
- •Учебная программа дисциплины - Syllabus
- •Данные о дисциплине:
- •1.5 Краткое описание дисциплины
- •1.6 Виды заданий и сроки их выполнения 4 семестр
- •1.7 Список рекомендуемой литературы
- •1.8 Контроль и оценка знаний
- •Календарный график сдачи всех видов контроля по дисциплине
- •Тема 1: «Радиотехника»
- •Тема 2. « Электроника»
- •Тема3.«Телекоммуникация»
- •1.9 Политика и процедура курса
- •2 Содержание активного раздаточного материала
- •2.1 Тематический план курса
- •2.2 Планы практических занятий
- •Civil Engineering (Гражданское строительство)
- •Mechanical Engineering (Машиностроение)
- •Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Электротехника и Электроника)
- •Electric Power and Machinery (Энергетика и энергомашиностроение)
- •Electronic engineering (Электроника)
- •Communications and Control (Техника средств связи и управление)
- •Computers engineering (Компьютерная техника)
- •Aeronautical and Aerospace Engineering (Авиакосмическая техника)
- •Naval Engineering (Кораблестроение)
- •Chemical Engineering (Химическое машиностроение)
- •Nuclear Engineering (Ядерная техника)
- •Safety Engineering (Техника безопасности)
- •Technician engineers Text b
- •Craftsmen/women Text c
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Radio Communication
- •Vocabulary:
- •Task 1. Read the text: Electronics and Microelectronics (part I)
- •Vocabulary:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Методические рекомендации:
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Colour Television
- •Telemedicine
- •How VoIp phone systems work
- •2.3 Планы занятий в рамках самостоятельной работы студентов под руководством преподавателя (сроп)
- •4 Семестр
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Input Hardware
- •Processing Hardware
- •Storage Hardware
- •Output Hardware
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Vocabulary:
- •10.1. Learn the dialogue by heart.
- •10.2. Answer the following questions:
- •2.4 Планы занятий в рамках самостоятельной работы студентов срc
- •4 Семестр
- •1. Read the text: Robots in Industry
- •2. Answer the questions:
- •3. Translate into English:
- •2. Define what conjunction could be inserted in the following joined clauses:
- •3. Translate the following dialogue into English:
- •4. Answer the following questions:
- •2. Answer the following questions orally:
- •1. Answer the questions:
- •Flexible Production and Industrial Robots
- •2. Распределите сочетания на три тематические группы:
- •3. Образуйте глагольные сочетания, соединив глаголы с существительными, ориентируясь на содержание текста. Переведите их. Распределите их по тем же тематическим группам:
- •4. На какие вопросы отвечают выделенные слова? Отметьте формальные признаки, которые определяют значение этих форм. Проверьте перевод этих форм в предложениях текста. Какие из них совпадают?
- •5. Какие из выделенных действий происходят: 1) в течение длительного времени в настоящее время; 2) регулярно; 3) должны произойти?
- •Laser Technology
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •2. Answer the following questions to the text:
- •3. Retell the text using new lexical words.
- •2. Answer the following questions about the text.
- •3. Match each word with the correct definition
- •4. Are the following statements true or false?
- •5. Fill in the gaps.
- •2. Answer the following questions:
- •1.Read the text: Computers
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •2.Answer the questions:
- •1.Read the text: Internet
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •2.Answer the questions:
- •1.Read the text: Satelites and telecommunications
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •2.Answer the questions:
- •1.Read the text: Hardware
- •Storage hardware
- •Output hardware
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •1. Answer the questions:
- •1.Read the text: Software
- •Vocabulary notes:
- •2. Answer the questions:
- •«Профессионально-ориентированный английский язык»
Методические рекомендации:
Особое внимание уделить содержанию текста. Прорабатывать упражнения после того, как студенты ознакомятся самостоятельно с соответствующим поурочным словарём. Перескажите первую часть текста.
Рекомендуемая литература: 1(осн.) стр. 46-48
Контрольные вопросы:
1) What does the term «computer» describe?
2) What are five components of computer system?
3) Why people are the most important component of a computer of a computer system?
4) In what way terms «data» and «information» differ?
5) How does computer convert data into information?
6) What are the most important applications of computer? (Are computer
games just a «waste of time» or it is a nice hobby and a lot of fun)
7) What is storage hardware? What is CD–ROM used for? Can a user
record his or her data on a CD? What kind of storage hardware can contain more information: CD–ROM, RAM or ROM?
8) What is the tendency in application software market in the recent
years?
9) What do you think is more expensive—hardware or software?
Практическое занятие № 10
Theme: The Internet
Task 1. Read the text: How the Internet Works
The 2 most popular aspects of the Internet are electronic mail, o e-mail, and the World Wide Web, which may be thought of as a graphical environment that can be navigated through hyperlinks-from one site you click on hyperlinks to go to related sites. The Internet involves 3 basic elements: serve, client, and network. A server is a computer program that makes data available to other programs on the same or other computers-it “serves” them. A client is a computer that requests data from a server. A network is an interconnected system in which multiple computers can communicate, via copper wire, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, radio waves, etc. When you use a browser to go to a site on the World Wide Web, you access the site’s files.
Here are the steps in opening and accessing a file:
* In the browser, specify the address of the desired website-for example, www.usps.gov for the U.S. postal Service.
* The browser sends your request to the server of your Internet service provider (ISP), the company that supplies your connection to the Internet.
* That server sends the request to the server at the address specified. The official address of each computer connected to the Net, the so-called Internet Protocol (IP) address, is actually numerical. If, as is commonly done, you indicated the website address using letters and words-such as www.usps. Gov- then the Internet’s Domain Name Service automatically converts it into the appropriate IP address (in this case, 56.0.134.24).
* The file is sent to the ISP’s server, which sends it back to the browser, which displays the file.
Task 2. Match each word with the correct definition
1. a client a. the connection of computer networks across the World.
2. a network b. an organization that provides Internet connections.
3. a browser c. a main computer that provides a service on a network.
4. a server d. a program used for displaying webpages.
5.I.S.P. e. a system which connects up a number of computers and ommunications.
devices to enable messages and data to be passed between those devices.
6. Internet f. a network computer used for accessing a service on a server.
Task 3. Are the following statements true or false?
1. A network is an interconnected system in which multiple computers can communicate, via copper wire, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, radio waves, etc.
2. A server doesn’t make data available to other programs on the same or other computers.
3. A client requests data from a network.
4. When you use a browser to go to a site on the World Wide Web, you access the site’s files.
5. The official address of each computer connected to the Net, is called Internet Post Office.
Task 4. Fill in the gaps.
1. The browser ______ your request to the _______ of your Internet service provider
2. The file __ to the ISP’s server, which sends it back to ____, which displays the file.
3. When you use __ to go to a site on the World Wide Web, you ___ the site’s files.
4. ____ is a computer program that ________ data available to other programs on the same or other computers.
5. The Internet __________ 3 basic elements: _______.
6. A client is a computer that ________ data from ________.
Task 5. Translate the following sentences into your own language.
1. A network is an interconnected system in which multiple computers can communicate, via copper wire, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, radio waves, etc.
2. The browser sends your request to the server of your Internet service provider (ISP), the company that supplies your connection to the Internet.
3. The official address of each computer connected to the Net, the so-called Internet Protocol (IP) address, is actually numerical.
4. The file is sent to the ISP’s server, which sends it back to the browser, which displays the file.
Task 6. Speak on the basic elements of the Internet.
Task 7. Find in (b) the Russian equivalents to the English words and word combinations in (a):
hence; for example; according to; by means of; i.e.; etc.; always; just; on the other hand; since; any; in its turn; sometimes; the same; while; in this way; instead (of); usually.
то есть; например; всегда; только что; с другой стороны; так как; в свою очередь; иногда; тот же самый; любой; следовательно; и так далее; в то время как; таким образом; вместо; согласно; обычно; посредством.
Task 8. Arrange synonyms in pairs:
Semiconductor technology; to execute; to write; to control; memory; to sense; to choose; to form; to feel; storage; to store; to set up; to handle; solid-state technology; to perform; to keep; to select; research; to put in; investigation.
Методические рекомендации
Нацелить студентов на чтение специальных текстов по теме и умение находить в них необходимую и достаточную информацию. Для успешного усвоения лексического материала необходимо выучить их наизусть.
Рекомендуемая литература: 1(осн.) стр. 46-482(осн.) стр. 2752 осн. стр.
Контрольные вопросы:.
1. What are the most popular aspects of the Internet?
2. What elements does the Internet involve?
3. What does a server do?
4. What is the function of a network?
6. How is called the official address of each computer connected to the Net?
7. What is Internet used for?
8. Why so many activities such as e-mail and business transactions are possible through the Internet?
9. What is World Wide Web?
10. What is Web browser?
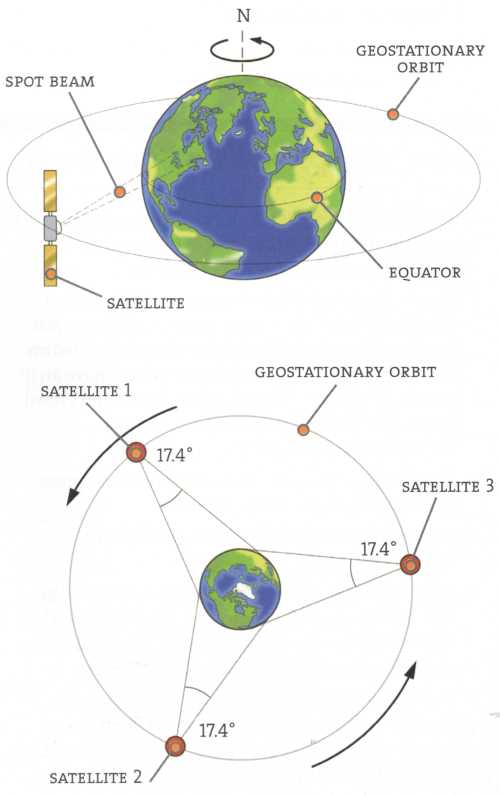
Практическое занятие № 11
Theme: Satellites and telecommunications
Task 1. Read the text:
Our world is becoming an increasingly complex place in which, we are very dependent on other people and organizations. An event in some distant part of the globe can rapidly and significantly affect the quality of life in our home country.
This increasing dependence, on both a national and international scale, forced us to create systems that can respond immediately to dangers, enabling appropriate defensive or offensive actions to be taken. These systems are operating all around us in military, civil, commercial and industrial fields.
A worldwide system of satellites has been created and it is possible to transmit signals around the globe by bouncing them from one satellite to an earth station and then to another satellite and so on.
Originally designed to carry voice messages, they are able to carry hundreds of thousands of separate simultaneous calls. These systems are being adopted to provide for business communications, including the transmission of voice and facsimile messages, data and video data.
It is probable that future wide use of satellites in the area of telecommunications will provide a great variety of information services to transmit directly into our homes, possibly including personalized electronic mail. The electronic computer is at the heart of many such systems, but the role of telecommunications is not less important. There will be a further convergence between the technologies of computing and telecommunications. The change of this kind will lead us to the database culture, the cashless society, the office at home, the gigabit-per-second data network.
One cannot doubt that the economic and social impact of these concepts will be very significant. Already, advanced systems of communication are affecting both the layman and the technician.
The new global satellite-communication systems offer three kinds of service.
The first one is voice messages. Satellite telephones are able to make calls from anywhere on the Earth to anywhere else. That makes them especially useful to use in remote, third-world villages (some of which already use stationary satellite telephones), for explorers. Today’s mobile phones depend on earth-bound transmitters, whose technical standards vary from country to country. Satellite telephones can solve this problem, but it is not a cheap service.
The second service is messaging. Satellite messages have the same global coverage as satellite telephones, but carry text alone, which is extremely useful for those with laptop computers. As we see, the Internet works in space too. The only problem for ordinary users is one way transmissions. This problem is solved by using combine transmissions, when you make a call using land communications and receive ordered information through your satellite plate.
The third service is tracking. Voice and messaging systems also tell their users where they are to within a few hundred meters. Combined with the messaging service, the location service could help rescue teams, to find lost, adventurers, the police to find stolen cars, exporters to follow the progress of cargoes and so on.
Satellite systems provide better positioning information to anyone who has a receiver for their signals.
To my thinking, satellite method of communication is the future for all kind of telecommunications.
