
- •Theme № 14 Radio methods of the thoracic cavity organs examination. Radio signs of the respiratory organs diseases
- •Methods of roentgenological examination
- •Symptoms of lungs disease
- •Syndromes of pulmonary pathology
- •Transparency change of the lung field
- •Bronchitis
- •Pneumonia
- •Pleurisy
- •Pneumoconiosis
- •Tuberculosis
- •Tumours of lungs
- •Metastatic tumours of lungs
- •Lungs and pleurAl traumatic damages
- •The bronches and lungs foreign bodies
- •The pulmonary edema
- •Thromboemboly of pulmonary artery
- •The diaphragm diseases radio signs
- •Additional:
- •3) Special:
Syndromes of pulmonary pathology
1. SPACIOUS COMPRESSIONS of PULMONARY TISSUE are compressions, which occupy not less than a 2/3 pulmonary field, are at the loss of airness of whole lung or lobe, at the accumulation of liquid in a pleura cavity.
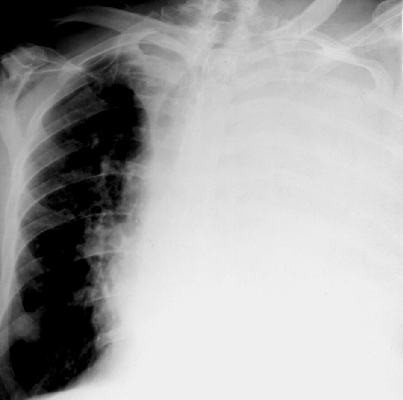


Fig.14.17. Total and subtotal shade
Differences between intrapulmonar process from extrapulmonar. If the process is lobar- that lobe has a certain form and border on interlobar pleura, and if the volume of it is not diminished, it can be inflammatory process. In default of displacement of mediastinum in a sick side atelectasis is eliminated. A structure of shades at inflammation can be heterogeneous becouse of the foci which were angered, and at atelectactics air resolves and the structure of compact lobe are homogeneous; there is no visible road clearance of bronches on tomogramas.
If a lobe compression is disposed in the inferior departments of thorax and meets with the cupula of diaphragm, does not respond the size and form of lobe and homogeneous on a structure, and the organs of mediastinum are displaced in a healthy side this is a liquid in a pleura cavity. In horizontal position a free liquid moves and changes a form and position.
2. LIMITED COMPRESSION OF LUNGS
The limited compression is a part of lungs - lobe or segment or their parts. On two patterns in anterior al and lateral projections determine on a form and localization what part this compression belongs to. If itcorrespond to localization of lobe or segment - it is an intrapulmonar process; in difficult cases it is necessary to revolve a patient during roentgenoscopy, to specify if the compression does not belong to encapsulation in a pleura cavities, and whether it does not adjoin to the thorasic wall, or it is formed by ribs or soft tissues. A liquid can encapsulated in interlobar fissuras in such cases in lateral projections has a form of biconvex lens, form of triangle (in the projection of interlobar fissura).
The diminishing of lobe should be different between atelectics and cirrhosis, which is the development of scar connecting tissue. Displacement of mediastinum in a sick side is observed in atelectasis and mostly in one-sided cirrhosis, however the specify character of shades and functional symptoms allow to specify nature of the pathological process.



Fig.14.18. the limited compression and spherical shade
3. SPHERICAL SHADES
The rounded educations are the shades which exceed the size 1х1 sm in a diameter. It is necessary to take into consideration a size, form, contours, structure, reaction of surrounding tissue. If a form is rounded, correct, contours are clear, a structure is homogeneous, it can be bening tumour or cyst, if a form is wrong, contours are unclear – it can be a malignant tumour, and if a cavity is inwardly determined with a horizontal level - it is an abscess, calcification into the rounded shade and foci around - tuberkuloma. If a shade is disposed near the wall and its center is after a thorasic wall - it is an encapsulated pleurisy (with a liquid), and if a shades adjoin to mediastinum, does not become separated from him and greater part of shade is designed on mediastinum – it is the tumour of mediastinum.
4. LINEAR COMPRESSIONS
The linear compressions of interlobar pleura - linear shades are the result of fibronic impositions at fresh inflammatory processes (a contour will be unclear) or at development of scar tissue at old process. Linear shades have certain interlobar localization. Joints can be in different departments, and their anterior alion does not conside with the location of lung pattern vessels. Besides the linear shades arise up at development of vessels and bronches compression - at stagnation in lungs, at a chronic bronchitis (when scar tissue develops on motion of intermediate tissue, peribronchial and perivascular, it deforms, changes motion of lung pattern and shows up focusular deformation). Linear shades can be the distribution of tumour in couse of bronches or lymphatic vessels at a primary tumour or metastases of lymphogenic origin.
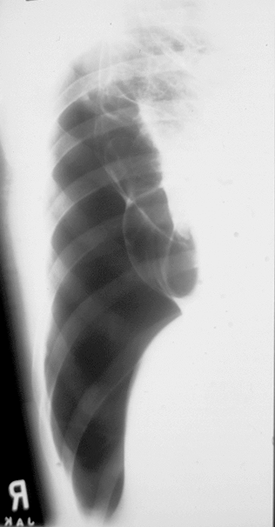
Fig.14.19. Linear shades
5. FOCUSES and limited dissemination, widespread DISSEMINATION.
Foci are the small compressions to 1 sm. Their forms are various: from rounded to wrong. Take into account prevalence of focus, their contours and intensity, state of lung pattern around. If foci are localized in the area of apex and above a collar-bone - it is more frequent to be tubercular; in inferior segments - more characteristically for pneumonia. The contours of foci at inflammatory processes are unclear, washed out; the clearer are at tuberculosis in the phase of compression. Widespread, occuping both lungs, by sizes 1-2mm, rounded, identical closeness foci keen apexes of lungs are at acute tubercular dissemination. Various sizes of foci, more frequent rounded, clear, dense are meet on both sides oris often spread down, to the diaphragm – is significant to their metastatic nature.


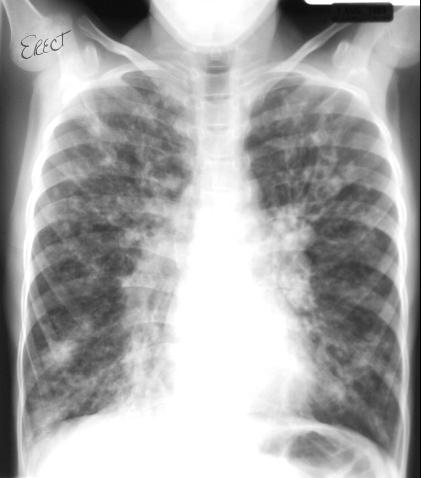
Fig.14.20. Focal and disseminated shades
It is important to estimate intensity of foci, a small and middle closeness is more frequent at pneumonia and tuberculosis. Lokalisation of pathological process and loud speaker of pathological changes have the defined value. Pneumonia resolves quickly, and tubercular changes are saved for months. If in a focus there are calcareous depositions it is the sign of old tuberculosis.
A small rounded shade can be the sign of lungs cancer, for determination of the shades structure it is necessary to do tomography. The sizes of tumour are increased in course of time. At pneumonia and tuberculosis foci are plural, and at a primary lungs tumour are single.
Widespread foci can be becous of at the professional diseases of the lungs - but they are more frequent in the middle departments of the lungs, on a background pneumosclerosis, in anamnesis - a work in dustinal conditions. Foci more frequent the shallow, nodeted shades, which well appeared on the sciagrams of the body, executed by a short exposition.
7. PATHOLOGY OF THE LUNG PATTERN
Anatomic substrates of the lung pattern are the blood vessels, bronches, lymphatic vessels, peribronchial and perivascular conecting tissue, and lymphatic nodes. In norm the lung pattern image is predefined mainly by blood vessels. At the pathology of each enumerated elements lung pattern changes.
Distinguish limited, widespread and total lung pattern change. He can increase - if vessels are spread (stagnation) or enriched (if the amount of vessels are increased in unit of area or volume lungs due to the increase of shallow vessels).
The lung pattern can be impoverished at emphysema lungs. A lung pattern can relax, if it recoveres shallow foci.
A lung pattern can be deformed in combination of strengthening with incorrect motion of vessels through scar development of the connecting tissue in intermediate stroma. There can be Kerli lines of at mitral stenosis - in inferior departments, lateral horizontal strips long to 2-2,5 and breadthways 1-2mm due to an interstitial edema.
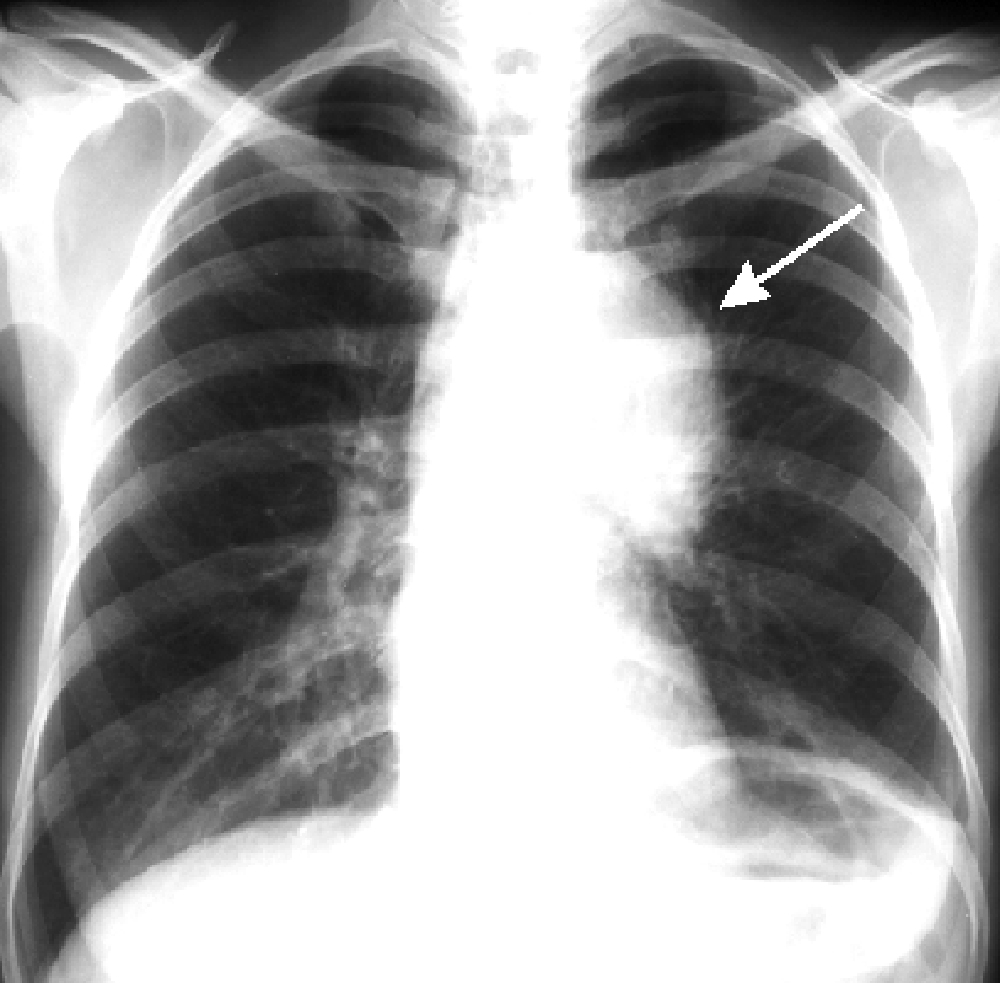


Fig.14.21. Pathological changes of lung pattern and lungs root
8. PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES OF THE LUNGS ROOT
Shades of root lungs are mainly predefined by pulmonary artery on a sciagram; however root lungs consist of large bronches, lymphatic nodes, and cellulose. Each of these elements can change and a root can change as a result of it. Changes of root lungs can be independent or accompany to other diseases.
A width of the right root is 1-1,5 sm, length 6-8 sm, to the left part of it is a heart recovered. Between the right root and shades of the heart there is a light strip - a Prozorov path - a road clearance to the inferior lobular bronchus.
Necessarily take into account prevalence of changes - one- or bilateral defeat of root, is combined with other processes in lungs, eyelids of patient; contours and structure of root. Children more frequent have a one-sided defeat at tuberculosis, for adults more frequent at cancer. Polycyclic contours specify on the defeats of lymphatic nodes, unclear on infiltration of cellulose at inflammation or germination of tumour. Combination of root expansion with atelectasis can be at tumular bronchoadenitis and tumour.We can observed calcification of the lymphatic nodes.
8. SYNDROME of the LIMITED ring SHADES or CAVITIES (see a Fig. 22.). Anatomic cavities in lungs are characterised by ring shades with air inwardly (Fig.22.). It is important to set their topography, because cavities can simulate changes in ribs and joints in a pleura cavity. In lungs a cavity can have thin even walls without a liquid, which is typical for an air cyst, if around are foci and strengthening lung pattern or fibrous lineas - it is a cavity.During an abscess a wall is thick to 2-4mm, with unclear contours and horizontal level of liquid.
For a tumour which disintegrates - a cavity of a wrong form, wall of different thickness, there is no liquid or it may be rarely.An important value has the state of pulmonary tissue, surrounding cavity: there are foci around at tuberculosis, a strengthening of a vascular pattern at an abscess, at an air cyst - a lung pattern is normal or impoverished.
Plural cavities can be at cystic disease, at abscess formation pneumonias and bronchoectasis.
Sometimes a bronkhography is used at bronchoectasis for clarification of diagnosis.
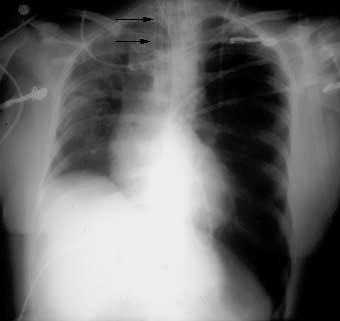


Fig.14.22. Spacious (pneumothorax) and limited (cavity) increase of lungs transparency
9. SPACIOUS INCREASE OF LUNG’S TRANSPARENCY
Is observed both at an intrapulmonar process and at presence of air in a pleura cavity - pneumothorax. Pulmonary process can be limited (lobe or a few segments) at compensate hyperinflation (at atelectasis in contiguous lobes and segments) and widespread - at obstructive lung emphysema. The lung’s pattern becomes impoverished - less shallow vessels, the size of thorax increases, ribs are disposed horizontally in the superior departments of thorax, and the diaphragm goes down. At respiratory practically transparency does not change.
At pneumothorax a pulmonary collapse which slept is disponsed, in an uprooted department with an external clear contour, in intercostals spases lung pattern is not evident. Pneumatization of lungs can be observed at congenital hypoplasia of lungs.
