
- •Змістовий модуль і Об’єднане королівство Великобританії та Північної Ірландії
- •Тема 2. Національні символи Великобританії. Стратифікація Британського суспільства. Монархія.
- •Education[edit]
- •Northern Ireland[edit]
- •Scotland[edit]
- •Wales[edit]
- •Outdoor education[edit]
- •Formal classifications[edit] Archaic[edit]
- •20Th century[edit]
- •21St century[edit]
- •Great British Class Survey[edit]
- •Results[edit]
- •Elite[edit]
- •Established middle class[edit]
- •Technical middle class[edit]
- •New affluent workers[edit]
- •Traditional working class[edit]
- •Emergent service sector[edit]
- •Precariat[edit]
- •Middle class[edit]
- •Upper middle class
- •Working class[edit] Unskilled and semi-skilled working class[edit]
- •Skilled working class[edit]
- •Middle class[edit] Lower middle class[edit]
- •Middle class[edit]
- •Upper middle class[edit]
- •Upper class[edit]
Змістовий модуль і Об’єднане королівство Великобританії та Північної Ірландії
Тема 2. Національні символи Великобританії. Стратифікація Британського суспільства. Монархія.
What are the national symbols of Great Britain?
T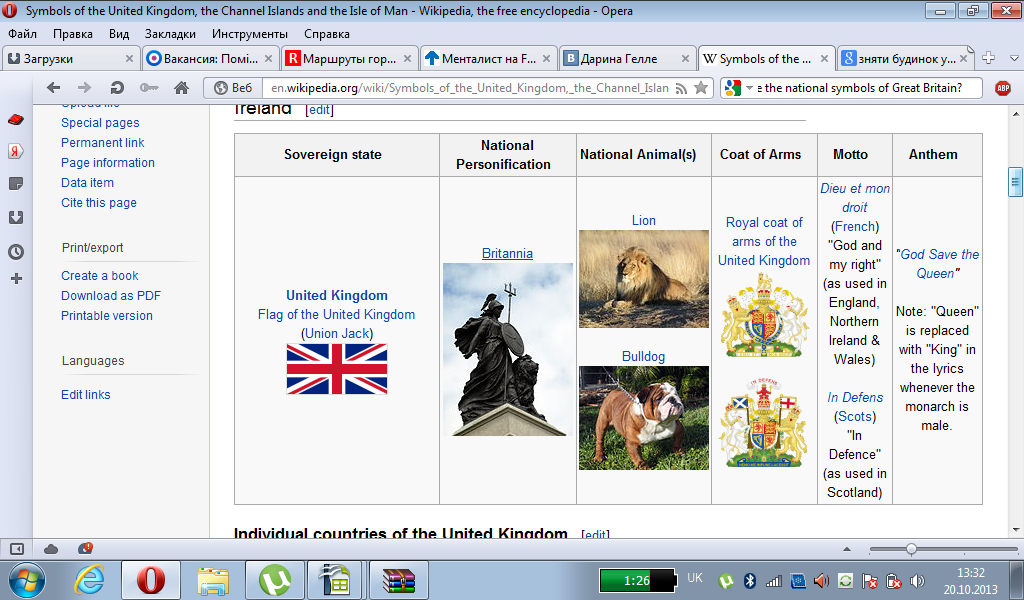 he
Lion is a national animal of England. Lion was the nickname of
England's medieval warrior rulers with a reputation for bravery, such
as Richard I of England, known as Richard the Lionheart.[16] Lions
are frequently depicted in English heraldry, either as a device on
shields themselves, or as supporters. They also appear in sculpture,
and sites of national importance, such as Trafalgar Square. The lion
is used as a symbol of English sporting teams, such as the England
national cricket team.[15]
he
Lion is a national animal of England. Lion was the nickname of
England's medieval warrior rulers with a reputation for bravery, such
as Richard I of England, known as Richard the Lionheart.[16] Lions
are frequently depicted in English heraldry, either as a device on
shields themselves, or as supporters. They also appear in sculpture,
and sites of national importance, such as Trafalgar Square. The lion
is used as a symbol of English sporting teams, such as the England
national cricket team.[15]
The rose is the national flower of England. It is usually red,[15] and is used, for instance, in the emblems of the English Golf Union and England national rugby union team.
The oak is the national tree of England,[15] representing strength and endurance. The Royal Oak and Oak Apple Day commemorate the escape of King Charles II from the grasps of the parliamentarians after his father's execution; he hid in an oak tree to avoid detection before making it safely into exile.
W
 hat
do you know about the history and design of the flag of the UK?
hat
do you know about the history and design of the flag of the UK?
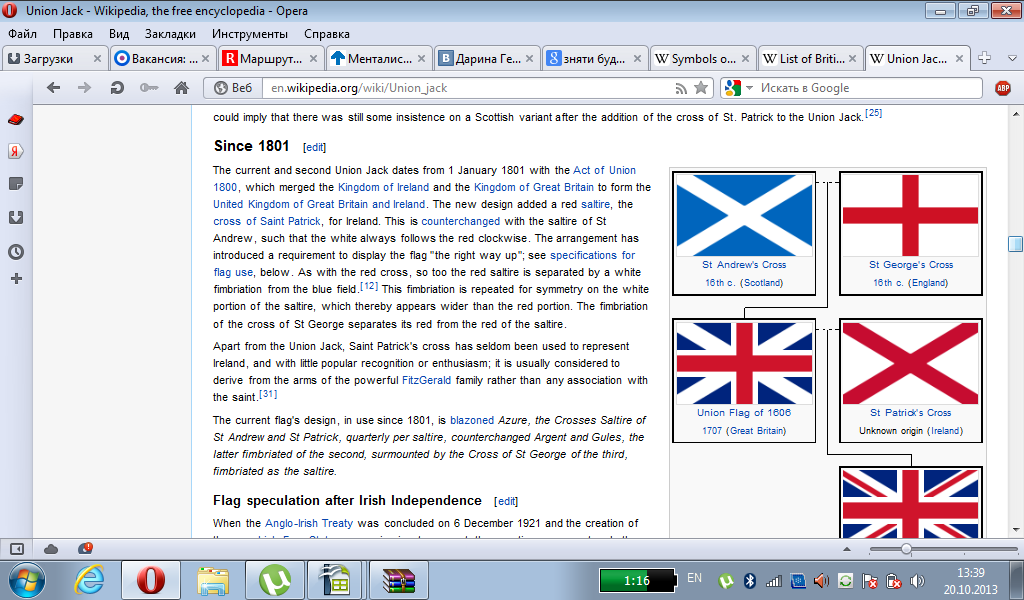
 The
current and second Union Jack dates from 1 January 1801 with the Act
of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Ireland and the Kingdom of
Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and
Ireland. The new design added a red saltire, the cross of Saint
Patrick, for Ireland. This is counterchanged with the saltire of St
Andrew, such that the white always follows the red clockwise. The
arrangement has introduced a requirement to display the flag "the
right way up"; see specifications for flag use, below. As with
the red cross, so too the red saltire is separated by a white
fimbriation from the blue field.[12] This fimbriation is repeated for
symmetry on the white portion of the saltire, which thereby appears
wider than the red portion. The fimbriation of the cross of St George
separates its red from the red of the saltire. Apart from the Union
Jack, Saint Patrick's cross has seldom been used to represent
Ireland, and with little popular recognition or enthusiasm; it is
usually considered to derive from the arms of the powerful FitzGerald
family rather than any association with the saint.
The
current and second Union Jack dates from 1 January 1801 with the Act
of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Ireland and the Kingdom of
Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and
Ireland. The new design added a red saltire, the cross of Saint
Patrick, for Ireland. This is counterchanged with the saltire of St
Andrew, such that the white always follows the red clockwise. The
arrangement has introduced a requirement to display the flag "the
right way up"; see specifications for flag use, below. As with
the red cross, so too the red saltire is separated by a white
fimbriation from the blue field.[12] This fimbriation is repeated for
symmetry on the white portion of the saltire, which thereby appears
wider than the red portion. The fimbriation of the cross of St George
separates its red from the red of the saltire. Apart from the Union
Jack, Saint Patrick's cross has seldom been used to represent
Ireland, and with little popular recognition or enthusiasm; it is
usually considered to derive from the arms of the powerful FitzGerald
family rather than any association with the saint.
The current flag's design, in use since 1801, is blazoned Azure, the Crosses Saltire of St Andrew and St Patrick, quarterly per saltire, counterchanged Argent and Gules, the latter fimbriated of the second, surmounted by the Cross of St George of the third, fimbriated as the saltire.
What is the national flag of Scotland like? Вверху на картинке!
What is the national flag of England like?
What is the national flag of Ireland like?
What is the national flag of Wales like?
What can you say about the national anthem of the United Kingdom?
God Save the Queen is the de facto British national anthem and also has this role in some British territories. It is one of two national anthems for New Zealand (since 1977) and for several of Britain's territories that have their own additional local anthem. It is the royal anthem of Australia (since 1984), Canada (since 1980[3]), Barbados, Jamaica,[citation needed] and Tuvalu. In countries not previously part of the British Empire, the tune of "God Save the Queen" has provided the basis for various patriotic songs, though still generally connected with royal ceremony.[4] In the United States, the British anthem's melody is used for the patriotic "My Country, 'Tis of Thee".
Beyond its first verse, which is consistent, it has many historic and extant versions: Since its first publication, different verses have been added and taken away and, even today, different publications include various selections of verses in various orders.[5] In general, only one verse is sung. Sometimes two verses are sung, and on rare occasions, three.[6]
The sovereign and his or her consort are saluted with the entire anthem, while other members of the royal family who are entitled to royal salute (such as the Prince of Wales) receive just the first six bars. The first six bars also form all or part of the Vice Regal Salute in some Commonwealth realms outside the UK (e.g., in Canada, governors general and lieutenant governors at official events are saluted with the first six bars of "God Save the Queen" followed by the first four and last four bars of "O Canada"), as well as the salute given to governors of British overseas territories.
What are the national emblems of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland like?
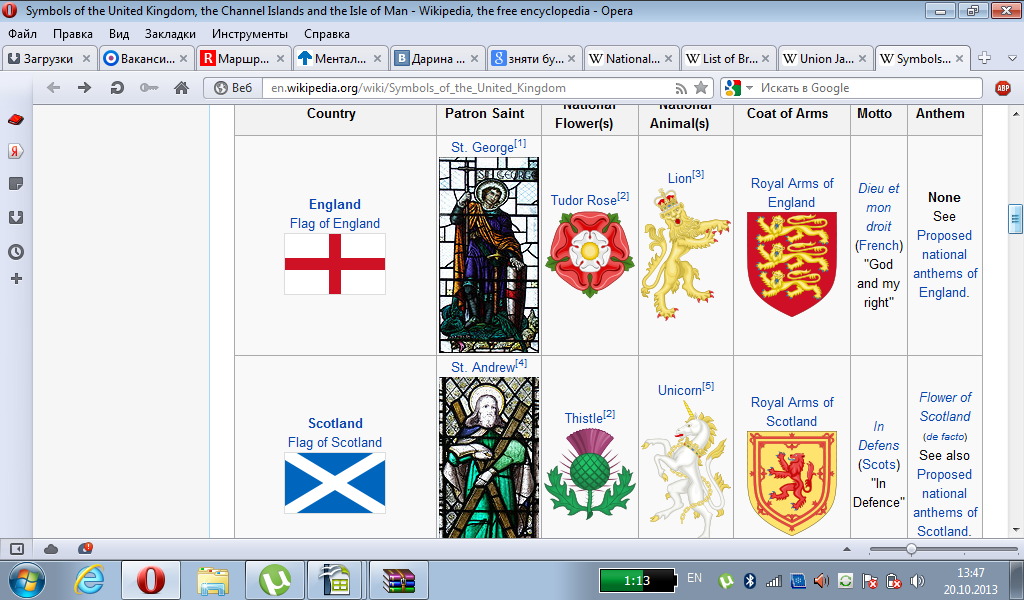
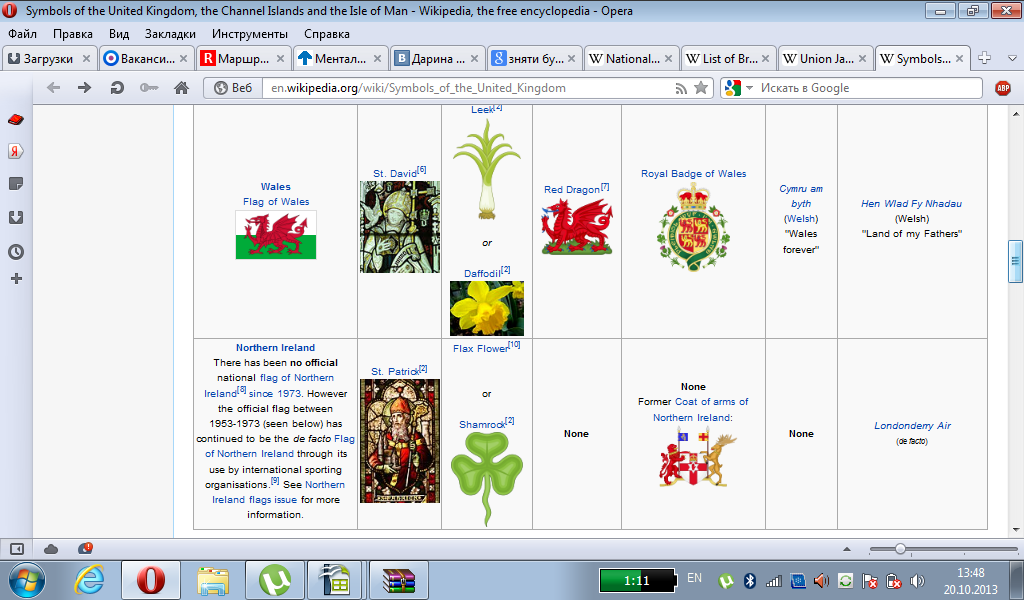
Who are the patron saints of England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland? Вверху смотрите :)
What can you say about the population of the UK?
What is known about national minorities of Britain?
What do you know about language families of Great Britain?
What languages do the British speak?
What forms of address do you know? What can you say about accent?
What is the correct use of titles in the United Kingdom?
What is the popular picture of the twentieth-century aristocrat?
What can you tell about English humour?
What are the English, the Welsh, the Scots and the Irish like?
19.How do the British give help and money to charity?
20.Why do young people in Britain don’t want to live for long with their parents?
Most 18 and 19 year-olds in Britain are quite independent people. Relationships within the British family are different now. Children have more freedom to make their own decisions.For example, children aged 13 may be employed part time in Great Britain. Aged 16 they can leave home, marry with "parents' consent". Age 18 can vote, get married, drink in pubs.
21.What can you say about British homes? Whataretheylike? (домов много, есть все виды и дома и квартиры, престижно жить в доме)
There are 22 million homes in Britain — big homes and small homes, old cottages and new buildings, houses and flats. Many British people love old houses and these are often more expensive than modern ones. They also love gardening and you will see gardens everywhere you go: in towns, villages and out in the country. Two third of the families in Britain own their houses.Millions of these houses are the same with two or three bedrooms and a bathroom upstairs, dining-room and kitchen downstairs. To pay for their house, home owners borrow money from a "building society" and pay back a little every month.
There are a great many different kinds of homes in Britain, but there are not enough! It is often very difficult for young people to find a home when they want to start a family. British homes are usually smaller than American homes. Дети, родители и старые люди вместе не живут, каждый сам по себе.
22.What way do the British spend their free time?
holiday camps, foreign holiday package tours, gambling of many kinds from bingo to horse-race betting, and the transformation of the traditional English pub by trendy interior decoration.
The English weekend is the occasion for countryside trips and for outdoor activities from fishing to mountaineering.
England gave to the world the sports of cricket, association football and rugby football, but team and spectator sports tend to be giving way to more individualistic activities.(уступаюместоиндивидуальномуотдыху).Englishpeople likestay-at-home.Domestic comforts, epitomized in the cosy charm of cottages and gardens and the pervasive ritual of afternoon tea, continue to figure prominently in the character of English life.
23.What can you tell about recreation in Great Britain?
Outdoor pursuits in Britain are a very popular pastime with walking, mountaineering, caving, climbing and cycling all easy to arrange. The British countryside is beautiful and varied and ranges from rolling hills and pleasant farmland to looming mountains and long coastal stretches - with this type of terrain, all kinds of walks are possible.
There are walking organisations in Britain, such as the Youth Hostels Association (YHA), that provide a network of cheap hostel-style accommodation and produce leaflets for organised trips and group walks.
Most of the land in Britain is privately owned so you just can't walk anywhere without first gaining permission from the landowner.(гулятьбезпред.разрешениявладельца).
Britain also has many sporting events for spectators. Football, cricket, rugby, golf and tennis, and so on were all invented in Britain and are still avidly followed and played by many enthusiasts.
Football is the most popular spectator sport and seeing a match for the first time, especially between the big premiership teams, is awesome! Cricket and tennis tournaments are played in the summer chiefly in, while rugby is particularly popular in both England and Wales. Betting on horse racing and motor racing is so a popular pastime throughout Britain. England also hosts world class rowing and sailing regattas (академическойгреблекласса и парусныерегаты), and are regarded as important social events.If you're into your golf, there are courses in every corner of Britain, including some of the most famous in the world.
24.What do you know about food and drink in Britain?
Breakfast time is between seven and nine a.m. A traditional English breakfast is a very big meal. It consists of juice, porridge, a rasher or two of bacon and eggs, toast, butter, jam or marmalade, tea or coffee.
The two substantial meals of the day are lunch and dinner. Lunch is usually taken at one o'clock. For many people lunch is a quick meal. Office workers usually go to a cafe at this time. They take fish, poultry or cold meat (beef, mutton, veal and ham), boiled or fried potatoes and all sorts of salad. Some people like a glass of light beer with lunch. Pubs also serve good, cheap food. School children can have a hot meal at school. Some of them just bring a snack from home.
Tea is very popular among the English; it may almost be called their national drink. Tea is welcome in the morning, in the afternoon and in the evening. Tea means two things. It is a drink and a meal.Dinner time is generally between six and eight p.m. The evening meal is the biggest and the main meal of the day. Very often the whole family eats together. They begin with soup, followed by fish, roast chicken, potatoes and vegetables, fruit and coffee.The British enjoy tasting delicious food from other countries, for example, French, Italian, Indian and Chinese food. Modern people are so busy that they do not have a lot of time for cooking themselves. So, the British buy the food at the restaurant and bring it home already prepared to eat. So we can conclude that take-away meals are rather popular among the population.
25.What prominent people in Great Britain are known all over the world?
ВильямШекспир – writer. 37plays wrote,famous Othello, Romeo and Juliet, King Lier, Hamlet.
ИсаакНьютон scientist (училматематикувКембридже), discovered the law of gravitation, he showed that white light consist of a rainbow colorus.
ЧарльзДиккенс – novelist, showed a real world and people of Victorian England. Самое популярное «ДевидКопертфильд», «Оливер Твист»
Принцесса Диана (iscalledEnglishrose), Дарвин (теория эволюции),
JeromeKlapkaJerome (писатель), Джо Кокер (блюз-рок, группа Ролинстоун),Джоан Роулинг (Гарри Поттер), Джон Леннон (Битлз),Сэр Джеймс Пол Маккарти, Дэвид Бекхэм, ДэниелРэдклифф(играл Гарри Поттера), Фредди Меркьюри (Квин группа), Элтон Джон.
26.What is the attitude of the British to dressing?Очень вано как одется на встречу! А вообще они стиляжные люди)))
When invited to a formal/business function there is nothing worse than discovering you've dressed incorrectly. If you receive an invitation that gives no indication of dress requirements, telephone your host and ask.
Semi-formal |
|
Men |
Women |
|
|
Formal |
|
|
|
BlackTie |
|
|
|
WhiteTie |
|
|
|
Play it safe. For the men colourful ties and cummerbunds are not businesslike. For the ladies low-cut, slinky, sexy dresses are not suitable for business functions.
27.Who on Earth was King Arthur?
King Arthur is a legendary British leader of the late 5th and early 6th centuries, who, according to medieval histories and romances, led the defence of Britain against Saxon invaders in the early 6th century. The details of Arthur's story are mainly composed of folklore and literary invention, and his historical existence is debated and disputed by modern historians. The sparse historical background of Arthur is gleaned from various sources, including the AnnalesCambriae, the HistoriaBrittonum, and the writings of Gildas. Arthur's name also occurs in early poetic sources such as Y Gododdin.
Традиції англійців у різних районах Великобританії / Traditions of the British in different areas of Great Britain.
The culture of the United Kingdom is the pattern of human activity and symbolism associated with the United Kingdom and its people. It is informed by the UK's history as a developed island country, liberal democracy and major power, its predominantly Christian religious life, and its composition of four countries—England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales—each of which has distinct customs, culturesand symbolism. The wider culture of Europe has also influenced British culture, and Humanism, Protestantism and representative democracy developed from broader Western culture.
British literature, music, cinema, art, theatre, media, television, philosophy and architecture are influential and respected across the world. The United Kingdom is also prominent in science and technology. Sport is an important part of British culture; numerous sports originated in the country, including the national game, football. The UK has been described as a "cultural superpower",[3][4] and London has been described as a world cultural capital.[5][6][7][8]
The Industrial Revolution, with its origins in the UK, had a profound effect on the socio-economic and cultural conditions of the world. As a result of the British Empire, significant British influence can be observed in the language, culture and institutions of a geographically wide assortment of countries, including Australia, Canada, India, Republic of Ireland, New Zealand, Nigeria, Pakistan, South Africa and the United States. These states are sometimes collectively known as the Anglosphere, and are among Britain's closest allies.[9][10] In turn the empire also influenced British culture, particularly British cuisine.[11]
