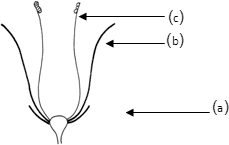
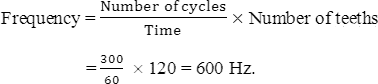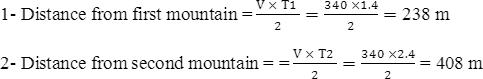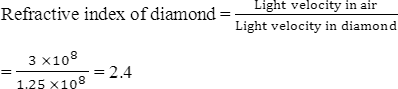1) Natural:
Done by many ways as rhizoids buds as in:
a- Sweet potatoes (roots)
b- Potatoes (stem)
c- Sugar cane
d- Palm
2) Artificial reproduction by vaccination:
a- Vaccination by sticking.
b- Vaccination by stamen.
c- Tissue culture.
Lesson Two
* Aim of reproduction for human beings is to keep the kind from extinction.
* Reproduction in human beings is conjugal sexual reproduction done between two matures by reproductive systems.
Male reproductive system:
1) Two testes:
Oval shape glands exist inside skin bag called (scrotum) to keep the testes outside the body.
Function of testes:
1. Production of male reproductive cells (sperms)
2. Production of testosterone hormone which is responsible for male secondary sex characters.
Puberty features in male are:
a. Growth of hair in different parts of body.
b. Rough sound and growth of muscles.
c. Growth of sexual organs.
2) Uriengental duct:
Transfer sperms from two testes and it end by penis.
3) Sexual glands: (Cowper’s – prostate – seminiferous)
They produce seminal liquid which causes:
(1) Feeding of sperms.
(2) Facilitate their movement.
(3) Neutralize the acidity uriengental duct.
Female reproductive system:
It consists of:
(1) Two ovaries:
It has a size of a peeled almond their function is:
a- Production of (ova) each 28 days from each ovary.
b- Production of hormones (estrogen and progesterone) to appear female secondary sex characters.
Puberty features in female:
a- Soft sound, growth of breasts.
b- Growth of hair.
c- Menstrual cycle each 28 days.
(2) Fallopian tube:
Funnel-shaped tube catches ovum and pushes it towards the uterus.
(3) Uterus:
Muscular organ has a pear shape lined from inside by many blood vessels to feed the embryo till the birth.
(4) Vagina:
Tube ended by gentle open in female.
Fertilization in human:
The (ovum) is large in size storing food for embryo, it consists of nucleus contains hereditary substance, cytoplasm and surrounded by cellular wall.
The sperm:
Consists of head contains hereditary substance then neck and tail which is responsible for the movement of the sperms.
Fertilization:
Fusion of sperm head with 23 chromosomes with nucleus of ovum with 23 chromosomes to form zygote contain 46 chromosomes which grow to form embryo.
Stages of growth of embryo:
1) First stage:
Till the sixth week where the head is formed.
2) Second stage:
From the seventh week to the twelfth week where the face, limbs and sexual organs are formed.
3) Third stage:
From the 13th week to the 22 nd week where bones and blood circle then motion of embryo.
4) Fourth stage:
From 23rd to the time of birth where all the systems of the body are formed.
Venereal diseases:
Diseases attack the reproductive systems can be divided into:
1. Diseases without sexual connection as uterus cancer or prostate cancer or labour fever.
2. Diseases due to sexual connection between two individuals one of them is infected as:
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- AIDS
Unit One |
Oscillatory motion |
The wave motion |
Unit Two |
Properties of sound waves |
Reflection of sound |
Nature of light waves |
Reflection and refraction of light |
Unir Three |
Reproduction in flowering plants |
Lesson Two |
General Exams |
Q 1- The complete vibration includes ……… displacements, each is called ……… . four – amplitude
|
2 - Frequency is measured by unit called ……… and its symbol is ……… . Hertz – (HZ)
|
3 - Frequency × Periodic time = ……… . 1
|
4 - The maximum displacement reached by the vibrating body far from its original position is ……… . amplitude
|
5 - The vibrational motion is done by the vibrating body at ……… of original position. both sides
|
6 - The complete vibration is done when the vibrating body passes ……… in the same direction. Two successive times
|
7 - A Pendulum makes 30 complete vibrations in 6 seconds, its frequency = ……… 5HZ
|
8 - Kilo Hertz = ……… HZ while Mega Hertz = ……… HZ. 1000 – 1000,000
|
Q uestion two: Write the scientific term: 1- The motion done by the vibrating body at both sides of its original position. Vibrational motion
|
2 -The maximum displacement reached by the vibrating body far from its original position. Amplitude
|
3 - Number of complete vibrations done in one second. Frequency
|
4 - The time needed to make one complete vibration. Periodic time
|
5 - Measuring unit of frequency equals 1× 109 Hertz. Giga Hertz
|
Q uestion three: Give reasons for: 1- The frequency decreases by increasing Periodic time. Because frequency inversely proportional with Periodic time.
|
2 - The vibration motion is a Periodic motion. Because it repeats itself at equal time intervals.
|
Q uestion four: What is meant by ? 1- Number of complete vibrations made by vibrating body in time of 10 seconds is 500. This means that frequency = 50 HZ.
|
2 - The amplitude is 6 cm. It means that the maximum displacement reached by the vibrating body far from its original position is 6 cm.
|
3 - Frequency of tuning fork is 600 complete vibrations / second. It means that it makes 600 complete vibrations in one second.
|
4 - The Periodic time of simple pendulum is 0.01 second.. It means that it makes one complete vibration in 0.0.1
|
5 - The time of 60 complete vibrations is one minute. It means that periodic time is 1 second.
|
Q uestion five: Choose the correct answer: 1- The maximum displacement reached by the vibrating body away from its original position is ……… (frequency – complete vibration – amplitude – vibrational motion) amplitude
|
2 - One amplitude is ……… of complete vibration. (four times – equal one – quarter – half) quarter
|
3 - A musical instrument produces frequency of 256 Hertz, this means that the chord of instrument ……… . (has length of 265 cm – produces waves of 256 cm wave length – produces waves of velocity 256 cm/second – vibrates by 256 complete vibrations in one second) vibrates by 256 complete vibrations in one second
|
4 - A body makes 480 complete vibrations in one minute, its frequency is ……… (2 – 4 – 6 – 8) 6
|
5 - If the frequency of vibrating body is 6 Hertz so it makes ……… complete vibrations in one minute. (30 – 60 – 360 – 600) 360
|
Q uestion one: Complete the following: 1- Waves are classified due to their ability to propagate in space into ……… and ……… . electromagnetic waves – mechanical waves
|
2 - The crest in ……… waves represented by ……… in longitudinal waves. transverse – rarefaction
|
3 - Radio waves are ……… waves which can propagate in space by speed ……… . electromagnetic – 3 × 108 m/sec
|
4 - If the distance between the centre of third compression and center of fifth compression in longitudinal wave is 20 cm, so the wave length is ……… .
10 cm
|
5 - In transverse waves particles vibrate in ……… direction propagation direction. perpendicular
|
6 - The longitudinal wave consists of ……… and …….. . compressions – rarefactions
|
7 - Particles vibrate in the longitudinal wave in ……… direction of wave propagation. the same
|
8 - The wave length of transverse wave equals the distance between ……… or ……… . two successive crests – two successive troughs
|
9 - Radio waves are ……… waves, while the sound is ……… waves. electromagnetic – mechanical
|
Q uestion two: Write the scientific term: 1- Transverse waves can propagate in space. |
2 - The maximum displacement of particles upwards. Crest
|
3 - The maximum displacement of particles downwards. Trough
|
4 - The distance between two successive crests or troughs. Wave length of transverse wave
|
5 - A disturbance in the medium where particles vibrate in perpendicular direction of wave propagation. Transverse wave
|
6 - Disturbance in the medium where particles vibrate along the wave propagation direction. Longitudinal wave
|
7 - Places where particles are very close. Compression
|
8 - The distance between centres of two successive compressions or rarefactions. Wave length of longitudinal wave
|
Q uestion three: Give reasons for 1- Radio waves are electromagnetic while sound waves are mechanical. Because radio waves can propagate in space while sound waves need a medium to propagate.
|
2 - Water waves are mechanical transverse waves. Because they consist of crests and troughs.
|
3 - We see lightning first then hearing thunder. Because lightning is electromagnetic waves of high speed while thunder is mechanical waves.
|
Q uestion four: What is meant by 1- Wave length of longitudinal wave is 25cm. It means that the distance between centres of two successive compressions or rarefactions is 25 cm.
|
2 - Wave length of transverse wave is 2 meters. It means that the distance between two successive crests or troughs is 2 metres.
|
3 - The light velocity is 3 × 108 m/sec. It means that distance travelled by light in one second is 3 × 108 metres.
|
Unit Two
Properties of sound waves
Sound is an external effect affects on ear causing sense of hearing.
Sound is produced due to vibration of bodies, and it stops when vibration stops.
Sound is mechanical longitudinal waves, propagate in medium as spherical waves and its centre is the source of sound.
Sound velocity in air is 340 m/sec and it increases or decreases in different media.
Properties of sound are:
1) Sound pitch
2) Sound intensity
3) Sound quality
1- Sound pitch:
The property by which human ear can distinguish between sharp and rough sounds.
Sound pitch depends on frequency:
- High frequency :- sharp
- Low frequency :- rough
2- Sound intensity:
The property by which the human ear can distinguish between strong and weak sounds.
Sound intensity is measured by unit Watt/m2
Intensity of noise is measured by unit Decibel.
Factors that affect sound intensity:
a- Distance between sound source and ear
b- Amplitude of sound
c- Surface area of vibration
d- Density of medium
e- Wind direction
Application on sound intensity:
Ears blocks that are made of silicon to protect ears from noise.
3- Sound quality
The property by which human ear can distinguish between sounds from different sources even they have the same pitch and intensity.
We can distinguish between sounds due to presence of harmonic waves that accompany the fundamental waves produced.
Audible and non-audible waves.
Audible waves (sonic waves) have frequency ranges between 20:20.000 Hz.
Non-audible waves:
- Infrasonic waves’ frequency less than 20 Hz.
- Ultrasonic waves’ frequency more than 20.000 Hz.
Uses of ultrasonic waves:
1) Decaying of stones in kidney and ureters.
2) Diagnosis of some diseases and treatment of cancer.
3) Sterilizing of food.
4) Detection of explosives underground (Landmines).
Q uestion One: Complete the following: 1- Sound is produced due to ……… of objects. vibration
|
2 - Sound waves are ……… waves that consist of ……… and ……… . longitudinal – compressions – rarefactions
|
3 - Sound waves transfer as ………, it center is……… . spheres – source of sound
|
4 - Audible sound ranges between ……… and ……… Hz. 20 – 20.000
|
5 - The distance travelled by sound in one second is ……… . velocity
|
6 - From sound properties is ……… by which we can distinguish between weak and strong sound. sound intensity
|
7 - Noise is measured by unit called ……… . Decibel
|
8 - The intensity of sound is ……… proportional with amplitude. directly
|
9 The intensity of sound is measured by unit ……… . Watt/m2
|
1 0- The man has ……… sound, while sound of woman is ……… . rough – sharp
|
1 1- If the direction of wind opposes the direction of sound, the intensity of sound ……… . decreases
|
1 2- ……… wheel in used to prove the relation between ……… and pitch of sound. Savart – frequency
|
1 3- The source of sound produces ……… and ……… tones. fundamental – harmonic
|
Q uestion two: Write the scientific term: 1- Sound waves of frequency ranges between 20:20.000 Hz. Audible waves
|
2 - Sound waves with frequency more than 20.000 Hz. Ultrasonic waves
|
3 - Sound waves with frequency less than 20. Hz. Infrasonic waves
|
4 - Distance travelled by sound in one second. Sound velocity
|
5 - V = r Law of wave propagation in sound
|
6 - The property by which ear can distinguish between sharp and rough sounds. Sound pitch
|
7 - The property by which ear can distinguish between strong and weak sounds. Sound intensity
|
8 - The property by which ear can distinguish between different sounds. Quality of sound
|
9 - Instrument used to find a relation between frequency and pitch of sound. Savart wheel
|
1 0- The measuring unit of sound intensity. Watt/m2
|
1 1- The basic tone in sound quality. Fundamental tone
|
1 2- Tones are used to distinguish between sounds. Harmonic tones
|
1 3- External factor affects on ear causing hearing. Sound
|
Q uestion Three: Give reasons for… 1- Ears can distinguish between sounds of musical instruments. Due to difference in harmonic tones.
|
2 - Sound intensity in carbon dioxide is more than air. Because carbon dioxide has higher density.
|
3 - Ultrasonic waves used to sterilize milk. Because its high frequency kills the microbes.
|
4 - The woman has sharp sound while the man has rough sound. Because frequency of sound is high in the woman while sound of the man has low frequency.
|
5 - Sound intensity decreases as we go far from source of sound. Because sound intensity is inversely proportional with square of distance.
|
6 - When the vibration of the wings of mosquito stops we don’t hear sound. Because sound is produced due to vibrations of objects.
|
Q uestion Four: Problems: 1) Calculate frequency of savart wheel rotates by 300 cycle/minute when it touches a gear of 120 teeths.
|
2 ) Calculate the number of cycles in savart wheel produces 500 cycle/sec. If the number of teeths is 25 teeths.
|
Reflection of sound
Sound reflection:
The rebounding of sound waves when they fall on a reflecting surface.
Laws of sound reflection:
1) Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
2) The incident sound ray, reflected sound ray, and the perpendicular line from point of incidence on reflecting surface are all in one plane perpendicular to the reflecting surface.
Echo:
The repetition of sound due to reflection.
Conditions of echo:
1) Huge reflecting surface.
2) Time not less than 0.1 second.
3) Distance not less than 17 metres.
Applications on echo:
1) Determine sound velocity in air
2) Concentration of sound by using concave surfaces.
3) Estimation of sea depth and places of fish gathering.
4) Examining weldings of metals in industry.
5) Medical examinations.
6) Used by bats to fly in darkness.
Q uestion One1: Complete the following: 1- For echo to happen it needs ……… as ……… . huge surface – mountain
|
2 - The ……… sound ray, ……… ray and ……… line are all in one plane. incident – reflected – perpendicular
|
3 - Sound reflection is used to determine ……… inside alloys. holes
|
4 - Angle of incidence = ………. . Angle of reflection
|
|
Q uestion Two: Write the scientific term: 1- Repetition of sound due to reflection. Echo
|
2 - Rebounding of sound when it falls on surface. Sound reflection
|
3 - Focusing sound by concave surfaces. Concentration of sound
|
4 - Property by which bat can fly at night. Sound reflection
|
Q uestion Three: Give reasons for: 1- Fox has large and concave ears. To collect sound waves and concentrate it inside ears.
|
2 - Dolphins don’t not collide with things during swimming. Because they produce ultrasonic waves determine places of things in front of them.
|
3 - In great mosques sound is strong without loud speakers. Because they have concave surfaces that collect sound and concentrate it.
|
4 - We can determine depth of sea. By using ultrasonic waves we determine depth from relation.
|
Q uestion Four: Problems: 1) Calculate the depth of sea when waves are sent with velocity 1490 m/sec and time of reflection is 0.1 sec.
|
2 ) A person stands between two mountains then he made a sound he heard two echoes. The first after 1.4 seconds and the second after 1 second from the first echo. Calculate the distance between him and each mountain taken that speed of sound in air 340 m/sec.
|
Nature of light waves
Visible light waves:
Electromagnetic waves, their wave length ranges between “380 : 700” nanometre.
Light velocity:
The distance travelled by light in one second = 3 108 m/sec.
The main source of light is the sun.
Light analysis:
- The white light consists of (7) colours called spectrum colours (Red – Orange – Yellow – Green – Blue – Indigo - Violet)
- Light can be analyzed by (Triangular prism)
- Energy of light quantum is composed of (Photons)
- Energy of light quantum = constant (Planck’s constant) Frequency of photon
Light behaviour in different media: Media can be classified due to their ability to allow light to pass through into:
1- Transparent:
That primits light to pass (air – pure water).
2- Opaque:
Doesn’t primit light to pass (paper – wood)
3- Semitransparent (translucent):
Primits part of light to pass and absorb another part.
Ex: rough glass.
- The increase in thickness of transparent medium decreased its ability to transmit light through.
- Light travels in straight lines can be controlled in its thicknes.
Light intensity (Brightness):
- The amount of light that falls perpendicular to a unit area unit area in one second.
- Light intensity decreases by increasing the distance between the surface and source of light.
The Inverse Square Law:
The light intensity that falls of a surface is inversely proportional to the square of distance between the surface and the source of light.
Q uestion One: Complete the following: 1- Light is considered as ………. waves. Their wave length ranges between ………. : ………. Nanometer. electromagnetic – 380 – 700
|
2 - ………. is the distance travelled by light in one second. Light speed
|
3 - The white light consists of ………. colours started with ………. and ended by ………. . seven – red – violet
|
4 - Energy of light quantum = ……… × frequency. constant
|
5 - Increasing the thickness of medium decreasing the ……… of light through it. transmission
|
6 - The light propagates in air as ………lines. straight
|
7 - Light intensity is the amount of light that falls ……… on the unit area in one second. perpendicular
|
8 - Light intensity ……… proportional with square of distance between surface and ……… inversely – source of light.
|
9 - Air is ……… medium, while milk is ……… transparent – opaque
|
1 0- We can use ……… to analyze light. prism
|
Q uestion Two: Give Reasons for: 1- The energy of red light is smaller than orange colour. Because the frequency of red colour is smaller than orange colour.
|
2 - We can’t see impurities in black honey. Because black honey is an opaque body.
|
3 - Energy of light quantum depends on its frequency. Because energy = frequency × constant, so as frequency increases energy increases.
|
4 - Light intensity is inversely proportional with square of distance. Because when the distance increases the light intensity decreases.
|
Q uestion Three: Write the scientific term: 1- Electromagnetic waves travel in straight lines. Light
|
2 - Dispersing white light into seven colours. Light analysis
|
3 - Instruments used to analyze white light. Triangular prism
|
4 - The colour of lowest frequency. Red colour
|
5 - The scientist who proved that light consists of quantum of light. Max Planck
|
6 - A medium that doesn’t allow light to pass through. Opaque
|
7 - The amount of light that falls perpendicular on the unit area in one second. Light intensity
|
8 - The light intensity is inversely proportional with square of distance between surface and source of light. Inverse square law
|
Reflection and refraction of light
Light reflection:
The rebounding of light waves when they fall on reflecting surface.
Kinds of reflection:
1) Regular reflection:
The reflected rays rebound in one direction when they fall on smooth surface.
2) Irregular reflection:
The reflected rays rebound in many directions when they incident on a rough surface.
Laws of Light Reflection:
1) Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
2) The incident light ray, reflected light ray and the perpendicular line are all in one point perpendicular to the reflecting surface.
Note:
If an incident light ray is perpendicular on a reflecting surface, it reflects on itself because angle of incidence = angle of reflection = zero
Some instruments that depend on light reflection:
1) Periscope:
Used in submarines and watching dangerous reactions.
2) Optical fibers:
Used in medical scopes
Light refraction:
The change in direction of light due to its transference from transparent medium to another with different optical density.
Optical density:
The ability of transparent medium to refract the light rays.
Angle of incidence:
The angle between incident light ray and the perpendicular line.
Angle of refraction:
The angle between the refracted ray and the perpendicular line.
Emergency angle:
The angle between emergent light ray and perpendicular line.
Laws of light refraction:
1) When light transfers from low optical density to high optical density, it refracts near the perpendicular line.
2) When light transfers from high optical density to low optical density, it refracts far from the perpendicular line.
Refractive index is more than 1
Critical angle:
If the refraction angle in the medium of low optical density equal 90o, the angl in the medium of the high optical destiny is the critical angle of this medium.
Total internal reflection:
When light ray falls from high optical density with incident angle is greater than the critical angle, it reflects to the same medium.
Natural phenomena:
Related to reflection and refraction:
1) Seeing objects with up normal shape.
2) Seeing objects in virtual positions.
3) Mirage.
Q uestion One: Complete the following: 1- The rebounding of light rays back to the source is called ……… of light. reflection
|
2 - The reflection of light can be divided into ……… or ……… . regular – irregular
|
3 - When the light falls on rough surface it is called ……… reflection. irregular
|
4 - Angle of incidence = ……… . angle of reflection
|
5 - If the light ray falls ……… it reflects on itself where angle of ……… =……… equal zero. perpendicular – incidence – angle of reflection
|
6 - The ……… instrument is used in submarines. periscope
|
7 - The light ……… are used in medical ……… to make operations without surgery. fibers – scopes
|
8 - The ability of medium to refract light is called ……… . optical density
|
Q uestion Two: Give reasons for: 1- Occurrence of Mirage. Due to the refraction of light indifferent atmosphere layer in temperature
|
2 - The perpendicular light ray reflects on itself. Because angle of incidence = angle of reflection = zero.
|
3 - Objects are seen some times upnormal. Due to light refraction.
|
4 - The bottom of swimming pool is seen higher than its real place. Due to light refraction.
|
5 - The refractive index is greater than (1). Because velocity of light in air is greater than its velocity in any medium.
|
6 - Occurrence of light refraction. Due to the change in light velocity indifferent media with different optical density.
|
Q uestion Three: Write the scientific term: 1- The rebounding of light waves on falling on a reflecting surface. Light reflection
|
2 - The reflection of light rays in one direction on falling on smooth surface. Regular reflection
|
3 - The reflection of light rays in different directions from rough surface. Irregular reflection
|
4 - Angle of incidence = angle of reflection First law of reflection
|
5 - Instrument used in submarines to see under water. Periscope
|
6 - The angle between refractive ray and perpendicular line. Angle of refraction
|
7 - The change of light direction on transferring from transparent medium to another. Light refraction
|
8 - The relation between light velocity in air and light velocity in medium. Refractive index
|
9 - The angle when the incident angle in the medium of lowest density = 90ْ Critical angle
|
Q uestion Four: What is meant by: 1- Refractive index of water is 1.3 It means that ratio between light velocity in air and velocity in water is 1.3
|
2 - Seeing objects upside dwon in desert at noon time. Mirage
|
3 - Light reflects on itself. It means that light falls perpendicular.
|
Q uestion Five: Problems: Calculate the refractive index of diamond if the light velocity in it is 1.25 × 108 m/sec
|
Unir Three
Q uestion One: Complete the following: 1- The flower grows on ……… bud on the ……… . floral – stem
|
2 - The male organ in flower is ……… while the female organ is ……… . stamen – pistil
|
3 - The male flower has ……… whorls which are ………, ……… and ……… . three – calyx – corolla – stamen
|
4 - The stamen consists of ……… ended by ……… . filament – anther
|
5 - The pistil in flower consists of ………, style and ……… . stigma – ovary
|
6 - The anther consists of ……… sacs contain ……… . four – pollen grains
|
7 - Pollination is done by transferring ……… from ……… to ……… . pollen grains – anther – stigma
|
8 - Pollination in large coloured flowers is done by ……… . insects
|
9 - The flower that has four whorls is called ……… and its sex is ……… . typical – bisexual
|
1 0- As an example for unisexual flower is ……… . palm
|
1 1- The flower is the ……… organ in plant. reproductive
|
1 2- The pollination in the same flower is ……… . Self - pollination
|
1 3- If the ovary contains many ovums it forms ……… seeds as in ……… plant. many – bean
|
1 4- A sexual reproduction in plants is divided into ……… and ……… natural – artificial
|
Q uestion Two: Write the scientific term: 1- The reproductive system in flowering plants. Flower
|
2 - The complete flower. Typical flower
|
3 - Male reproductive organs in flower. Androcium
|
4 - Female reproductive organs in flower. Genocium
|
5 - Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma. Pollination
|
6 - Green coloured leaves surround the flower. Calyx
|
7 - Swollen part hold the flower parts. Receptacle
|
8 - Reproduction by green parts in flower. Vegetation
|
9 - Male cells spread in air. Pollen grains
|
1 0- The cell formed from combination of male cell with female cell. Zygote
|
1 1- The flower that contains pistil and stamen. Bisexual flower
|
Q uestion Three: Give reasons for: 1- Palm trees are unisexual flower. Because male flowers are separated from female flowers.
|
2 - Sun plant is not having self pollination. Because it is a unisexual flower.
|
3 - Stigma of flowers are sticky. To stick with pollen grains.
|
4 - Flowers have coloured petals. To attract insects to make pollination.
|
5 - Onion flower is typical bisexual flower. Because it contains all flower parts and male and female organ.
|
6 - Bees have important for plants. Because it helps in pollination process.
|
7 - Some flowers are hanged in air anthers. To spread pollen grains with air.
|
8 - Olive plant contains one seed. Because its flowers contains one ovum.
|
9 - Man make pollination in some plants. To produce important crops as date in palm
|
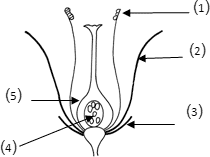
Q uestion Four: Study the following figure then answer:
1)
Label the figure.
1- Receptacle 2- Calyx 3- Corolla 4- Anther 5- Ovary
|
2 ) Write function of: 2 – 4 – 5 Function: 1- Protect the flower parts. 2- Produce pollen grains. 3- Contain ovules.
|
Lesson Two
* Aim of reproduction for human beings is to keep the kind from extinction.
* Reproduction in human beings is conjugal sexual reproduction done between two matures by reproductive systems.
Male reproductive system:
1) Two testes:
Oval shape glands exist inside skin bag called (scrotum) to keep the testes outside the body.
Function of testes:
1. Production of male reproductive cells (sperms)
2. Production of testosterone hormone which is responsible for male secondary sex characters.
Puberty features in male are:
a. Growth of hair in different parts of body.
b. Rough sound and growth of muscles.
c. Growth of sexual organs.
2) Uriengental duct:
Transfer sperms from two testes and it end by penis.
3) Sexual glands: (Cowper’s – prostate – seminiferous)
They produce seminal liquid which causes:
(1) Feeding of sperms.
(2) Facilitate their movement.
(3) Neutralize the acidity uriengental duct.
Female reproductive system:
It consists of:
(1) Two ovaries:
It has a size of a peeled almond their function is:
a- Production of (ova) each 28 days from each ovary.
b- Production of hormones (estrogen and progesterone) to appear female secondary sex characters.
Puberty features in female:
a- Soft sound, growth of breasts.
b- Growth of hair.
c- Menstrual cycle each 28 days.
(2) Fallopian tube:
Funnel-shaped tube catches ovum and pushes it towards the uterus.
(3) Uterus:
Muscular organ has a pear shape lined from inside by many blood vessels to feed the embryo till the birth.
(4) Vagina:
Tube ended by gentle open in female.
Fertilization in human:
The (ovum) is large in size storing food for embryo, it consists of nucleus contains hereditary substance, cytoplasm and surrounded by cellular wall.
The sperm:
Consists of head contains hereditary substance then neck and tail which is responsible for the movement of the sperms.
Fertilization:
Fusion of sperm head with 23 chromosomes with nucleus of ovum with 23 chromosomes to form zygote contain 46 chromosomes which grow to form embryo.
Stages of growth of embryo:
1) First stage:
Till the sixth week where the head is formed.
2) Second stage:
From the seventh week to the twelfth week where the face, limbs and sexual organs are formed.
3) Third stage:
From the 13th week to the 22 nd week where bones and blood circle then motion of embryo.
4) Fourth stage:
From 23rd to the time of birth where all the systems of the body are formed.
Venereal diseases:
Diseases attack the reproductive systems can be divided into:
1. Diseases without sexual connection as uterus cancer or prostate cancer or labour fever.
2. Diseases due to sexual connection between two individuals one of them is infected as:
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- AIDS
Q uestion One: Complete the following: 1- The function of tests is the production of ……… and ……… hormone. sperms – testosterone
|
2 - The function of ovary is the production of ……… and the two hormones ……… and ……… . ovum – estrogen – progesterone
|
3 - The sexual glands in male reproductive system are ………, ……… and ……… Cowper’s – prostate – seminiferous
|
4 - The ovary exist ……… abdominal cavity, while the two tests exist in ……… outside abdominal. inside – scrotum
|
5 - The female reproductive system contain ……… in size of peeled almond. ovary
|
6 - Secondary sex characters in male are due to ……… hormone. testosterone
|
7 - From the secondary sex characters in female is ……… which happen each 28 days. menstrual cycle
|
8 - The menopause age in female at age ……… years. 44:50
|
9 - The ovum moves inside ……… towards the uterus. fallopian tube
|
1 0- The sperm consists of ………, ……… and ……… . head – neck – tail
|
1 1- The male cell contains ……… chromosome and the female cell contains ……… chromosome. 23:23
|
1 2- When a sperm combines with ovum, ……… is formed. zygote
|
1 3- The growth of embryo takes ……… stages. four
|
1 4- The ……… has big size due to storing food. ovum
|
1 5- From venereal diseases that infect without sexual connection are ……… and ……… . uterus cancer – prostate cancer
|
1 6- The incubation period of gonorrhea is ……… weeks. 2:3
|
1 7- The urine has ……… effect, while seminal liquid has ……… effect. acidic – alkaline
|
Q uestion Two: Write the scientific term: 1- Two oval glands exist outside abdominal cavity. Two tests
|
2 - Fluid secreted by sexual glands. seminal fluid
|
3 - Female organ in size of peeled almond. Ovary
|
4 - Female organ where the embryo grows. Uterus
|
5 - Funnel shaped tube lined with cilia. Fallopian tube
|
6 - Male hormone secreted by tests. Testosterones
|
7 - One of the puberty features in female happens each 28 days. Menstrual cycle
|
8 - The time between infection and appearance of symptoms. Latent period
|
9 - The cell formed due to combination of sperm and ovum. Zygote
|
1 0- The stage of embryo in which bones and blood circle is formed. Third stage
|
Q uestion Three: Give reasons for: 1- The two tests exist outside the abdominal cavity. To keep the temperature of tests lower than the body to produce sperms.
|
2 - The seminal liquid has alkaline effect. To neutralize the acidity of uriengental duct.
|
3 - Removing of prostate cause sterility. Due to the stop of production of seminal liquid.
|
4 - Fallopian tube has cilia. To push the ovum inside towards the uterus.
|
5 - The uterus is lined with many blood vessels. To feed the embryo until birth.
|
6 - The baby can be born alive in the seventh month. Because all systems of his body is completed.
|
7 - Reproduction in human is sexual. Because it is done between two mature individuals male and female.
|
Q uestion Four: Write the function of: 1- Two tests Production of sperms and testosterone hormone.
|
2 - Urinogenital Transfer sperms from testes.
|
3 - Sexual glands Produce seminal fluid.
|
4 - Fallopian tube Push ovum inside uterus
|
5 - Uterus: Protect and feed embryo until birth
|
6 - Seminal liquid Feed sperms and facilate their movement.
|
7 - Testosterone: Appearance of male secondary sex characters.
|
8 - Progesterone and estrogen: Appearance of female secondary sex characters.
|
Q uestion Five: What will happen if? 1- Stop production of testosterone. The disappearance of secondary sex characters in male.
|
2 - Two tests exist inside the abdominal cavity. It will stop produce sperms.
|
3 - Fallopian tube was blocked. Ovum will not reach uterus and fertilization will not happen.
|
4 - Infection with Gonorrhea. It will cause sterility.
|
General Exams
EXAM 1
Q uestion One: A- Complete the following: 1- The complete vibration includes ……… displacement, each one is called ……… . four – amplitude
|
2 - Air is ……… medium, while milk is ……… medium. transparent – opaque
|
3 - The type of pollination done between two flowers is ……… while in the same flower is ……… . mixed – self
|
Q uestionTwo: A: Give reasons for: 1- Seeing lightning first then hearing thunder. Because the speed of light is much greater than the speed of sound.
|
2 - We hear sound of bells when they vibrate while no sound produced on being stopped. Because sound is produced due to the vibration of bodies and stopped when the vibration stops.
|
3 - Bees are important for farmers. Because they help in pollination between flowers.
|
4 - The semen fluid has alkaline effect. To neutralize the acidity of urienogental duct.
|
B :Choose the correct answer: 1- The frequency of pitch tone is ……… . (high – low – medium – none) high
|
2 - The energy of green light is ……… energy of yellow colour. (more than – lower than – equal to – all the previous) more than
|
3 - Genocium is a group of ……… . (stamens – pistils – petals – sepals) pistils
|
4 - Incubation period of labour fever is ……… days. (1:4 – 1:6 – 2:3 – 1:3) 1:4
|
Q uestion Three: A: Write the scientific term: 1- Producing one ripe ovum each 28 days from ovary. Ovulation
|
2 - The intensity of sound is inversely proportional with the square of distance between source of sound and surface. The inverse square law
|
3 - The measuring unit of noise. Decibel
|
B : What is meant by 1- Frequency of tuning fork is 600 HZ. It means that the tuning fork makes 600 complete vibrations in one second.
|
2 - Absolute refractive index of glass is 1.3. It means that ratio between light velocity in air and its velocity in glass is equal to 1.3.
|
3 - Man has rough sound. It means that frequency of man sound is low.
|
Q
uestion
Four:
1- Label the following diagram, then answer:
a- Sepal b- Petal c- Stamen
|
2 - What is the sex of this flower? Bisexual
|
3 - Function of organ (3) Producing pollen grains (male organ)
|
B : What will happen if: 1- A light ray is incident perpendicular on a reflecting surface. It will reflect on itself.
|
2 - Light ray transfers from lower transparent medium to another with high density. It will refract near the perpendicular line.
|
3 - Tiding or closing of Fallopian tube. Ovum will not reach the uterus and no fertilization will happen.
|
EXAM 2
Q uestionOne: A:Complete the following: 1- Kilo Hertz = ……… Hertz while Mega Hertz equals ……… Hertz. 1000 – 1000.000
|
||||||||||||
2 - The instrument ……… is used to prove the relation between ……… and pitch of sound. savart – frequency
|
||||||||||||
3 - The visible light waves have wave length of ……… to ……… nanometers. 380 – 700
|
||||||||||||
B : Compare between male and female organ flower:
|
||||||||||||
Q uestionTwo: A- Write the scientific term: 1- The amount of light energy falling perpendicular on unit area in one second. Light in density
|
||||||||||||
2 - Angle of incidence = angle of reflection. First law of reflection
|
||||||||||||
3 - One of artificial reproduction to produce large number of plants similar to the original plant. Tissue culture
|
||||||||||||
4 - The period between infection and appearance of symptoms. Incubation period
|
||||||||||||
B
:
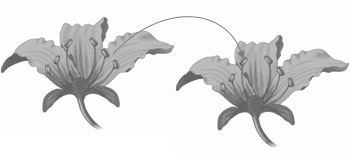
1- Mention the kind of pollination in the figure: Mixed pollination
|
||||||||||||
2 - What are the methods of pollination in each of? a- Large coloured flowers Insects
|
b - Hanging anthers flowers Air
|
c - Palm Man
|
Q uestion Three: A-Give reasons for: 1- Fallopian tube has a funnel shape and cilia. To catch ovum and push it towards uterus.
|
2 - Dolphins are not hitting obstacles during swimming. Because they produce ultrasonic waves.
|
3 - Ear can distinguish between musical instruments even they have the same intensity. Because they produce harmonic tones differ from fundamental tones.
|
4 - Petals are having beautiful colours. To attract insects to make pollination.
|
B : Write one function for: 1- Urenogental duct transfers sperms from testes
|
2 - Estrogene hormone essential for pregnancy
|
3 - Savart wheel finds the relation between frequency and pitch of sound
|
Q uestion Four: A: Choose the correct answer: 1- Menstrual cycle in female happens each ……… days. (14 – 23 – 28 – 56) 28
|
2 - Latent period of gonorrhea is ……… . (three days – week – three weeks – month) three weeks
|
3 - Sound doesn’t propagate in ……… . (water – air – space – solids) space
|
B : If you know that refractive index for salt solution is 1.53 and light speed in air is 3 × 108 m/sec Calculate light speed in salt solution |
EXAM 3
Q uestion One: Complete the following: 1- All of the following are parts of male reproductive system except ……… . (prostate – ovary – penis – Cowper’s) ovary
|
|||||||||
2 - Light refraction happens due to change in ……… of light in transparent media. (speed – intensity – frequency – concentration) speed
|
|||||||||
3 - Bats depend on ……… of sound to catch preys. (refraction – reflection – deviation –diffusion) reflection
|
|||||||||
4 - If the angle between incident ray and reflected ray is 30ْ , the angle of reflection = ……… (60ْ - 30ْ - 15ْ – 7.5 ْ ) 30ْ
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Two: A: Complete the following: 1- The anther consists of ……… sacs which contain ……… . four – pollen grains
|
|||||||||
2 - As examples of asexual reproduction in plants ……… and ……… . vegetation – tissue culture
|
|||||||||
3 - The menstrual cycle starts in females at age of ……… to ……… . 11 – 14
|
|||||||||
4 - From venereal diseases that transfer without sexual connection are ……… and ……… . uterus cancer – birth fever
|
|||||||||
B : Compare between male and female hormones (source - name):
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Three: Give reasons for: 1- Water waves are mechanical transverse. Because it needs a medium and consists of crests and troughs.
|
2 - Sound intensity in carbon dioxide is more than intensity in air. Because carbon dioxide has more density than air.
|
3 - Old mosques make sound loud without microphones. Because they have concave surfaces that concentrate the sound.
|
4 - Palm trees are unisexual plants. Because they contain male plants separated from female plants.
|
Q uestion Four: A: Write the scientific term: 1- The tone that accompanies the fundamental tones. Harmonic tones
|
2 - Sound waves less than 20 Hertz. Infrasonic
|
3 - The organ of sexual reproduction in plant. Flower
|
4 - Reproductive organ of a pear shape where the embryo grows. Uterus
|
B : Correct the word between brackets: 1- The formation of embryo in plant strain (Fallopian tube). ovary
|
2 - Gonorrhea is a disease caused by (virus). bacteria
|
3 - The least energy colour is (violet). red
|
4 - The ray that falls perpendicular the incidence angle = 90 zero
|
C : What is meant by: 1- Angle of incidence = 30ْ The angle between the incident ray and perpendicular line = 30ْ
|
2 - Ovulation: Production of female cells (ovum) from ovary each 28 days.
|
EXAM 4
Q uestion One: Write the scientific term: 1- Female organ in size of peeled almond produces ovum. Ovary
|
|||||||||
2 - Swollen part hold parts of flower. Receptacle
|
|||||||||
3 - 340 m/sec. Sound velocity
|
|||||||||
4 - The time taken by vibrating body to make one complete vibration. Periodic time
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Two: A: Give reasons for: 1- The oscillatory motion is periodic motion. Because it repeats the motion with time.
|
|||||||||
2 - Radio waves are used in communication in space. Because they are electromagnetic waves that can propagate in space.
|
|||||||||
3 - Man has rough sound while woman has sharp one. Because sound of man has low frequency while woman has high frequency.
|
|||||||||
4 - Onion flower is typical bisexual flower. Because it consists of 4 floral parts including male and female organs.
|
|||||||||
B : Compare between audible and non-audible sounds:
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Three: A: Choose the correct answer: 1- The venereal diseases are diseases that attack ……… (eye – liver – reproductive system –respiratory system) reproductive system
|
2 - The measuring unit of sound intensity is ……… (watt/m2 – decibel – hertz – m/sec) watt/m2
|
||||
3 - The ultrasonic waves are having frequency of ……… (less than 230 – more than 20.000 – less than 2000-2000) more than 20.000
|
||||
4 - The maximum displacement reached by the body is ……… (periodic time – frequency – amplitude – complete vibration) amplitude
|
||||
B : Write one use for: 1- Ultrasonic waves sterilizing of food
|
||||
2 - Radio waves communications in space
|
||||
3 - Sexual glands producing seminal fluid
|
||||
4 - Calyx protecting inner parts of flower
|
||||
Q uestion Four: Compare between: Mechanical and electromagnetic waves:
|
EXAM 5
Q uestiom One: (A) Give reasons for: 1- The intensity of sound decreases to 1/4 when the distance is doubled. Because intensity of sound is inversely proportional with square of distance.
|
|||||||||
2 - Refractive index is greater than (1). Because velocity of light in air is greater than its velocity at any medium.
|
|||||||||
3 - Human beings are reproduced sexually not asexually. Because human beings are unisexual organisms.
|
|||||||||
B : What happens if 1- Number of complete vibrations in one second increases. Frequency of body will increase.
|
|||||||||
2 - Sound falls on a mountain far a distance of 18 metres. Echo will be produced.
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Two: A: Write the scientific term: 1- Measuring unit for frequency = 1 × 109 Hertz Gega Hertz
|
|||||||||
2 - Distance traveled by sound in one second. Sound velocity
|
|||||||||
3 - Medium that doesn’t permit light to pass through. Opaque body
|
|||||||||
4 - The female organ in flower. Pistil
|
|||||||||
B : Complete the following: 1- The flower is short …….. whose leaves are modified to do ……… . stem – reproduction
|
|||||||||
2 - Pollination is the transfer of ……… from ………to……… . pollen grains – anther – stigma
|
|||||||||
3 - Sound intensity is measured by unit watt/m2 while noise is measured by……… . Decibel
|
|||||||||
4 - For echo to happen time should be more than ……… second. 0.1
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Three: (A) What is meant by… 1- Number of complete vibrations in 10 seconds is 500 cycles. It means that frequency =50HZ
|
|||||||||
2 - Bisexual flower It means the flower contains male and female organs.
|
|||||||||
3 - Periodic time is 0.7 sec. It means that the body takes 0.7 seconds to make one complete oscillation.
|
|||||||||
4 - Wave length of longitudinal wave is 0.28 m. It means that the distance between centers of two successive compressions or rarefactions is 0.25m.
|
|||||||||
Q uestion Four: A: Compare between: ovary, Testes.
|
|||||||||
B : Choose the correct answer: 1- The periodic time of wave its frequency is 6 Hz is ……… (0.6 – 1/6 – 0.3 – 1/3) 1/6
|
|||||||||
2 - The medium that permits light to pass through is……… (transparent – wood – opaque - Milk) transparent
|
|||||||||
3 - The angle of reflection for a ray that is incident perpendicular is ……… (90 – 0 o – 180 o – 45o) o
|
|||||||||
4 - The white light composed of ……… colours. (eight – nine – seven - four) seven
|