
- •Abstract
- •Introduction
- •Methods
- •What is stroke
- •87% Of strokes are ischemic, the rest are hemorrhagic.
- •Figure 4 Molecular process of neuronal ischaemia. (Colledge, Walker and Ralston., 2010, p. 1182)
- •Available treatments for stroke
- •Figure 5 Mechanism of t-pa action, (Genentech, 2014)
- •Induced pluripotent stem cells
- •Mesenchymal stem cells
- •Figure 8 Differentiation potential of msCs into a variety of tissue types, depending on signals produced by the local physiological environment. (Kishk et al., 2010)
- •MsCs for treatment of stroke
- •Migratory mechanisms of msCs
Figure 4 Molecular process of neuronal ischaemia. (Colledge, Walker and Ralston., 2010, p. 1182)
Available treatments for stroke
Patients, who have already endured a stroke, are at high risk of stroke recurrence. The medicines used for treatment of ischemic stroke at the moment are: thrombolytics (e.g.alteplase), anti-platelet medication (e.g. aspirin), anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin) and mechanical thrombectomy.
Aspirin reduces in the risk of stroke in 23% of the cases. (Diener., 2002) As soon as ischaemic stroke has been recognized, usually within 48 hours after the onset of symptoms, aspirin is given to the patient in moderate doses (160-350 mg/d), improving survival and reducing the risk of recurring strokes.
The benefits of aspirin in stroke patients are due to its ability to suppress prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis, by irreversibly inactivating prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase(PTGS) enzyme. Platelets do not possess DNA and are therefore unable to produce more PTGS, thus aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation, preventing blood clot formation.
However, haemorrhagic strokes cannot be treated or prevented with aspirin, as it can cause excess bleeding, especially in high doses or during long-term use, and increase the risk of another haemorrhagic stroke.
Aspirin is cost-effective and widely available and can be used in combination with other anti-platelet agens, such as dipyridamole to prevent strokes. For treatment of embolic strokes in high risk patients, aspirin is not sufficient and stronger anti-coagulants, such as warfarin are used.
Thrombolysis medication, such as recombinant tissue plasminogen activators(rt-PA), an example of which is alteplase, work by binding to the fibrin rich clots via the fibronectin finger-like domain and the Kringle 2 domain. Plasminogen is the inactive precursor of plasmin and is activated by rt-PA. The protease domain in rt-PA then cleaves the Arg561 - Val562 peptide bond in plasminogen to form plasmin. Plasmin is a serine protease and can cleave the haemostatic clot, consisting of polymerized fibrin and platelets by proteolytic digestion. Therefore, Rt-PA mediates recanalization of the congested vessels. (Figure 5)
Figure 5 Mechanism of t-pa action, (Genentech, 2014)
Rt-PA is contraindicated in hemorrhagic stroke and older ischaemic stroke patients with mild or resolving symptoms and thrombophilia, as it increases the risk of intracranial bleeding.
Thrombectomy is the surgical removal of the blood clot, mechanically recanalising the obstructed vessels, used in patients unsuitable for rt-PA therapy or in combinations with it. It can be proximal and distal. (Figure 6) In proximal thrombectomy manual suction is performed by placing an aspiration catheter at the proximal surface of the thrombus. Then, manual aspiration is applied and the catheter is retrieved under constant negative pressure. Distal thrombectomy is more technically challenging. To deliver the device distally to the thrombus, a microcatheter is passed at the occlusion site. To avoid thromboembolic problems, a balloon guide catheter is placed in the cervical internal cerebral artery and aspiration during device retrieval is recommended for most devices.
|
|
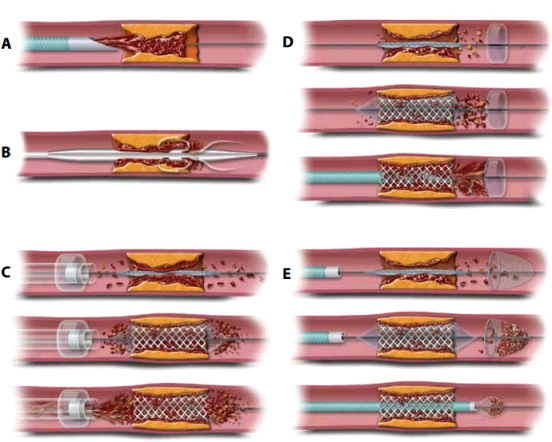
Figure
6 Thrombectomy illustrated.
(Mordasini P. et al.,
2012)
A
- Catheter aspiration thrombectomy
B
- Mechanical thrombectomy devices
C
- Proximal embolic protection devices
D
and E - Distal embolic protection devices
Stem cells
Stem cells can be distinguished from other cell types by the following characteristics:
They are unspecialized cells capable of self-renewal through mitosis, even after being inactive for a long time.
Certain physiological or experimental conditions can induce stem cells to become and function as an organ or tissue specific cells.
Types of stem cells include:
