


Lesson one
Q
 .1:
Write the scientific term for each of the following:
.1:
Write the scientific term for each of the following:
1- Ability to do work.
[----------------------------]
2- Energy stored in the object due to a work done on the object. [----------------------------]
3- Work done during the motion of an object.
[----------------------------]
4- The sum of potential and kinetic energies.
[----------------------------]
5- The stored energy in a car toy. [----------------------------]
Q. 2: Give reason for each of the following:
1- When the falling object reaches the ground, its mechanical energy equals the kinetic energy only.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2- When the launched object reaches the maximum high, its mechanical energy equals the potential energy only.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3- Potential energy increases as weight of object in increased.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4- Potential energy increases by the increase of height at which the object reaches.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q. 3: Solve the following problems:
1- Calculate the potential energy of an object with weight = 2N at a height = 3m. from the earth's surface.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2- What is the kinetic energy of a 5 kg. body moves with 3m/s peed.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
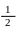 3-
A friend launched your ball upward and vertically with 3m/s speed, at
a 5m. height Determine the work done on the ball if you knew that its
weight = 4 N with kg mass.
3-
A friend launched your ball upward and vertically with 3m/s speed, at
a 5m. height Determine the work done on the ball if you knew that its
weight = 4 N with kg mass.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q. 4: Tick () or (x) in front of the following statements:
1- Mechanical energy equals the sum of kinetic and light energy. ( )
2- Chemical energy is stored in the stretched spring. ( )
3- The mechanical energy for the falling object on earth's surface equals the kinetic energy only. ( )
4- Kinetic energy is inversely proportional with its speed. ( )
5- Kinetic energy is directly proportional with its mass. ( )
6- During the falling of object downwards, its potential energy decreases and its kinetic increases. ( )
7- During raising a ball, its potential increases and its kinetic decreases. ( )
Q.5: Complete:
1- Potential energy = -------------- x ----------------
2- Kinetic energy = -------------- x ----------------
3- Weight = -------------- x ----------------
4- Factors affecting kinetic energy are ---------------------, ---------------------
5- Factors affecting potential energy are ---------------------, -------------------
6- Mechanical energy is the sum of ---------------------, ------------------------
Q.6: What is meant by?
Energy: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Kinetic: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Potential energy: -----------------------------------------------------------------------
Mechanical energy: --------------------------------------------------------------------
Q.7: Compare between:
Kinetic and potential energies
Kinetic |
Potential |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lesson 2
Q
 .1:
Give the scientific term for:
.1:
Give the scientific term for:
1- The sum of potential and kinetic energies of an object under the effect of gravity is constant. [----------------------------]
2- It composed of an acid solution with two different metals dipped in that connects from outside with electric wire. [----------------------------]
3- Energy is neither destroyed nor created from nullity but can change from one from into another. [----------------------------]
4- The pollution which caused by the cellular phones stations.
[------------------------------]
5- The pollution which is caused by car exhausts. [----------------------------]
Q.2: Write the scientific reason for:
1- Law of conservation of mechanical energy is applied by the motion of simple pendulum.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2- The needle of magnetic compass moves (deflects) in the lemon and electricity activity.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3- There is some harm of technology applications of energy transformation.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4- The motion of the swing looks like the motion of the pendulum.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5- Increasing the temperature of the electric lamp after a period of turning it on.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6- It is preferable to establish the stations of cellular phones away from the human buildings.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q.3: Choose the correct answer:
1- In the solar heaters, the solar energy is directly transforms into ------------- energy. [Kinetic – sound – electric – light]
2- The electric energy transforms into kinetic energy in ---------------------
[Electric lamp – cellular phone – electric fan – electric bell]
3-when you pull the arrow and strings the -------------energy is changed into ------------ energy.
[Kinetic into potential – potential into kinetic – kinetic into heat]
3- During the hitting a -------------, ------------------- energy is transformed into ------------------ energy.
[Kinetic – sound – kinetic – potential – sound – kinetic]
4- Sum of potential and kinetic energies is ----------------- energy.
[Mechanical – chemical – light]
Q.4: What is meant by (Define):
* Law of conservation of mechanical energy.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Energy conservation law.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Q.5: Complete the following:
1- During rubbing of your hand -------------- energy is converted into ----------- energy.
2- Any body still conserve the --------------------- energy that changes between --------------------- and potential energies.
3- Energy neither -------------------- nor ------------------ but change from one form to another form.
4- In the electric cell ----------------- energy is changed into ------------ energy.
5- In the dynamo ----------------- energy is changed into -------------- energy.
6- In photosynthesis ----------------- energy is changed into -------------- energy.
7- In motor ----------------- energy is changed into -------------- energy.
