
- •Section 11
- •5.The nuclear imaging of the skeleton visualisation
- •The soft tissues of extremities
- •The radio anatomy of the musculoskeletal system
- •Syndrome of bones tumour:
- •Questions for self control:
- •Section 12 The radio diagnostics of inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- •Questions for self-control:
- •Section 13
- •Questions for self-control:
Section 11
The radial methods investigation of the musculoskeletal system. The radio symptoms of pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Section contents:
The roentgenologic methods of the bones and joints visualisation are sciagraphy, tomography, fistulography, pneumoartrography, angiography, and densitometry. The normal roentgenanatomy and bases of physiology of bones and joints, old age features of skeleton structure. The order of study and description of results of roengenological visualisation of bones and joints. Basic indications and contra-indications.
The radionouclear methods of visualisation of bones and joints are planar osteoscintigraphy, SPECT-scintigraphy. The basic principles of radionouclear visualisation of the musculoskeletal system, RPhP, which used for osteostcintigrapgy. The radionouclear semiotics of tumour defect of bones and joints (primary and secondary), inflammatory processes, traumatic damage, degenerative-dystrophic changes of the musculoskeletal system. Basic indications and contra-indications.
The possibilities of US, CT, MRI in visualisation of the musculoskeletal system. Basic indications and contra-indications.
The radiological signs (symptoms) of diseases of the musculoskeletal system are changes of the form, size, position of bones; changes of contours (periosteitis, periostosis, paraostosis), changes of structure (osteoporosis, osteosclerosis, destruction, osteonecrosis, osteolisis and atrophy), changes of joint space (narrowing, disappearance, compression of joint surfaces, regional bone excrescences, disparity of joint ends).
The radiological methods of musculoskeletal system visualisation
1. Roentgenologic method (see fig 11.1): multi-projection (roentgenography) sciagraphy, functional sciagraphy (vertebral column, joints, foot), planar tomography, panoramic tomography (mainly perform to visualisation of jaws). To examine the vessels of musculoskeletal system, as well as other organs and systems, angiography is used. To other X-ray opaque methods belong sinusography (use for examine of paranasal sinuses) and artrography (to purpose for medical survey of joint cavities and used radiolucent (air) or radiopaque agents), fistulography (roentgenography after introduction of radiopaque to the fistula), densitometry (method of estimation of bone tissue density by the agency US or x-ray examination).
1
 2
2
 3
3
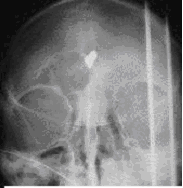
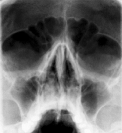
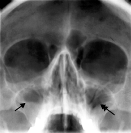
Fig.11.1 X-ray film (sciagram): 1 – maxillary sinuses are norm; 2 – maxillitis; 3 – foreign body into the cerebrum – bullet.
2. The Ultrasound visualisation (US) (see fig11.2) that is sonography of musculoskeletal system is used for the study of soft tissues. It is applying for the examination of children. This method dosn’t have contra-indications. Sonography is more frequently use for estimation of instability of hip joint (at the displasy), the exudate or haematoma in the cavity of large joints, damages of articular cartilage, tendons and ligaments, and also for foreign bodies especially radiolucent. The needle aspiration or biopsy is used under US vision.
1
 2
2
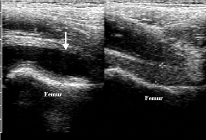
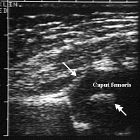
Fig.11.2 US: 1 – normal hip joint; 2 - exudates into a joint.
3. The CТ (see fig 11.3) exceeds possibilities of roentgenography; it is performed after previous roentgenologic visualisation. Intravenous contrast for study of location of large vessels in relation to bones and pathological formations is used.
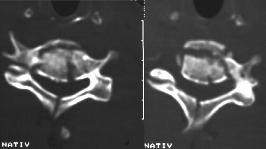
Fig.11.3 The CT: fracture of neck vertebra.
4. The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (see fig 11.4) is more advantages CT in the case of visualisation of soft tissues and marrow. Performed in axial, sagital, and coronal (frontal) projections. MRI don’t use for study a bone structure and calcification.
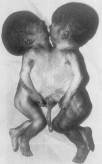
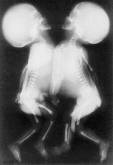
Fig.11.4 Siamese twins: original appearance, sciagrams, MRI.
