
- •Did the construction of the plant cause any ecological damage or change?
- •What is done to reduce the environmental impact of the plant?
- •What investments were made into the project?
- •What is the principle of work of this power plant?
- •What machinery and equipment is used here? (generators, turbines, pumps, reactors, engines etc)
- •5. Tidal power (tidal energy) facts
- •6. La Rance Barrage
- •9. La Rance Tidal Power Plant
What machinery and equipment is used here? (generators, turbines, pumps, reactors, engines etc)
• 24 x 10 MVA alternators operating in air
under 2bar (28.44psi) absolute pression; AI
3.5kV
• 6 x operational units (« assembly »)
comprising 4 bulb-units each: ancillary
components in common + turbine
adjustment and alternator energizing
purposes
• 3 transformers units (3.5/3.5/225kV):
80MVA power, cooled by oil and
blown-air circulation
• Connection to the 225kV station
by oil-filled cables under pressure
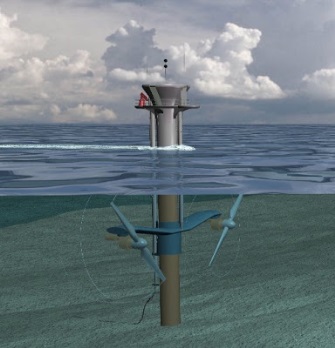
The technology required to convert tidal energy into electricity is very similar to the technology used in traditional hydro-electric power plants - dam, gates and turbines.
The system used consists of a dam 330m long and a 22km2 basin with a tidal range of 8m, it incorporates a lock to allow passage for small craft. 24, 5.4m diameter Bulb turbines, rated at 10MW were connected to the 225kV French Transmission network. Bulb Turbines (капсульная турбина) were developed by Electricite de France. This allows generation on both ebbs of the tide. These axial flow turbines (турбина с осевым направлением потока, осевая турбина) were also designed to pump water into the basin. This type of turbine is popular with Hydropower and has been used on mainland Europe in dams on the Rhine and Rhone rivers.
The plant consists of 24 bulb type turbine generators 5.35 metres in diameter, 470 tonnes in weight, and rated at 10MW each which generate electricity whether the tide is going in or out (developed by Électricité de France). This peak of 240MW of power is sufficient to power 4% of the homes in Brittany - equivalent to the consumption of a town the size of Rennes. The average power generated is 68MW for an annual output of around 600 million kWh units of electricity.
What is the installed capacity of the power plant? (What is its power output? How much energy does it produce?)
The installed capacity of the plant is 240 MW.
Its capacity factor is 40%. Its annual generation is 600 GWh.
With a peak rating of 240 Megawatts, generated by its 24 turbines, it supplies 0.012% of the power demand of France. With a capacity factor of approximately 26%, it supplies an average 62 Megawatts, giving an annual output of approximately 540 GWh.
What area does the plant supply electricity to? (What are the customers of the power plant?)
The Rance tidal power plant accounts for 90% of the electricity generated in Brittany (France). The number of homes that this quantity of electricity provides for in a year is 192131
Is it a base load power plant or a peaking power plant or a load following power plant?
One of the major drawbacks about tidal energy is that it is not a constant source of electricity. There are two tides a day, when the tidal range is at is maximum, and the generating capacity will be at it’s maximum, however there are times when the water level on either side will pretty much be equal, so it will produce no power.
Is the power plant efficient?
The major advantage of tidal energy is its economical benefits. For example, tidal energy does not require any fuel. Tides rise and fall every day in a very consistent pattern.
Tidal energy is perceived as having the potential to provide a reliable source of green energy because it is predictable and guaranteed, unlike wind turbines, which are dependent on the weather.
Tidal energy has an efficiency of 80% in converting the potential energy of the water into electricity.
In spite of the high development cost of the project, the costs have now been recovered, and electricity production costs are lower than that of nuclear power generation (1.8c per kWh, versus 2.5c per kWh for nuclear).
Is it labour intensive to operate? (How many people work there?)
EDF Staff: 28 employees for operation and routine maintenance
What are the duties of the people working there?
They perform operation and routine maintenance of the station. The turbine hall in the Rance tidal power plant is 300 meter long. The technicians move around it on bicycles.
How is the generated electricity distributed?
In practice the amount of power it actually produces is about 96MW, supplying approximately 600GWh per year to the grid, which would power approximately 130,000 houses a year
Are people happy to have this plant nearby?
Tidal power can provide secondary benefits such as bridges and roads, which are built over the tidal generators.
The facility attracts approximately 70,000 visitors per year and a canal lock in the west end of the dam permits the passage of 20,000 vessels each year between the English Channel and the Rance. The highway on the barrage linking Dinard and La Rance is used by 26,000 vehicles each day.
The plant has become a tourist attraction. The facility attracted approximately 40,000 visitors in 2011. The facility is a bridge constructed across a bay.
Like any large-scale hydrological alteration, tidal power stations have economic and social impacts. In the past, the La Rance plant provided some unique regional development benefits because it was wide enough to support a road that connected two previously isolated communities, and it allowed further development of the local distribution network for raw materials and finished goods. Beyond the power generation of the land in which the plant was built on, was used to join communities across a bay, that were otherwise isolated from each other. It is part of France’s highway network with between 30,000 and 60,000 vehicles per day crossing it.
Tidal energy is one of the 5 sources of renewable green energy and it is a renewable source which even though it does not attract much attention due to the large investments needed for a tidal energy plant, it is one of the promising Renewable Energy Sources.


LITERATURE
La Rance Tidal Barrage http://www.esru.strath.ac.uk/EandE/Web_sites/01-02/RE_info/tidal1.htm
Rance Tidal Power Station . http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rance_Tidal_Power_Station
Électricité de France S.A. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C3%89lectricit%C3%A9_de_France
EDF. Marine Energies. http://businesses.edf.com/generation/hydropower-and-renewable-energy/marine-energies/our-strategy-43776.html
http://businesses.edf.com/generation/hydropower-and-renewable-energy/marine-energies/key-figures-43778.html
