
Билет № 22
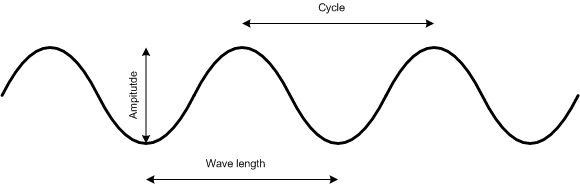
1). Cycle - The interval between any two points that measures the completion of a single wave movement.
2). Amplitude modulation (AM) - is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength (amplitude) of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent. For example, changes in signal strength may be used to specify the sounds to be reproduced by a loudspeaker, or the light intensity of television pixels. This contrasts with frequency modulation, in which the frequency of the carrier signal is varied, and phase modulation, in which the phase is varied, by the modulating signal.
3). At what Frequency operate NDB. These facilities normally operate in a frequency band of 190 to 535 kilohertz (kHz), according to ICAO Annex 10 the frequency range for NDBs is between 190 and 1750 kHz, and transmit a continuous carrier with either 400 or 1020 hertz (Hz) modulation. All radio beacons except the compass locators transmit a continuous three-letter identification in code except during voice transmissions.
Билет № 23
1). Hertz - Hertz (abbreviated: Hz) is the standard unit of measurement used for measuring frequency. Since frequency is measured in cycles per second, one hertz equals one cycle per second.
2). Frequency modulation (FM) - is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. In analog signal applications, the difference between the instantaneous and the base frequency of the carrier is directly proportional to the instantaneous value of the input-signal amplitude.
Frequency modulation uses the information signal, to vary the carrier frequency within some small range about its original value.
3). At what Frequency operate VOR - VORs operate within the 108.0 to 117.95 MHz frequency band and have a power output necessary to provide coverage within their assigned operational service volume. They are subject to line-of-sight restrictions, and the range varies proportionally to the altitude of the receiving equipment.
Билет № 24
1). Keying - refers to the modulation. Modulation is the process of impressing intelligence upon such a wave. Carrier waves may be changed to transmit information in the following ways: Keying consists of starting and stopping the continuous carrier wave so as to break it up in the form of dots and dashes. A radio navigation facility may break its carrier to identify itself by means of dots and dashes.
2). Describe the term Polar Diagrams - a diagram in which a point of origin is surrounded by a curve whose radius at any given point is proportional to the magnitude of some property measured in the direction of that point.
3). At what Frequency operate GNSS - by frequency we have receivers that operate with navigation signals in more than just the standard upper L-band from about 1560–1610 MHz where we find GPS L1, Galileo E1, Compass B1, and GLONASS L1. The obvious additional frequency is the lower L-band, from about 1170 to 1300 MHz, where again the same four constellations have signals.
