
- •Раздел 1
- •Список использованной литературы
- •Література додаткова
- •Література довідкова
- •Марков в.І. "Воздушная навигация", Кіровоград, код, 2003, 2006, 2009, 2011рр.,
- •Марков в.І., підручник "Розрахунок безпечних траєкторій польоту в ра", длау 2000р, 2010р.
- •Бєлан в.В. "Авіаційна картографія" Учбовий посібник, 1993р.
- •Довідник по повітряній навігації. Автори : Белкін а. М., Міронов н. Ф., Рублев ю. І., Сарайський ю. Н, м : Транспорт 1988.
- •Тема 1. Картографическое обеспечение полетов.
- •План лекции
- •1. Модели, выбранные для аппроксимации земной поверхности.
- •2. Координаты точки (на линии, на плоскости, на поверхности глобуса).
- •Координаты точки на поверхности сфероида (глобуса). Геодезические координаты.
- •4. Определение координат, расстояний и направлений между точками на карте.
- •Перевод масштабов карт
- •5. Координаты точки на поверхности Земли. Астрономические координаты.
- •Тема 1. Картографическое обеспечение полетов.
- •План лекции
- •2. Расчет путевых углов и расстояний между точками маршрута.
- •3. Расчет расстояний на сфере заданного радиуса.
- •4. Картографические проекции.
- •5. Классификация картографических проекций
- •Классификация проекций по положению полюса.
- •Классификация проекций по характеру искажений.
- •Тема 1. Картографическое обеспечение полетов.
- •План лекции
- •Введение
- •Типы аэронавигационных карт ісао. Общие требования к публикуемой информации на картах икао.
- •6. Датировка аэронавигационной информации
- •7. Написание географических названий
- •8. Государственные границы
- •13. Аэронавигационные данные
- •15. Общие системы отсчета
- •2. Назначение, содержание, формат, масштаб и точность информации на картах icao|?
- •1:1000000 (Икао) обязат
1. Модели, выбранные для аппроксимации земной поверхности.
С точки зрения геометрии наша планета - Земля представляет собой тело неправильной формы. Несмотря на близость к сферической форме, форма Земли грушевидная, сплюснутая у полюсов и выпяченная на экваторе (Показ слайда). Для проведения математических расчетов требуется математическая поверхность, близко соответствующая форме Земли, и наиболее близкой аппроксимацией (приближением – замена сложных форм более простыми) в первом приближении к соответствующей в действительности форме Земли дает геоид.
Геоидом называется эквипотенциальная поверхность в гравитационном поле Земли, которая совпадает со средним уровнем моря (MSL) и его продолжением под материками. Таким образом, поверхность геоида отличается от физической поверхности Земли отсутствием гор.
Эквипотенциальная поверхность - физическая поверхность в силовом поле земли все точки которой имеют одинаковый потенциал.
So you can imagine how to perform these tasks, consider an example: You need to get from point A to point B - from Kirovograd to Kiev on the car at that time.
- It is necessary to plan a route (which way to go) - the choice of the airway;
- Check-out time / departure depending on the time of arrival and the time on the road, and in the proper way:
- Always know the location on the track, a place where it is necessary to perform a turn;
- Correction of time driving on the highway, fuel economy, if you can refuel on the ground at any time, the lack of fuel in the air can end in tragedy.
I want to note:
- Illiterate, poor planning and preparation for the flight may By gross violations of flight mode, fly in the other direction, landing on another airport, etc.
- Should the pilot always know the location of aircraft?
Yes. He should determine the direction of flight and time when the set point at any time of the flight..
- The most difficult phase of flight is of approach requires a precision maneuver in the narrow path and runway.
1. The models chosen to approximate the surface.
From the point of view of the geometry of our planet - the earth is a body of irregular shape. Despite its proximity to the spherical shape, the shape of the Earth's pear-shaped, flattened at the poles and wider at the equator (slideshow). To carry out mathematical calculations required mathematical surface closely matches the shape of the earth, and the closest approximation (approximation - the replacement of complex forms easier) to a first approximation to the corresponding shape of the Earth actually gives the geoid.
Geoid is called an equipotential surface in the gravity field of the Earth which coincides with the mean sea level (MSL) extended continuously through the continents. Thus, the geoid surface differs from the physical surface of the earth absence mountains.
Equipotential surface - the physical surface of the earth in a force field which all points have the same potential.
Геоид математически выражается с помощью коэффициентов сферических гармоник. Например, геоид WGS 84, Гравитационная модель Земли (EGM 96), использует коэффициенты сферических гармоник для полиномов до 360 порядка. Для полного уравнения геоида EGM 96 требуется более 60 000 коэффициентов. Ясно, что использовать их все для расчета поверхности слишком сложно.
Геоид строится в настоящее время по спутниковым данным. Интересно, что поднятия и впадины геоида не совпадают с топографией Земли. Это говорит о том, что существует компенсация масс (изостазия) в континентальных масштабах.
Ввиду того, что точное определение положения поверхности геоида в заданной точке невозможно, для этой цели используется, условно построенная с учетом усредненной (нормальной) Модели гравитационного поля Земли поверхность называемая квазигеоидом.
Квазигеоид – это воображаемая поверхность близкая по форме к геоиду, созданная на поверхности общеземного эллипсоида с учетом аномалий высоты. Поверхность квазигеоида отступает от поверхности геоида в пределах нескольких сантиметров в равнинной местности и до 2 метров в горной. От поверхности квазигеоида отсчитываются высоты точек земной поверхности, опубликованные на картах.
Аномалией высоты называется разница между высотой поверхности общеземного эллипсоида и поверхности нормального гравитационного поля Земли.
Кривизну поверхности геоида невозможно описать математически. Поэтому навигационные задачи решаются на поверхностях, которые имеют относительно простое математическое описание. К таким поверхностям относятся сфероид и сфера.
Второе приближение к физической поверхности Земли дает аппроксимация некоторого эллипсоида вращения (сфероида). При решении навигационных, геодезических и картографических задач чаще используется аппроксимация с помощью эллипсоида вращения, который не учитывает экваториальное сжатие. Такой эллипсоид характеризуется:
расположением его геометрического центра относительно центра Земли;
ориентацией основных осей;
размерами большой (экваториальной) полуоси – а, малой (полярной) полуоси – b, полярным сжатием – с, квадратом первого эксцентриситета – е2 и квадратом второго эксцентриситета – (еʹ)2.
The geoid is expressed mathematically by using the coefficients of the spherical harmonics. For example, the geoid WGS 84 Earth Gravitational Model (EGM 96), uses a spherical harmonic coefficients for the polynomials of order up to 360. For the full equation EGM 96 geoid requires a 60,000 coefficients. It is clear that using all of them to calculate the surface too hard.
The geoid is currently under construction on satellite data. Interestingly, the raising of the geoid and troughs do not coincide with the topography of the Earth. This suggests that there is a compensation masses (Isostasy) on a continental scale.
Because the exact position of the geoid determination at a given point can not be used for this purpose, conventionally constructed taking into account the average (normal) models of the gravitational field of the earth surface is called quasigeoid.
Quasi-geoid is imaginary surface which close in geoid form, created on the surface of the common terrestrial ellipsoid with the height anomalies. Quasigeoid surface recedes from the surface of the geoid to within a few centimeters in the plains and up to 2 meters in the mountain. Quasigeoid are measured from the surface of the earth's surface heights of the points listed on the maps.
Height anomaly is the difference between the height of the surface of the common terrestrial ellipsoid, and the surface normal of the gravitational field of the Earth.
The curvature of the geoid can not be described mathematically. Therefore, the navigation problem solved on surfaces which have relatively simple mathematical description. These surfaces include spheroid and sphere.
The second approach to the physical surface of the Earth gives some approximation of an ellipsoid of revolution (spheroid). In solving navigation, geodetic and cartographic tasks often used approximation using an ellipsoid of revolution, which ignores the equatorial compression. This ellipsoid is characterized by:
• the location of its geometric center of the earth's center;
• orientation of the main axes;
• size large (equatorial) axis - a, small (polar) axis - b, polar compression - with, first eccentricity squared - e2 and the square of the second eccentricity - (еʹ)2.
Эксцентриситет – величина, которая характеризует степень вытянутости эллипса. Чем больше разность полуосей (a–b), тем более степень вытянутости эллипса.
Для расчета полярного сжатия (с), квадратов первого и второго эксцентриситетов используются такие математические уравнения:
![]() ;
; ![]() ;
; ![]()
В зависимости от типа решаемых задач геодезии или навигации используются такие виды эллипсоидов вращения:
общеземной эллипсоид (ОЭ);
референц-эллипсоид (РЭ).
Общеземной эллипсоид (ОЭ) – эллипсоид вращения, центр и экватор которого совпадают с центром масс и экватором Земли и лучше всего аппроксимирует поверхность геоида в планетарном отношении. Примером ОЭ может служить модель всемирной геодезической системы WGS-84.
ВОПРОС: Каким условиям должен отвечать общеземной эллипсоид?
Центр совпадать с центром Земли, полуось b с осью ее вращения, уровень близок к геоиду.
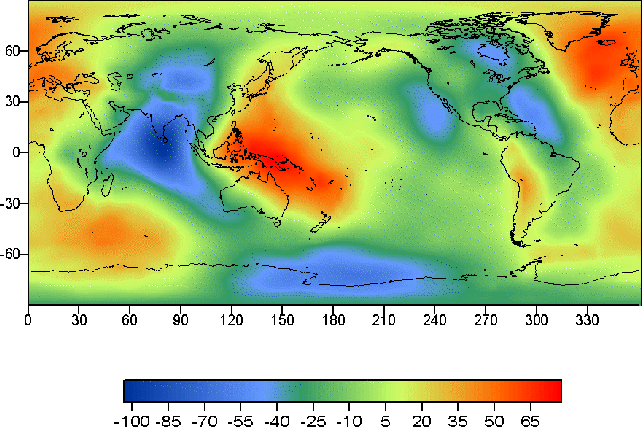
Отклонение геоида от эллипсоида (волна геоида) находится в пределах от ≈ -110м до ≈ + 80м. Сейчас на основе спутниковых наблюдений разработано несколько моделей геопотенциала, например, GRIM5 (Gravity Field Model), EGM96 (Earth Gravitational Model 1996). Модель геопотенциала EGM96 рекомендуется Международной службой вращения Земли для обработки астрометрических и геодезических наблюдений.
Eccentricity is a value which characterizes the degree of elongation of the ellipse. The higher the semiaxes (a-b), the more the degree of elongation of the ellipse.
To calculate the flattening (c), the first and second squares eccentricities mathematical equations are used:
; ;
Depending on the type of tasks surveying or navigation using such kinds of ellipsoids of rotation:
• common terrestrial ellipsoid;
• reference ellipsoid.
Common terrestrial ellipsoid – ellipsoid, the center and the equator coincide with the center of mass and the Earth's equator and is best approximates the geoid surface in planetary terms. An example of the MA can serve as a model of World Geodetic System WGS-84.
Q: What conditions should meet common terrestrial ellipsoid?
Center coincides with the center of the earth, b axis with an axis of rotation, the level is close to the geoid.
The deviation of the geoid from the ellipsoid (geoid undulations) is in the range of ≈-110m to ≈ + 80m. Now, based on satellite observations of the geopotential developed some models, for example, GRIM5 (Gravity Field Model), EGM96 (Earth Gravitational Model 1996). Geopotential model EGM96 recommended the International Earth Rotation Service for processing of geodetic and astrometric observations.
Отклонение геоида от эллипсоида вращения значительно меньше, чем было бы, если бы материки, имеющие меньшую плотность, чем плотность мантии, плавали на эллипсоидальной Земле. Поэтому для объяснения результатов была предложена теория изостазии: корни материков, представляющих блоки земной коры, глубоко вклиниваются в более плотную мантию, и за счет разности плотностей коры и мантии осуществляется компенсация изменений силы тяжести. Таким образом изменение высот геоида связано с состоянием глубоких слоев мантии, и, предполагается, определяется конвективными течениями в нижней мантии. Поэтому вопросу изучения формы геоида, ее изменений во времени уделяется большое внимание. В настоящее время осуществляется и планируется ряд космических проектов, главной задачей которых будет изучение изменения силы тяжести (и, следовательно, геоида) в пространстве и во времени. Гравитационные аномалии будут определены с относительной ошибкой ~10-8 и пространственным разрешением, равным 100 км. Высоты геоида будут определены с ошибкой 1 см.
- Необходимость создания WGS-84, причины.
- Где используется WGS-84.
- Основные параметры WGS-84.
Применение глобальных систем навигации требует создание глобальной системы координат. Основной мотивацией к тому послужила расхождение между координатами одной и той же точки на земле (например, РНТ, КТА аэродрома и т.п.), что в разнообразных координатных системах достигает 300–3000м. И это можно объяснить – ведь одна и та же самая точка на земной поверхности определяется численными значениями, отсчет которых проводился от различных начал отсчета и с различным ориентированием координатных линий.
Использование точных навигационных способов с разнообразными координатами в воздушной навигации неминуемо приведет к разнообразным траекториям полета ВС, что может вызывать путаницу в местоположениях и предопределить снижение уровня безопасности полетов, поэтому сложилась историческая необходимость в ее создании и внедрении. единой глобальной геодезической системы координат.
Такой системой является принятая к внедрению ІСАО в январе 1998 года всемирная геодезическая система координат WGS-84.
Внедрение этой системы предполагает отнесение координат всего аэродромного оборудования и способов навигации на маршруте к единой системе WGS-84.
WGS-84 определяется набором основных и второстепенных параметров.
The deviation of the geoid from the ellipsoid of rotation is much less than it would be if the continents, which have a lower density than the mantle, floating on an ellipsoidal Earth. Therefore, to explain the results of isostatic theory was proposed: the roots of continents, representing blocks of the Earth's crust, deep wedge into the denser mantle, and by the difference in densities of the crust and mantle is compensation for the gravity changes. Thus, changes geoid due to the state of the deep layers of the mantle, and is projected by the convective currents in the lower mantle. Therefore, the question of studying the form geoid, it changes over time paid much attention. Are currently being planned and a number of space projects, whose main task is to study the changes in the force of gravity (and hence the geoid) in space and time. The gravity anomalies will be identified with a relative error of ~ 10-8 and a spatial resolution of 100 km. Geoid height will be determined with an error of 1 cm.
- The need for WGS-84, causes.
- Where is use WGS-84?
- The main parameters of the WGS-84.
The use of global navigation systems require the creation of a global coordinate system. The main motivation to that served as the difference between the coordinates of the same point on the ground (for example, radio navigational point, the aerodrome reference point, etc.), in a variety of coordinate systems is 300-3000m. And this can be explained - in fact one and the same point on the Earth's surface is determined by the numerical values, the count of which was carried out by different starting time and with different orientation of the coordinate lines.
The use of accurate navigation coordinates with a variety of ways in aerial navigation will inevitably lead to a variety of aircraft flight paths, which can cause confusion in the locations and dominated by the lower level of safety, so there was a historical necessity in its creation and implementation. single global geodetic reference system.
Such a system is adopted to implement the ICAO in January 1998, World Geodetic System WGS-84 coordinates.
Implementation of this system involves the assignment of coordinates of the airport equipment and ways to navigate a route to a single system WGS-84.
WGS-84 is defined by a set of primary and secondary parameters.
Основные параметры предназначены для описания формы земного эллипсоида, его угловой скорости и массы Земли, которое заложенные в ОЭ.
Второстепенные параметры определены полной Моделью Гравитационного Поля Земли. Эти параметры используются потому, что WGS-84 применяется не только для определения координат при геодезии и навигации, но решение задач космических систем, например для организации и коррекции орбит ИСЗ системы NAVSTAR (GPS).
Основные параметры WGS-84:
большая полуось а = 6378137 м;
малая полуось b = 6356752,314 м;
сжатие эллипсоида с=3,35281066474×10–3;
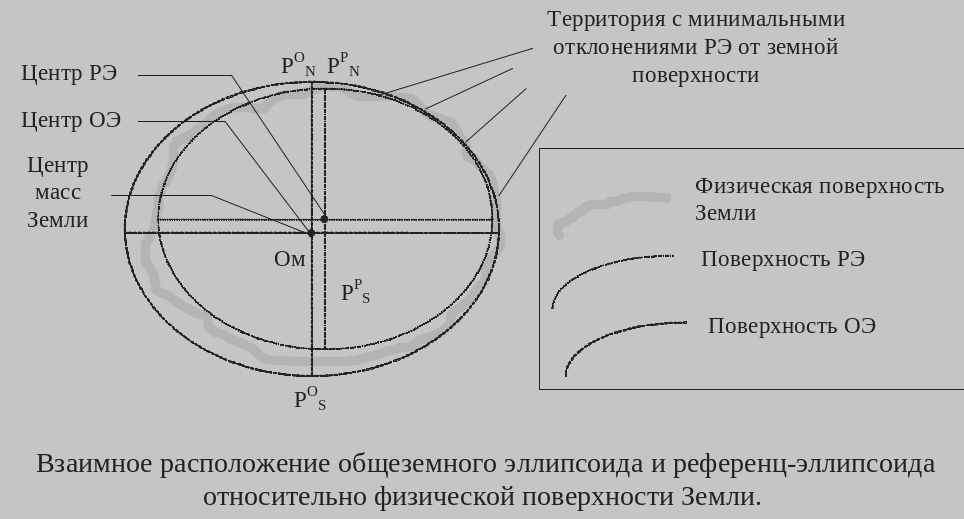
Однако с точки зрения геодезистов общеземной (средний земной) эллипсоид не является наилучшей фигурой. Он хорошо аппроксимирует геоид в среднем; на отдельных участках поверхности отличие эллипсоида от геоида может быть очень большим. Поэтому с помощью геодезических методов для разных участков земной поверхности были построены местные референц-эллипсоиды (в большинстве развитых стран еще до начала космической эры). Как правило, они лучше аппроксимируют геоид на некоторой площади, чем общеземной эллипсоид, однако оси референц-эллипсоида в некоторых случаях могут быть повернуты относительно осей среднего земного эллипсоида. Кроме этого, начало осей может не совпадать с центром масс Земли .
Отличие координат, измеряемых относительно осей среднего или референц-эллипсоидов, обязательно учитывается и в науке, и в повседневной жизни. Эта процедура выполняется, например, при посадке самолетов, координаты которых измеряются с помощью GPS в системе WGS84, на аэродром, координаты которого определены относительно осей местного референц-эллипсоида.
Референц-эллипсоид (РЭ) – эллипсоид вращения, имеющий характеристики, которые лучше всего аппроксимируют земную поверхность на заданной территории.
ВОПРОС: Какие преимущества референц-эллипсоида над общеземным эллипсоидом, какие характеристики РЭ не совпадают с ОЭ?
Наилучшая аппроксимация земной поверхности на данной территории, центры РЭ и ОЭ не совпадают (иногда направление полуосей).
С целью достижения минимума квадратов отклонений по высоте квазигеоида, базы данных электронной памяти современных GPS-приемников содержат, как правило, больше 100 различных РЭ, предназначенных для достижения высокой точности определений на конкретной территории.
Например, рекомендованный к использованию на территориях СНГ референц-эллипсоид Красовского обеспечивает точность определения высоты относительно поверхности квазигеоида не хуже 40 м.
The main parameters to describe the shape of the earth ellipsoid, its angular velocity and mass of the Earth, which is inherent in the common terrestrial ellipsoid.
Secondary parameters are defined full model of the gravitational field of the Earth. These parameters are used because the WGS-84 is used not only to determine the coordinates for geodesy and navigation, but the solution of problems of space systems, such as the organization and the satellite orbit correction system NAVSTAR (GPS).
The main parameters of the WGS-84:
• semi-major axis a = 6378137 m;
• semi-minor axis b = 6356752,314 m;
• compression ellipsoid = 3,35281066474 × 10-3;
However, from the point of view of common terrestrial Surveyors (middle earth) ellipsoid is not the best shape. It is a good approximation of the geoid, on average, in some parts of the surface of the ellipsoid of the geoid difference can be very large. Therefore, using geodetic techniques for different parts of the earth's surface were built local reference ellipsoid (in most developed countries before the start of the space age). As a rule, they are better approximate the geoid in some area than the common terrestrial ellipsoid, but the axis of the reference ellipsoid, in some cases, can be rotated about the axes of middle earth ellipsoid. In addition, the beginning of the axes may not coincide with the center of mass of the Earth.
The difference between the coordinate axes relative to the average of the measured or reference ellipsoid, be sure to take into account in science and in everyday life. This procedure is performed, for example, by landing aircraft, the coordinates of which are measured by GPS in the system WGS84, the airfield, the coordinates of which are defined relative to the axes of the local reference ellipsoid.
Reference ellipsoid (RE) - ellipsoid having the characteristics that best approximate the earth's surface in a given area.
QUESTION: What are the advantages of the reference ellipsoid of the common terrestrial ellipsoid, which characteristics of the reference ellipsoid does not coincide with the common terrestrial ellipsoid?
The best approximation of the earth's surface in the area, the centers RE and common terrestrial ellipsoid are not the same (and sometimes the direction of the semi-axes).
In order to achieve a minimum height squared deviations quasigeoid, databases modern electronic memory contain GPS-receivers are generally greater than 100 different Franz ellipsoids intended to achieve high-precision determinations on a particular site.
For example, recommended for use in the Commonwealth of Independent States Krasovskii reference ellipsoid provides accuracy determination of the height relative to the surface quasigeoid better than 40 m
|
Определение общеземного эллипсоида и референц-эллипсоида для области
|
Для территории Украины и стран СНГ используется референц-эллипсоид Красовского.
а=6378245 м в=6356863 м с=1/298,3.
Исползование сферы в целях навигации. Так как сжатие невелико, то форма Земли мало отличается от шара. Поэтому, при решении многих навигационных задач, не требующих высокой точности, Земля принимается за шар Все простейшие вычисления производятся на сфере.
Радиус сферы эквивалентный по площади РЭ Красовского применяемый для решения навигационных задач.
Rэкв = 6371 116 м.

The relative position of common terrestrial and the reference ellipsoid
on the physical surface of the Earth
B
A
Oʹ
Physical Earth’s surface





O
The
definition of common
terrestrial ellipsoid
and the
reference ellipsoid for
the area AB


For the territory of Ukraine and CIS countries used reference ellipsoid Krasousky.
a = 6378245 m b = 6356863 m c= 1/298, 3.
Sphere use for navigation. Since the compression is low, the shape of the Earth is not very different from the sphere. Therefore, when dealing with many navigation tasks that do not require high accuracy, the Earth is taken as the sphere. All basic calculations are made on the sphere.
Radius of the sphere equivalent in size Krasousky reference ellipsoid. It used to solve navigation problems.
Req = 6371 116 m

