
- •3 Colorimetric characteristics of tv and related systems
- •3.1 Introductory note
- •3.2 Relationship between color coordinates in xyz color space and rgb signal space
- •3.3 Colorimetric characteristics of analog television systems
- •3.4 Colorimetric characteristics of digital television systems
- •3.5 Colorimetric characteristics of ultra-high definition digital television (uhdtv) systems
- •3.6 Multimedia systems colorimetric characteristics
- •Table 3.8
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (Continued)
- •Table 3.8 (End)
- •3.7 Digital video coding system colorimetric characteristics referred toMpeg-2, mpeg-4, mpeg-4/avc
- •Table 3.9 (End)
- •Table 3.10 (End)
- •Table 3.11 (Continued)
- •Table 3.11 Continued)
- •Table 3.11 (End)

3 Colorimetric characteristics of tv and related systems
3.1 Introductory note
Colorimetric characteristics take a great role among video systems characteristics; they considerably influence on overall quality of transmitted and reproduced images. In this section information on colorimetric characteristics of television, multimedia and other related systems is summarized. The description of color spaces for some image compression systems is also shown.
A complete color space definition for digital video representation may include specification of the following aspects:
The chromaticity coordinates
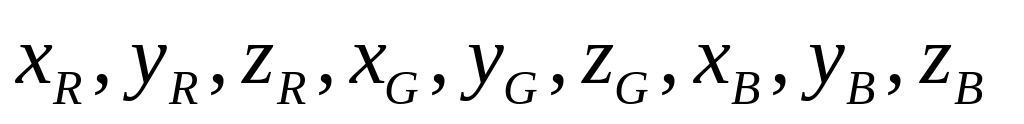 of
the source color primaries
of
the source color primaries
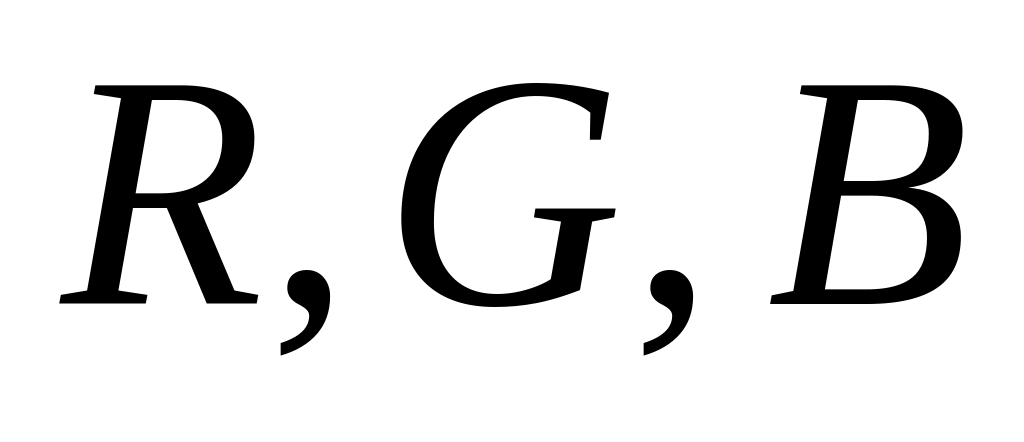 and coordinates
and coordinates
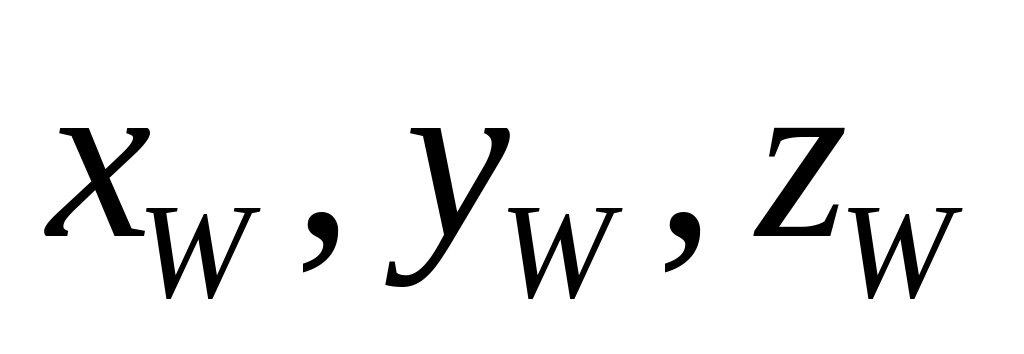 of reference white point.
of reference white point.The opto-electronic transfer characteristics of the source components (e.g., definition of
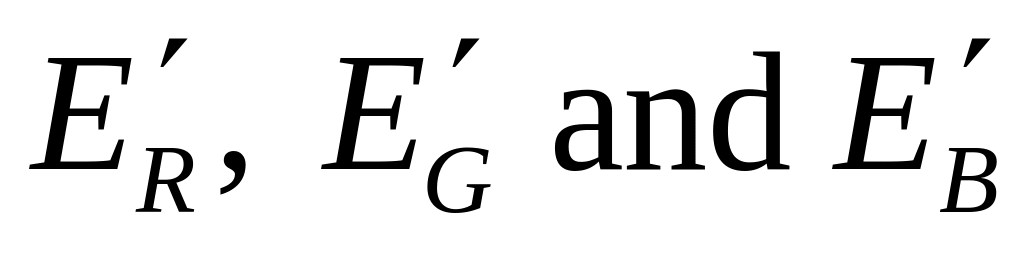 as a function of
as a function of
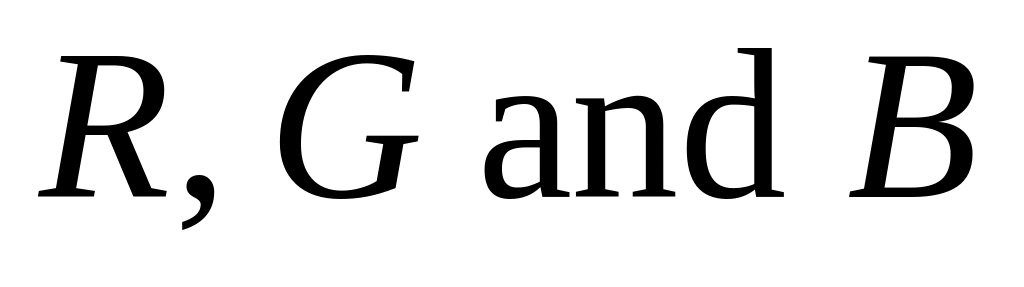 ).
).Matrix coefficients for transformation of the RGB components into luma and chroma components (e.g., definition of components
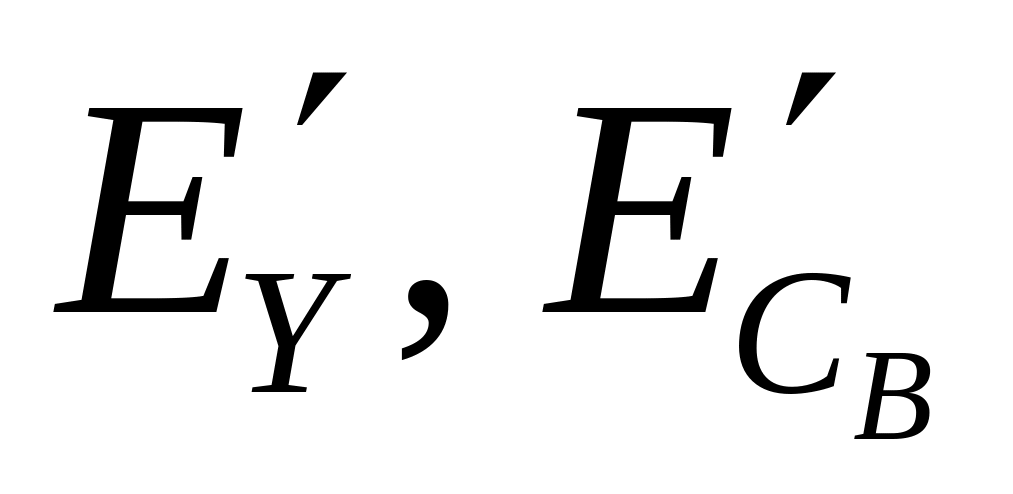 and
and
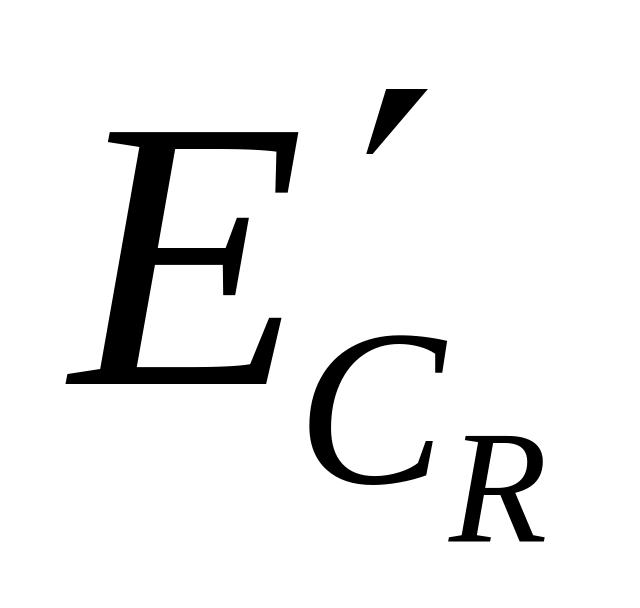 as a function of
as a function of
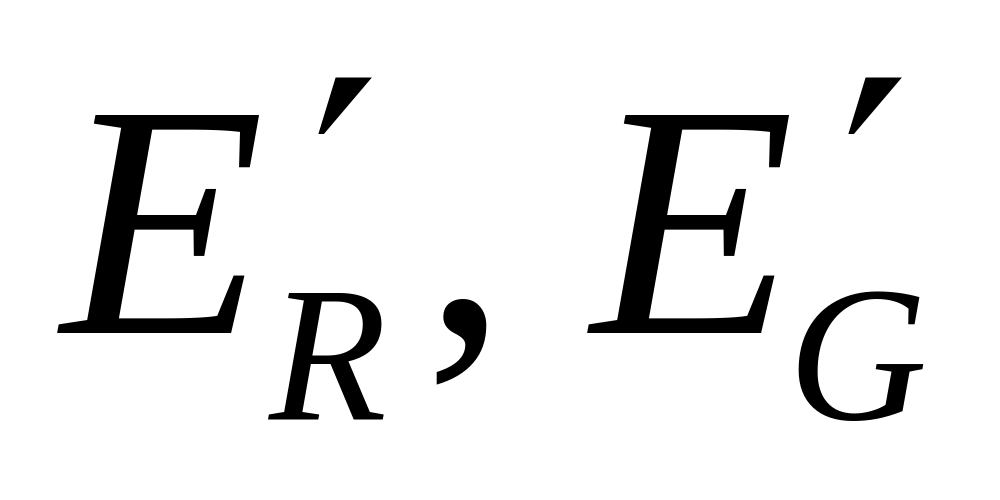 and
and 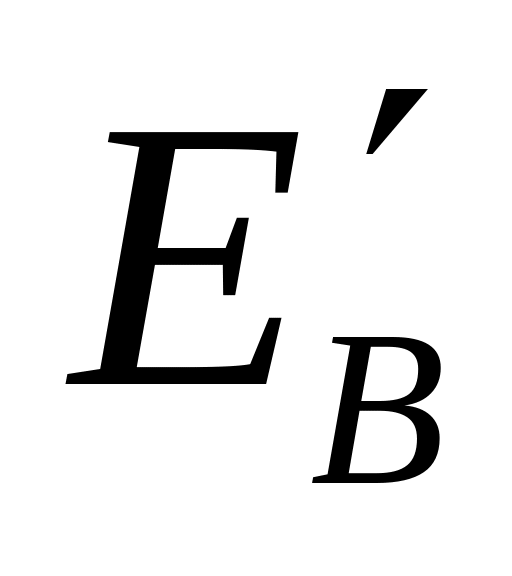 ).
).Definition of scaling, offsets, and quantization for digital representation.
A gamut boundary definition specifying the range of values over which effective representations of colors can be achieved.
3.2 Relationship between color coordinates in xyz color space and rgb signal space
The
correlations interrelating between
![]() 1931 color space and RGB
signal space of TV system in accordance with SMPTE RP 177 3.1
are represented
in this sub clause.
1931 color space and RGB
signal space of TV system in accordance with SMPTE RP 177 3.1
are represented
in this sub clause.
RGB
signal space coordinates are normalized in such a way, that reference
white is equi-primary signal
![]() .
.
For
transformations the
![]() matrix
of primaries chromaticity coordinates and
matrix
of primaries chromaticity coordinates and
![]() vector of reference white chromaticity coordinates
vector of reference white chromaticity coordinates
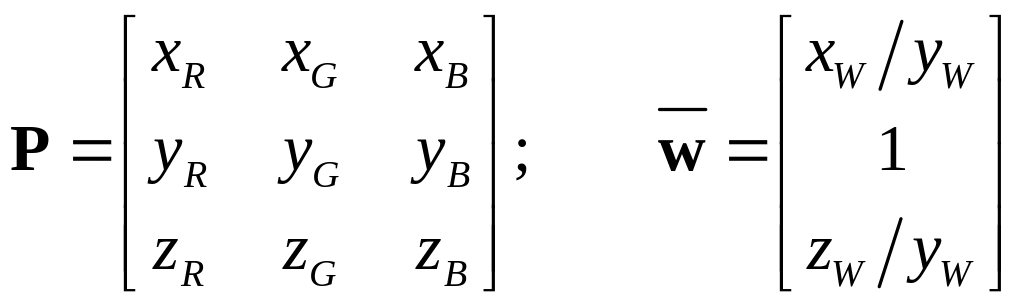 (3.1)
(3.1)
are used. vector normalization corresponds to reference white assignment with a unit luminance factor.
Signal
space in television is normalized to the unit range of
relative luminance change that corresponds to change of
![]() primary signal levels between the values 0 and 1. It corresponds to
such
primary signal levels between the values 0 and 1. It corresponds to
such
![]() space
normalization, that
space
normalization, that
![]() coordinate characterizing the image relative luminance values, takes
0 values on black and 1 on white.
coordinate characterizing the image relative luminance values, takes
0 values on black and 1 on white.
Relationship
between
![]() color
space and
color
space and
![]() signal space is carried out as
signal space is carried out as
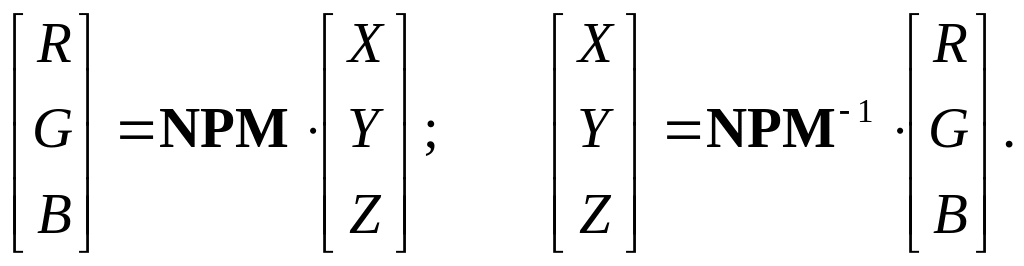 (3.2)
(3.2)
where system primaries coordinates matrix is:
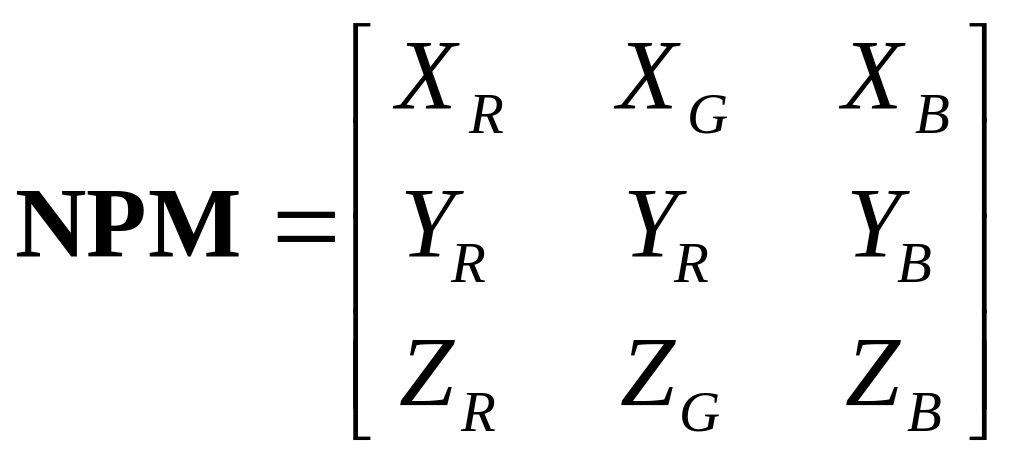 (3.3)
(3.3)
It is calculated with use of formula:
![]() (3.4)
(3.4)
The second row of normalized primary matrix represents the vector of primaries luminance factors, relative color luminance coordinates being determined as
![]() . (3.5)
. (3.5)
Thus
![]() characterize primaries relative luminance. They are also named
primaries luminance factors and designated:
characterize primaries relative luminance. They are also named
primaries luminance factors and designated:
![]() .
.
It
has been marked in 3.1
that as a result of calculations with the limited number of digits
(because of rounding) coefficients of the second row can turn out at
the calculation of
![]() matrix, the sum of which will differ from unit. For this case it is
recommended to normalize the matrix columns so that to obtain
equality of this sum to unit.
matrix, the sum of which will differ from unit. For this case it is
recommended to normalize the matrix columns so that to obtain
equality of this sum to unit.
3.3 Colorimetric characteristics of analog television systems
Colorimetric characteristics of analog television systems are presented in Table 3.1, in which it is marked:
![]() –
relative
luminance levels of
-components;
–
relative
luminance levels of
-components;
![]() –
gamma-corrected
-signals
relative levels (
–
gamma-corrected
-signals
relative levels (![]() );
);
![]() –
luminance
signal;
–
luminance
signal;
![]() – color-difference
signals of the PAL system;
– color-difference
signals of the PAL system;
![]() – color-difference
signals of the SECAM system.
– color-difference
signals of the SECAM system.
