
- •Overcoming Your Workplace Stress
- •Overcoming Your Workplace Stress
- •Martin r. Bamber
- •About the author
- •Preface
- •Acknowledgements
- •The ‘fight or flight’ response
- •Harmful stress
- •The consequences of harmful stress on the individual
- •The consequences of harmful stress for the organization
- •Conceptualizing stress
- •The ‘camera analogy’
- •The emergency response
- •Changes in thinking
- •Changes in motivation
- •Changes in emotion
- •Changes in behaviour
- •The development of stress syndromes
- •Dispelling some myths about stress
- •Answers for the stress quiz (Table 1.1) Statement 1
- •Statement 2
- •Statement 3
- •Statement 4
- •Statement 5
- •Statement 6
- •Statement 7
- •Statement 8
- •Statement 9
- •Statement 10
- •Statement 11
- •Statement 12
- •Statement 13
- •Statement 14
- •Statement 15
- •Statement 16
- •How well did you do in the quiz?
- •How stressed are you?
- •A stress checklist
- •Scoring and interpreting the checklist (Table 1.2)
- •Summary
- •Chapter 2
- •Identifying the causes of your occupational stress
- •Introduction
- •An overview of the causes of occupational stress
- •Individual factors
- •Genetic/inherited factors
- •Acquired/learned factors
- •Personality/trait factors
- •Factors in the work environment
- •Job demands
- •Physical working conditions
- •Control
- •Supports
- •Relationships
- •Pay and career prospects
- •The home–work interface
- •The employer’s ‘duty of care’ to provide a healthy working environment Case study: Schmidt
- •The impact of employment legislation
- •Demands
- •Control
- •Support
- •Relationships
- •Further developments in management standards
- •Identifying the main causes of stress in your own working environment
- •Interpreting the results of your questionnaire (Table 2.1)
- •Interpreting individual items
- •Interpretation of subscales
- •Summary and main learning points from Part I
- •About Part II of this book
- •Primary level interventions
- •Secondary level interventions
- •Tertiary level interventions
- •Doing a job analysis
- •Case study: Tony
- •The benefits of doing a job analysis
- •Interventions aimed at reducing the demands of your job Reducing the volume of work
- •Enlarging your job
- •Enriching your job
- •Improving your physical working environment
- •Interventions aimed at increasing the control you have over your job
- •Interventions aimed at increasing the supports you have at work
- •Interventions aimed at improving working relationships
- •Gather evidence
- •Find allies to support you
- •Stand up to the bully
- •Present the bully with the evidence
- •Be prepared for the backlash
- •Take things further if necessary
- •Interventions aimed at clarifying your role at work
- •Interventions aimed at improving the way that change is managed in your workplace
- •Interventions aimed at improving the home–work interface
- •Some tips for negotiating with your employer
- •What to do if your line manager is not receptive to your plight
- •What to do if you do not get the problem resolved within your workplace organization
- •Chapter 4 Living a healthy lifestyle
- •Introduction
- •Living a healthy lifestyle
- •Regular exercise
- •Some tips for doing more exercise
- •A healthy diet
- •Some tips for eating more healthily
- •Monitoring food intake
- •Medication and other drugs
- •Alcohol
- •Some tips for reducing your alcohol intake
- •Caffeine
- •Nicotine
- •Some tips for stopping smoking
- •Sleep and rest
- •Some tips to help you sleep better
- •Summary
- •An exercise
- •Developing your own ‘Healthy Lifestyle Plan’
- •Chapter 5 Developing effective time management skills
- •Introduction
- •Case study: John
- •Case study: Peter
- •What can we learn from the case studies of John and Peter?
- •Developing effective time management skills Plan ahead
- •Be clear about what your goals are
- •Manage your diary effectively
- •Create some ‘prime time’ for yourself
- •Prepare for meetings
- •Choose the best time to tackle difficult tasks
- •Overcome procrastination
- •Case study: Jenny
- •What can we learn from the case study of Jenny?
- •Learn to delegate
- •Stay focused
- •Prioritize tasks
- •Be organized
- •Developing an action plan to manage your time more effectively
- •Chapter 6 Developing assertiveness skills What is assertiveness?
- •Why are some people unassertive?
- •What are the consequences of being unassertive?
- •Case study: Caroline
- •Case study: Rosie
- •How can you become more assertive?
- •Education
- •Aggressive behaviour
- •Submissive behaviour
- •Manipulative behaviour
- •Assertive behaviour
- •Knowing your rights
- •A ‘Bill of Rights’
- •What can we learn from the case study of Caroline?
- •Developing assertive attitudes
- •Developing assertive behaviours
- •Other useful assertiveness techniques to help you
- •Use the ‘broken record’ technique
- •Use fogging
- •Be concise
- •Be specific
- •Clarify
- •Use ‘I’ statements
- •Active listening
- •Aim for a workable compromise
- •Negative assertion
- •Empathic confrontation
- •Self-disclosure
- •How assertive are you?
- •Table 6.1 scores and interpretation Scoring of individual items
- •Interpreting the total scores for the questionnaire
- •Developing an action plan to become more assertive
- •Chapter 7 Developing effective interpersonal skills
- •Introduction
- •What are interpersonal communication skills?
- •Why are some people interpersonally less skilled than others?
- •What are the consequences of being interpersonally unskilled?
- •Developing your own interpersonal skills
- •Body posture and gestures
- •Facial expressions
- •Eye contact
- •Voice projection
- •Personal space
- •Personal appearance and presentation
- •Verbal skills
- •Paraphrasing
- •Reflecting feelings
- •Summarizing
- •Minimal encouragers
- •Asking open questions
- •Immediacy
- •Concreteness
- •The use of small talk
- •Higher level interpersonal skills
- •Developing cognitive skills
- •How interpersonally skilled are you?
- •Developing an action plan aimed at becoming more interpersonally skilled
- •Chapter 8 Developing relaxation skills
- •Introduction
- •Informal relaxation techniques
- •Semi-formal relaxation techniques
- •Massage
- •Releasing your shoulder tension
- •Soothing your scalp
- •Relaxing your eyes
- •Formal relaxation techniques
- •Deep breathing exercises
- •A deep breathing exercise
- •Progressive muscular relaxation
- •A progressive muscular relaxation exercise
- •A brief relaxation exercise for the neck and shoulders
- •Mental relaxation techniques
- •Meditation
- •Mindfulness
- •Mental refocusing
- •Visual imagery
- •Summary and main learning points
- •Chapter 9 Changing the way you relate to your work
- •Introduction
- •Understanding the links between thoughts, feelings, behaviours and bodily reactions
- •The cat vignette exercise
- •Identifying unhelpful patterns of thinking
- •Labelling dysfunctional thinking styles
- •Catastrophic thinking
- •Jumping to conclusions and mind reading
- •Overgeneralization
- •Magnification
- •Minimization
- •Personalization
- •Black and white thinking
- •‘Should’ and ‘must’ statements
- •Challenging dysfunctional patterns of thinking
- •Examining the evidence
- •Exploring the alternatives
- •Identifying advantages and disadvantages
- •The friend technique
- •Checking it out
- •Estimating probabilities
- •Reattributing meaning
- •Conducting behavioural experiments
- •Case study: Sarah
- •Challenging work dysfunctions
- •Challenging patterns of over-commitment Modifying perfectionism
- •Modifying workaholism
- •Challenging patterns of under-commitment Modifying underachievement
- •Modifying procrastination
- •Summary
- •Chapter 10 Overcoming stress syndromes
- •Introduction
- •Treating anxiety syndromes
- •Performance anxiety
- •Case study: Philip
- •Treating Philip’s performance anxiety
- •What can we learn from the case study of Philip?
- •Panic attacks
- •Case study: Andrew
- •Treating Andrew’s panic attacks
- •Phobic avoidance
- •Treating phobic avoidance
- •Case study: Maxine
- •Treating the depression syndrome
- •Challenging depressive thinking
- •Challenging unhelpful behaviours
- •Activity scheduling
- •Conducting behavioural experiments
- •A note on the burnout syndrome
- •Treating burnout syndrome
- •Treating the hostility syndrome
- •Summary
- •The eight stages of a self-help plan
- •Make a problem list
- •Prioritize your problems
- •Set your goals
- •Establish the criteria of success
- •Plan your interventions
- •Develop a self-help treatment plan
- •Monitor and review your progress
- •Prevent relapse
- •Case study: Helen
- •Making a problem list and prioritizing the problems
- •Setting the goals and establishing the criteria of success
- •Comfort eating and weight gain
- •Avoidance
- •Procrastination
- •Unassertiveness
- •Anxiety
- •Poor self-image
- •Planning the interventions
- •Interventions for comfort eating and weight gain
- •Interventions for avoidance
- •Interventions for procrastination
- •Interventions for unassertiveness
- •Interventions for anxiety
- •Interventions for poor self-image
- •Developing a self-help treatment plan
- •Monitoring and reviewing progress
- •Summary
- •Chapter 12 Summary and conclusions
- •Appendix Useful books and contacts
Statement 16
‘Home and work life are separate’
(Answer: False)
While it may appear that work life and life outside of work are separate, this is not actually the case. Events at work can impact on home life and vice versa. For example, an employee who has a happy marriage, a good social support network and stable home life outside of work is likely to be in a better position to cope with a stressful work situation caused by a lack of support and social contact at work. The supports outside of work can act as a source of support which can buffer that individual against stress at work. However, someone who does not have these support networks in their personal life may be more vulnerable to experiencing stress at work. Also, if an employee is experiencing stress at work, they may become more irritable and moody with family, friends and acquaintances in their personal life. This in turn can lead to increased arguments and conflicts outside of work. Thus, it can be seen that home and work life can and often do impact on each other.
How well did you do in the quiz?
If you got 16 out of 16, well done! However, do not worry if you did not get full marks. What is important is that you learn from what you have read and that some of the myths surrounding occupational stress have been dispelled. Having tested your knowledge of stress, the next section in this chapter aims to help you identify how much stress you are currently experiencing.
How stressed are you?
Earlier in this chapter the physical, emotional, cognitive and behavioural signs and symptoms of stress in the individual were outlined (pp. 6–7). These have been summarized in the form of a checklist (Table 1.2). In order to identify the symptoms and the severity of the stress you are currently experiencing, you are requested to complete the checklist. You will notice that there are a number of physical symptoms listed. The assumption being made when you complete this checklist is that any medical causes of these symptoms have already been investigated and eliminated by your doctor. If this is not the case, it is important that you get these checked in the first instance by your doctor to exclude any medical condition. For example, it would be unwise to simply assume that breathlessness and palpitations are symptoms of stress without having this confirmed by your doctor. It is also important to be aware that this is not a sophisticated diagnostic tool but a checklist aimed at giving you an indication of how much stress and what symptoms you are experiencing at the present time.
Table 1.2 A stress checklist
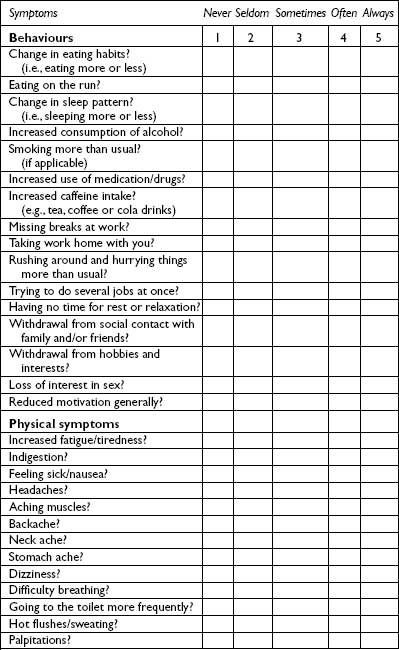
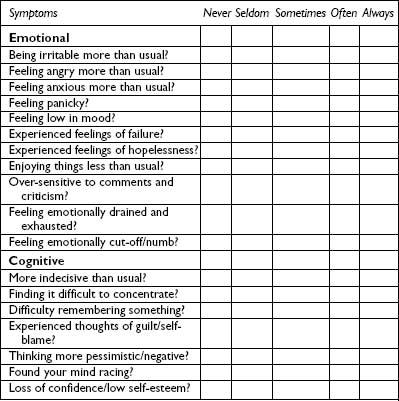
Note: This table is available to view and print from the following website: www.routledgementalhealth.com/9780415671781
A stress checklist
For each item presented in Table 1.2, please indicate on the 1 to 5 scale the symptoms and severity of the symptoms that you have been experiencing over the past month by ticking the appropriate box.
Scoring and interpreting the checklist (Table 1.2)
Each item on the checklist is rated from 1 to 5. A score of 1 on an item indicates that you have never experienced that symptom over the past month, whereas a score of 5 indicates that you have been experiencing that symptom constantly over the past month. The higher the score, the more severe the symptom (1 = Never; 2 = Seldom; 3 = Sometimes; 4 = Often; 5 = Always). If you scored between 47 and 93 this indicates that you are currently experiencing a low level of stress, a score between 94 and 140 indicates a moderate level of stress, a score between 141 and 187 indicates a high level of stress and a score of 188 or more indicates a very high level of stress.
