
- •29 Word study Verbs and related nouns
- •34 Language study Describing a process
- •3 6 Writing Describing a process
- •Tuning-in
- •66 Writing 2 Ordering components
- •74 Tuning-in
- •81 Listening
- •82 Language study Would
- •In the future, electronics are likely to become even more common in the home as multimedia entertainment systems and computer-controlled robots are developed.
- •Rf carrier
- •Introduction to Electronic Systems
- •16 Weeks X 2 VI hours
- •When is the lunch break?
- •10 These tolerances may seem to reflect poor manufacture but in most circuits they are, in fact, quite satisfactory. Relaxing the tolerance enables the makerto sell them more cheaply.
- •X varactor diode
- •Identify each of the following diodes:
- •10 The first stage consists of a transformer which steps down the voltage of the ac mains (see Fig. 2).
- •Smoothed dc input
- •15 Common is reverb (reverberation) which can make the music sound as if it was recorded in a very large building or a very small room.
- •Making a recording Places People Equipment
- •4 How is mixing down like developing and printing a photograph?
- •In this text which are additional to those given on the tape.
- •3 You must always keep an eye on the recording level.
- •1 A photodiode picks up rays from the remote control.
- •Ir diode
- •2 How many detection devices does it show? Name them.
- •4 If a burglar walks in front of a motion sensor,
- •7 A magnet on the moving part trips a switch if
- •Sensing device Used to detect
- •9V battery
- •In a frequency-modulated (fm) wave, the audio signal is combined with the rf carrier wave to vary the frequency of the carrier (see Fig. 2).
- •Af power amplifier
- •Via di Pietra Papa 00146 Roma
- •25 Die away naturally. As it dies, the current in the object reactivates the search coil. This voltage is then amplified to indicate with a sound or a flashing light that an object has been found.
- •4 The magnetic field a voltage in the search coil.
- •5 Noise is also by the low-frequency mains supply.
- •In left
- •In right о г
- •Interviewer: a test engineer. What would that involve?
- •I Is there any other kind of work you! enjoy?
- •15 Instead of recording the sound waves continuously, a drum з
- •4 These are converted to electrical signals by (use) a microphone.
- •15 Vinyl records are eliminated such as 'crackle' caused by dust and static, and 'jumping', due to scratches on the recording surface.
- •8 What might be the effect of so many people having cd players?
- •1 Unlike lPs, cDs use a digital recording system.
- •7 The electron gun in a crt a stream of electrons.
- •20 With an oscilloscope so that a visual display of the waveform can be seen.
- •45 Electrons.
- •Video cassette recorder
- •Italics from the text below. One has been done for you.
- •Vhs video-recorder mechanism
- •15 The number of iCs used in a computer, I.E. The chip count, can be reduced by connecting nand gates together to form other types of gates (see Fig. 3).
- •Integration as shown in Table 1. The 1с shown in Fig. 2 is an ssi 20 device but microprocessors used in computers are vlsi or slsi devices.
- •Input impedance low high
- •Instead of using the complicated springs, cogs, and wheels of a mechanical watch, the digital watch uses a vibrating crystal to keep time. It is accurate to one second in 10 years.
- •Vibrating crystal
- •15 Each one-second pulse triggers the microchip to send signals to the digital display to advance the numerals by one second.
- •Xdiaphragm
- •65 System.
- •1 Engineers developed optical fibre cables in the 1980s.
- •2 What is the purpose of the dielectric material in coaxial cable?
- •Insulator (e.G. Polyethylene) sheath
- •Insulator (e.G. Polyethylene) covering wire
- •25 Microwaves can be guided along rectangular copper ducts by a series of reflections from the inner walls (see Fig. 4).
- •If you make a mistake when keying in a number and you want to delete the last digit:
- •If you hold down clr,the whole numberwill be deleted and the p3 will go back to standby.
- •3 What is the difference between a mobile phone and a cellphone?
- •20 Telephone calls at the same time. To achieve this, each
- •30 Compromise between the number of frequency channels available in each cell and the interference between communications in different cells.
- •40 Calls from other cellphones and fixed telephones throughout the whole telephone system (see Fig. 2).
- •50 Call, the 8kHz signal is discontinued and the speech channel is enabled.
- •8 The signal indicates a suitable frequency channel for the call.
- •5 Converts the binary data into digital information (lines 21-22)
- •International international
- •40 As ordering goods and controlling bank accounts.
- •1 Avionics
- •2 Computing
- •3 Defence
- •1991-Present
- •1990-1991 Summer 1989
- •1 A technician with experience in servicing hospital equipment.
- •4900 University Avenue
- •If you would like to hear about outstanding opportunities in Europe to work in the expanding area of personal communication systems, write to:
- •If you can fill one of these vacancies, contact us at once.
- •I'm interested. I have the following training/ experience:
- •If a target is hit. .
- •Input signal
- •1 Manufacturing
- •2 Planning
- •3 Installation
- •4 Commissioning
- •If a target is hit. .
- •5 Maintenance
- •6 Sales
- •8 Research and Development
- •30 Large companies run their own r&d departments. Exciting
- •Induced in an inductor in opposition to the
- •Video image of the internal organs of a
- •2 [13] One side (left or right) of a stereo
- •In one unit and sharing a common
- •Voltage produced by an electrical source
- •241 Solid cylinder of metal oxide insulating
- •Video picture flip-flop /'flip йар/ [24] digital electronic
- •Instrument used for detecting pulses and
- •1 Or 0, high or low) long wave /'log weiv/ [10] range of radio
- •Voltage ac electricity supply maintain /mem'tem/ [22, 29] keep in good
- •Integrated circuit on one piece of silicon microcomputer/,maikraukam'pju:ta(r)/
- •Instrument for measuring various electrical quantities including voltage, current and resistance
- •Inputs are high natural frequency /.Naetjaral 'fri:kwansi/
- •Voltage ionizes the neon gas inside network /'netw3:k/ [26] system of
- •Interconnected devices network manager /,netw3:k 'тгепк1зэ(г)/
- •Interconnected telephone lines for use by
- •In a public telephone network which
- •Voltage which causes a component to pass
- •Various signals used in the test and
- •Integration: between 104 and 10s active
- •Voltage level from varying stable /'steibl/ [24] in a balanced state stage /steid3/ [5] circuit block: section of
- •In a circuit suppress /sa'pres/ [18] prevent a signal
- •Iks,tjemd3/ [28] switching centre for
- •Video signal teletype terminal /'telitaip ,t3:minal/ [28]
- •Images over long distances television receiver Ле1шзп n,si:v9(r)/
- •Isolating an ac supply voltage transistor /traen'zistsir)/ [1]
- •28] Cable or duct for guiding signals
- •Variable capacitor or resistor for making
- •V/VI:/[4, 11] volt
- •Vacuum tube /'vaekjuim tju:b/ [1 ]
- •Vdu /VI: di: 'ju:/ [28] visual (or video)
- •Video screen vdu terminal /VI: di: 'ju: ,t3:min3l/ [28]
- •Video recorders
- •Video-conferencing
- •Voltmeter I
20 With an oscilloscope so that a visual display of the waveform can be seen.
Reading
Information
transfer
The
task which follows provides further practice in combining
information from a diagram and a text when reading.
Task
5 With
the help of this diagram, complete the gaps in the text.
first
accelerating anode A1
Aquadag
coating
phosphor
coating on inner side of screen
focusing
anode A2
cathode
С
pins
for electrical connections
heater
filament
electron
gun section: cathode plus intensity and focusing system
deflection
system
(electrostatic)
CRT
construction
Fig.
7
Cathode
ray tube
Televisions
as well as computers, radar systems, and oscilloscopes use a cathode
ray tube (CRT) to produce an output display. The construction and
operation of the CRT is similar in each case but the simplest type
of CRT is found in oscilloscopes.
A
CRT is really a large vacuum tube valve. It has 1 main
sections.
The
first section is an electron which emits a stream of electrons.
The
electron gun contains an electron lens which 3 the
electrons
into
a narrow electron *
The
second section is a! system,
which allows the beam to be
moved
t or
horizontally. Oscilloscopes use charged metal
I to
give8 deflection,
whereas television sets use
electromagnetic
coils to give electromagnetic
The
last section is a screen with a - coating.
The electron beam
hits
the screen, making the phosphor glow and causing a spot to be
displayed. The colour of the spot depends on the type of phosphor
used.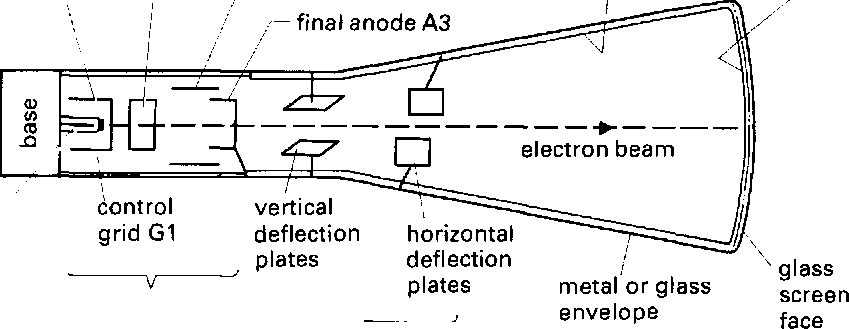
Language study Cause and effect, 2
Study these statements:
The electron beam hits the screen.
The phosphor glows.
Why does the phosphor glow? What is the relationship between statement (1) and (2)?
Statement (1) is a cause and statement (2) is an effect. We can link cause and effect statements in a number of ways. Study these ways, which use cause and make.
The electron beam hits the screen causing the phosphor to glow. The electron beam hits the screen making the phosphor glow. Now study these cause and effect statements:
The phosphor glows.
A spot is displayed.
The effect is in the passive. We can link cause and effect like this: The phosphor glows causing a spot to be displayed.
Link each of these cause and effect statements to make one sentence:
a A magnetic field is set up in the speaker coil,
b The coil vibrates.
a The coil pushes and pulls the speaker cone,
b Sound waves are produced.
a A voltage is applied to a quartz crystal, b The quartz crystal expands and contracts.
a A voltage is applied to the Y-plates. b The electron beam is deflected.
a Current flows through the filament, b The heater glows.
Word Study Compound nouns, 2
Study these examples of compound nouns:
a signal generator = equipment for generating signals a cassette player = equipment for playing cassettes a battery tester = equipment for testing batteries
What do we call equipment for ... playing CDs? receiving radio (signals)? charging batteries? amplifying aerial (signals)? filtering (out) noise? synthesizing speech? cleaning cassette heads? amplifying (the) power (of a signal)? sensing vibration?
scanning (the human) body (for disease)?
Technical reading Cathode ray oscilloscope
Task 8 Work in groups of three: A, B, and C.
Student A: Read Electron gun and take notes. Student B: Read Deflection system and take notes. Student C: Read Phosphor screen and take notes.
Using your notes and Fig. 1 on page 104, explain to the others in your group how your section of the CRT works. A should start. В may use Fig. 2 as part of the explanation.
Electron gun para
A stream of electrons is released from the surface of the cathode (C) 1 when it is heated by the heater filament. The electrons are accelerated towards the screen by a set of three positively-charged cylindrical anodes (A1, A2, A3). Each anode has a higher charge 5 than the one before. As the electrons move towards the anodes, they pass through a hole in a negatively-charged metal disc. This disc is known as the control grid. By adjusting the intensity control on the oscilloscope, the charge on the grid can be varied. This allows the number of electrons reaching the screen, and therefore io the brilliance or brightness of the spot on the screen, to be adjusted.
The three anodes form the electron lens. The oscilloscope focus 2 control allows the ydltage on the second anode (A2) to be varied and causes the stream of electrons to be focused into a narrow beam. If the oscilloscope has an astigmatism control, it is used to 15 vary the voltage an the third anode (A3). This allows the shape of the spot on the screen to be adjusted to make it perfectly round.
Deflection system
After leaving the electron gun, the electron beam is deflected by з two pairs of parallel metal plates. The pairs of deflection plates are situated at right angles to each other.
20 The signal to be measured is amplified by the Y-amplifier in the 4 oscilloscope, then applied to the first set of deflection plates, known as the Y-plates. This causes the electron beam to be deflected vertically in proportion to^he magnitude of the input signal.
The oscilloscope has a timebase generator which produces a 5
25 sawtooth wave output as shown in Fig. 2.

para
This is fed into the X-amplifier of the oscilloscope, then applied to 6 the second set of deflection plates, known as the X-plates. This causes the electron beam to be deflected in the horizontal direction in such a way that the spot moves from left to right across the 30 screen at a steady rate. When it reaches the right side of the screen, it rapidly returns to the left side again. This allows the screen to show how the measured signal varies with time.
Phosphor screen
The X and Y deflections of the electron beam cause the signal being 7 measured to be displayed in the form of a wave, with the 35 magnitude of the signal being given on the vertical axis and the time variation on the horizontal axis. A piece of transparent plastic known as a graticule is attached to the front of the screen. This has a grid of horizontal and vertical lines marked on it and allows accurate measurements of the signal to be made.
40 A large build-up of negative charge could be caused by the electron 8 beam hitting the phosphor screen. To help prevent this, the inside of the CRT, between the deflection system and the screen, is coated with a carbon compound known as Aquadag. This is attached to the high voltage anode (A3) to provide an escape path for the excess
