
- •Matlab r2013a
- •Технология SimEvents-моделирования
- •Основные характеристики субпакета SimEvents даны в подразделе Product Description раздела Getting Started with SimEvents:
- •Key Features(особенности)
- •Build a Discrete-Event Model(дискретно - событийная)
- •Overview
- •Open a Model and Libraries
- •Open a New Model Window
- •Open SimEvents Libraries
- •This window contains an icon for each SimEvents library. To open a library and view the blocks it contains, double-click the icon that represents that library. Open Simulink Libraries
- •Move Blocks into the Model Window
- •Responding(отвечая) to Blockage(блок) at the Entity Output Port(на выходе порта)
- •Dialog Box Entity Generation Tab
- •Initial seed
- •Blocking Tab
- •Entity Type Tab
- •Statistics Tab
- •Examples
- •Example: Responding to Blockage
- •Immediate Restart
- •Dialog Box fifo Queue Tab
- •Timeout Tab
- •Statistics Tab
- •Examples
- •Dialog Box Single Server Tab
- •Preemption Tab
- •Timeout Tab
- •Statistics Tab
- •Examples
- •See Also
- •Selecting Data for the Horizontal Axis
- •Dialog Box
- •Plotting Tab
- •X value from
- •Axes Tab
- •Figure Tab
- •X label
- •Data History Tab
- •Input port available for entity arrivals
- •Change Parameter Values
- •Connect Blocks
- •Run the Simulation
- •Resolve Solver Warnings
- •Results of the Simulation
- •Insert Blocks
- •Build a Model Using Model Construction Commands
- •Explore Simulations Using the Debugger and Plots
- •Explore the d/d/1 System Using the SimEvents Debugger
- •Start the Debugger
- •Run the Simulation
- •Query the Server Block
- •End the Simulation
- •For Further Information
- •Explore the d/d/1 System Using Plots
- •Enable the Queue-Length Signal
- •Plot the Queue-Length Signal
- •Simulate with Different Intergeneration Times
- •View Waiting Times and Utilization
- •Observations from Plots
- •Information About Race Conditions and Random Times
Observations from Plots
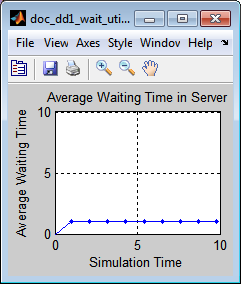
The average waiting time in the server does not change after the first departure from the server because the service time is fixed for all departed entities. The average waiting time statistic does not include partial waiting times for entities that are in the server but have not yet departed.
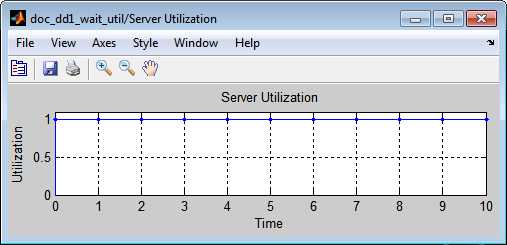
The utilization of the server is nondecreasing if the intergeneration time is small (such as 0.3) because the server is constantly busy once it receives the first entity.
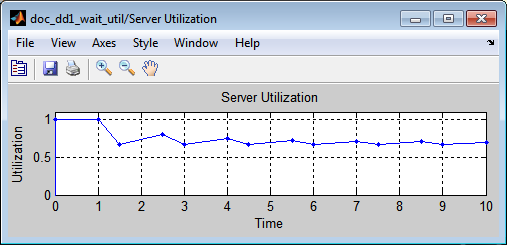
The utilization might decrease if the intergeneration time is larger than the service time (such as 1.5) because the server has idle periods between entities.
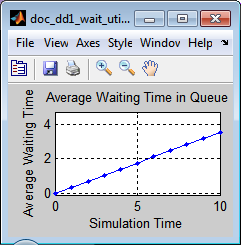
The average waiting time in the queue increases throughout the simulation if the intergeneration time is small (such as 0.3) because the queue gets longer and longer.
The average waiting time in the queue is zero if the intergeneration time is larger than the service time (such as 1.1) because every entity that arrives at the queue is able to depart immediately.
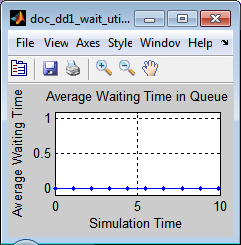
Information About Race Conditions and Random Times
Other examples modify this one by varying the processing sequence for simultaneous events or by making the intergeneration times and/or service times random. The modified examples are:
Using Random Intergeneration Times in a Queuing System (директория R2013a>SimEvents>Getting Started with SimEvents>Specify Intergeneration Times for Entities)
Random Service Times in a Queuing System (директория R2013a>SimEvents>Getting Started with SimEvents>Model Basic Queueing Systems)
Конец раздела Explore Simulations Using the Debugger and Plots директории R2013a>SimEvents>Getting Started with SimEvents.
