitrides of titanium and zirconium. Application of titanium, zirconium, hafnium and their compounds Questions and tasks
- •Make the equations o f the reaction
- •Experimental section
- •2. Chemical properties of titanium
In the series TiO2—ZrO2— HfO2 acid properties are weakened and basic properties are increased.
For instance,
TiО2 + 2KOH = K2TiO3 + H2O (acid properties predominate)
TiО2 + 2H2SO4 = TiOSO4 + H2O
TiО2+ - titanil, ZrO2+ - zirconil, and HfO2+ - hafnil are formed.
When melting: TiO2 + 2NaHSO4 = TiOSO4 + Na2SO4 + H2O
TiO2 + Na2S2O7 = TiOSO4 + Na2SO4 (pyrosulfate)
The preparation method of hydroxides is double replacement reaction, for instance:
EСl4 + 4NaOH = E(OH)4 + 4NaCl
Hydroxides Е(ОН)4 are compounds of nonstoichiometric composition ЕО2.nH2O. Ortho-titanic (-titanic) H4TiO4 (Ti(OH)4), and more inert meta-titanic(-titanic) H2TiO3 are known.
-titanic acid can be obtained:
TiCl4 + 4KOH = Ti(OH)4 + KCl
TiCl4 + 2K2CO3 + 2H2O = Ti(OH)4 + 2CO2 + 4KCl
-titanic acid is formed at:
H4TiO4 = H2TiO3 + H2O
TiCl4 + 2(NH4)2S + 3H2O = H2TiO3 + 4NH4Cl + 2H2S
and high temperature hydrolysis TiCl4:
TiCl4 + H2O = TiOCl2 + HCl
TiOCl2 + H2O = TiO(OH)2 + HCl
Oxo titanium (IV) salts exist in aqueous solutions:
ТіОSO4 + 2NaOH ТіО(ОН)2 + Na2SO4
ТіО(ОН)2 + 2HCl ТіОCl2 + 2H2O
H4TiO4 and H2TiO3 are very weak acids. Freshly precipitated compounds (-acid) contain significant content of ОН-groups and more reactive, than aged precipitates (-acid):
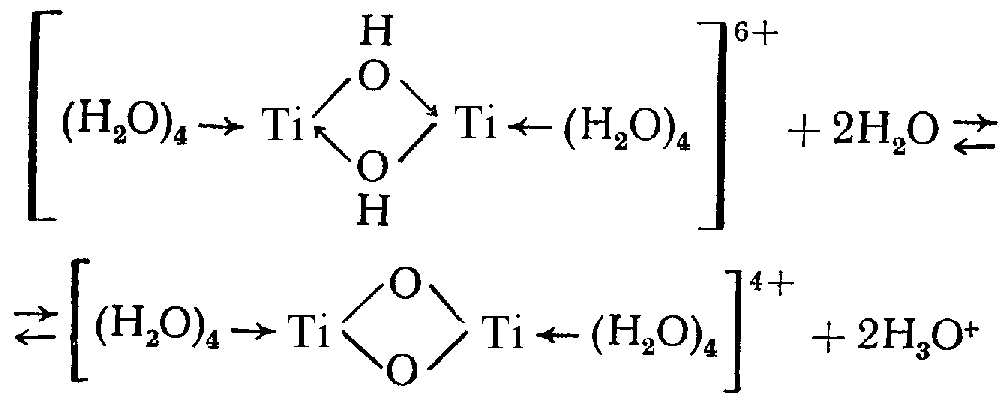
where Ti/ОН\Ti groups are displaced with Ti/О\Ti groups.
Amphoteric -zirconic acid ZrO2.xH2O (x > 1) can be obtained by the reaction:
ZrCl4 + 4NaOH(cold) = Zr(OH)4 + 4NaCl
-zirconic acid ZrO(OH)2 can be prepared:
Zr(OH)4 = ZrO(OH)2 + H2O
ZrCl4 + 4NaOH(hot) = ZrO(OH)2 + 4NaCl + H2O
When melting:
ZrO2 + 2KOH = K2ZrO3 + H2O (metazirconates)
ZrO2 + 4KOH = K4ZrO4 + 2H2O (orthozirconates)
Hf(OH)4 can be prepared by the hydrolysis reaction:
HfCl4 + 4NH4OH = Hf(OH)4 + 4NH4Cl
In the series Ti(OH)4—Zr(OH)4—Hf(OH)4 basic properties are strengthened.
Oxosalts are polymers where acid residues are situated between chains –O—Ti—O– as follows:
![]()
Oxosalts hydrolyse reversibly in aqeous solutions. Hydrolysis can be suppressed with the addition of an acid:
TiOCl2 + 2H2O TiO(OH)2 + 2HCl.
Hydrated ions Ti4+, Zr4+, Hf4+ don’t exist due to high charge. Therefore, soluble derivative of them hydrolyses strongly and irreversibly:
ЕСl4 + H2O = ЕOCl2 + 2HCl
Ті(SO4)2 + H2O ТіOSO4 + H2SO4.
Titanil and zirconil salts are stable in acid environment, when medium is neutral ortho- (H4ЕO4) and meta- (Н2ЕО3) acids are formed:
TiOSO4 + 2H2O = H2TiO3 + H2SO4
Peroxocompounds [Ti(O2)ОН]+, [Zr(O2)ОН]+ are formed under the action of Н2О2 on solutions containing ТіО2+ / ZrО2+. Peroxocomplex [Ti(O2)ОН]+ is of bright yellow colour. This fact is used in chemical analysis to detect Ti.
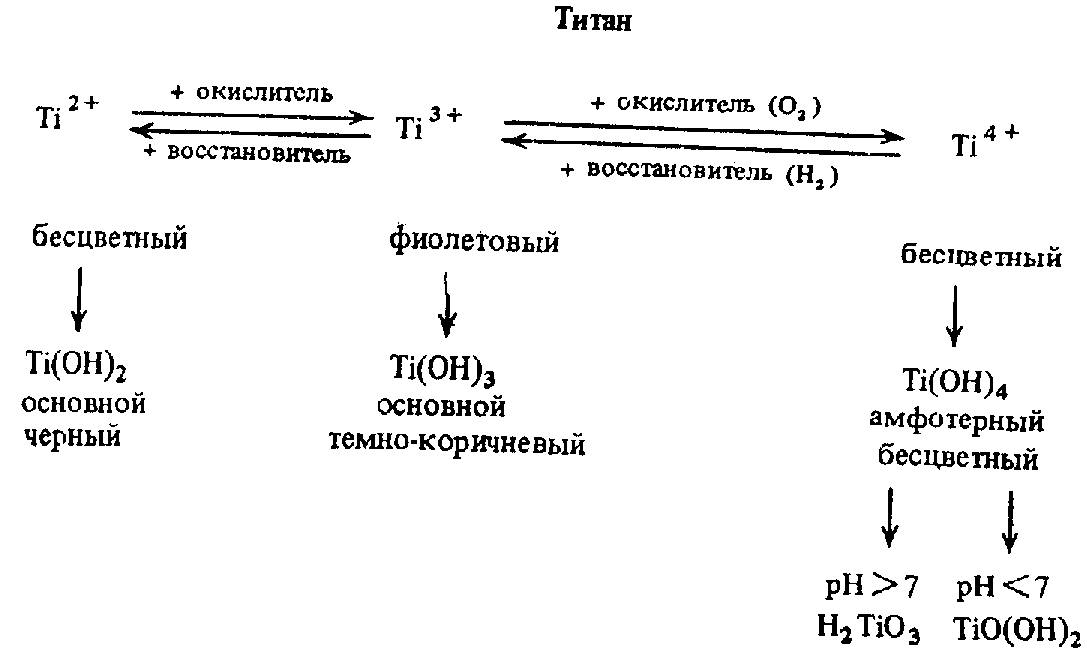
COMPOUNDS Ti(III). Oxidation state+3 is distinctive in case of Ti only; compounds of Zr3+, Hf3+ are less stable.
Ti(III) compounds preparation reactions are:
2TiO2 + H2 = Ti2O3 + H2O
2TiCl4 + H2 = 2TiCl3 + 2HCl
оr dissolution of metallic titanium in acids (HCl, diluted H2SO4, and HF):
2Ti + 6HF = 2TiF3 + 3H2
Ti3+ (aq) compounds can usually be synthesized by Ti4+(aq) reduction using hydrogen at the moment of liberation:
2TiOCl2 + Zn + 4HCl = 2TiCl3 + ZnCl2 + 2H2O
TiCl3 readily disproportionates when heated:
2TiCl3 = TiCl2 + TiCl4
Ti2O3 preparation methods are (it has violet colour) as follows:
2TiO2 + C = Ti2O3 + CO
3TiO2 + TiCl4 + 2H2 = 2Ti2O3 + 4HCl
Ті2О3 (tm 1900С) does not react with water. When heated /boiling with HNO3:
2Ti2O3 + O2 = 4TiO2
3Ti2O3 + 2HNO3 = 6TiO2 + 2NO + H2O.
The violet colour of Ti(ІІІ) salts aqeous solution is explained by the existence of aquacomplexes [Ti(H2O)6]3+, the presence of d-electron (3d1) in Ti(ІІІ), electron transitions from d to d-orbitals absorbing quanta of electromagnetic energy.
Compounds Ti(II). Corn-coloured TiO can be produced by interaction of free magnesium (or another reductant such as Zn, Ti, C) with TiO2 at high temperature. Compounds Ti(II) are strong reducing agents. For instance, TiO reduces hydrogen at dissolution in H2SO4:
2ТіО + 3H2SO4 Ti2(SO4)3 + H2 + 2H2O
Ті(ОН)2 gradually reduces hydrogen of water molecules:
2Ti(OH)2 + 2H2O 2Ti(OH)3 + H2
Colourless solution of ТіCl2 quickly becomes brown and then violet (Ті3+) in colour, afterwards the solution again becomes colourless.
Хімічні властивості деяких сполук титану:
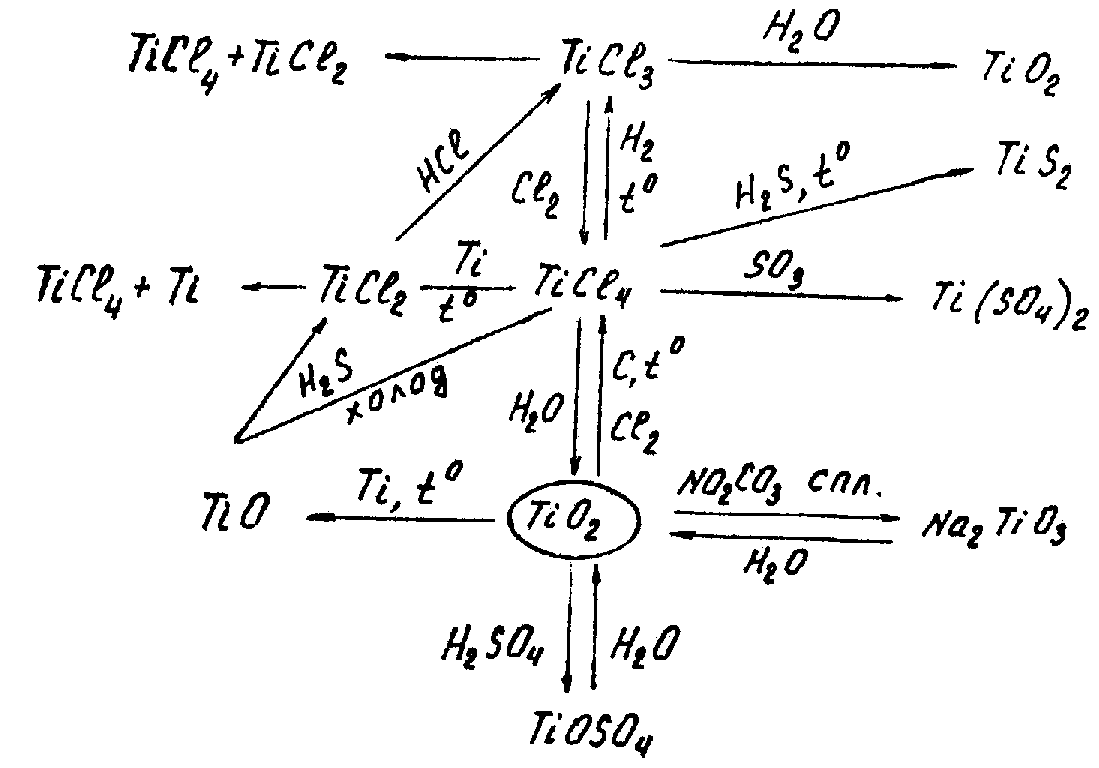
Хімічні властивості деяких сполук цирконію: