
- •Contents
- •Предисловие
- •1. Think of the place you live in and answer the following questions.
- •5. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Properties of Air
- •6. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions.
- •16. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the types of Conditionals.
- •17. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the functions of the verb “to have”.
- •18. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •19. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Indoor Environmental Quality
- •20. Correct the following statements.
- •21. Analyze the Figure 1.
- •22. Choose the best abstract for the text.
- •23. Write a summary of Text 2.
- •24. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •27. Fill in the table with the derivatives.
- •28. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the functions of the verb “to be”.
- •29. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •30. Do the following task and read the text below to check your answers.
- •How to Avoid In-Home Air Pollution
- •31. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •32. Answer the following questions.
- •33. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •39. Read the texts of Unit 1 again and make notes under the following headings. Then use your notes to talk about Indoor Environment.
- •1. Read the following text and fill in the phrases from the list below.
- •Indoor Air Pollution and Health
- •Качество воздуха внутри помещений
- •1. Answer the following questions.
- •2. Choose the right option. Heating Energy Sources
- •3. Translate the following text into English in written form.
- •4. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •5. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •From the History of Heating
- •6. Put the following sentences in the correct order according to the text.
- •7. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •8. Answer the following questions.
- •Heat Transfer
- •18. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •25. Translate the following text into English paying attention to Passive Voice and active vocabulary.
- •26. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases Adjectives
- •27. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Local Heating Systems
- •28. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •29. Correct the following statements if necessary.
- •35. Translate the following text into English in written form.
- •36. Make all types of questions to Text 3.
- •37. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •38. Read the title of the following text. What can this text deal with? Decide if the following statements are true or false. Read the text and check.
- •Central Heating Systems
- •39. What parts of the text can you define? Do they correspond to the paragraphs? What are the titles to each part?
- •40. Reread the part of the text dealing with warm-air heating (wah) and do the following tasks.
- •41. Reread the part of the text dealing with steam and hot-water heating systems (shwhs) and do the following tasks.
- •42. Reread the part of the text dealing with radiant heating and do the following tasks.
- •43. Reread the part of the text dealing with electric heating and do the following tasks.
- •44. Fill in the following table summarizing the whole information of Text 4.
- •45. Write a summary of Text 4.
- •46. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •47. Form the nouns from the following verbs.
- •48. Match the terms with their definitions.
- •49. Fill in the correct prepositions, translate the phrases, then choose any five items and make up the sentences of your own.
- •50. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •51. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Central heating... How does it work?
- •52. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •53. Correct the following statements if necessary.
- •54. Answer the following questions and give examples.
- •62. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •63. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Water Central Heating - The Pipework
- •64. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •65. Correct the following statements if necessary.
- •66. Answer the following questions and give examples.
- •67. Fill in the table using the information from Text 7.
- •74. Translate the following sentences paying attention to degrees of comparison.
- •75. Choose the contextual meanings of the words written in bold.
- •76. Think of the synonyms for the following words.
- •77. Read the following text and fill in the words from the list below.
- •78. Translate the following text into English in written form.
- •79. Read the texts of Unit 2 again and make notes under the following headings. Then use your notes to talk about Heating.
- •1. Fill in the gaps with the derivatives of the given words.
- •2. Translate the following words and phrases into English using the vocabulary of the unit.
- •1. Do the following tasks trying to memorize as many terms as possible commonly used in the field of ventilation.
- •Pressure
- •2. Translate the terms given below into English.
- •3. Match a device and its name.
- •4. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •5. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Ventilation
- •6. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •7. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •8. Answer the following questions and give examples.
- •13. Choose the odd word.
- •14. Match the words with their synonyms.
- •15. Match the words with their opposites.
- •Ventilation
- •18. Fill in the correct prepositions, translate the phrases, then choose any five items and make up the sentences of your own.
- •19. Find in Text 1 the sentences with the ing-forms. Translate them into Russian.
- •20. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •21. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Ventilation Methods
- •22. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •23. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •24. Answer the following questions.
- •25. Find key words and phrases which best express the general meaning of each part. Make the plan of Text 2. Write a summary.
- •26. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •27. Match the words with their synonyms.
- •32. Find in Text 2 the sentences with modal verbs. Translate the following sentences into Russian paying attention to modal verbs.
- •33. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •34. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Whole-House Ventilation System Designs
- •35. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •36. Answer the following questions.
- •37. Fill in the table using the information from Text b.
- •38. Make an oral report on the text.
- •39. Match the English and Russian equivalents.
- •40. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •41. Match the words with their synonyms.
- •42. Translate these phrases into English.
- •43. The following text is in the jumbled order. Put the steps in correct order. Steps for Designing a Whole-House Ventilation System
- •44. Find the Gerunds in the sentences below. Translate them into Russian.
- •46. Translate into English.
- •47. Read the texts of Unit 3 again and make notes under the following headings. Then use your notes to talk about Ventilation.
- •1.Match the terms with their definitions.
- •2. Choose the best option.
- •3. Read and translate the given part of the instruction “Installing a Bathroom Fan”, filling in the missing words.
- •1. Choose the right word.
- •2. Fill in the words listed below.
- •3. Make up the texts using the sentences below. Note how certain words refer forward and back to other words in the texts.
- •4. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •5. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •What is Humidification?
- •6. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •7. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •8. Answer the following questions.
- •9. Write an abstract for Text 1.
- •10. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •11. Match the words with their synonyms.
- •What is Humidification Process?
- •16. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •17. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •18. Answer the following questions.
- •27. Put the words in the correct order to make up sentences.
- •28. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •29. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Before You Buy a Room Humidifier
- •30. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •31. Answer the following questions.
- •36. Translate these phrases into English.
- •37. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the word worth.
- •38. Read the following text and fill in the words from the list below, answer the following questions and title the text.
- •39. Translate the following text into English. Увлажнители воздуха
- •40. Read the texts of Unit 4 again and make notes under the following headings. Then use your notes to talk about Humidification.
- •1. Read the following text and do the tasks given below.
- •6. Match the terms with their definitions.
- •7. Translate the following words and phrases into English using the vocabulary of the unit.
- •1. Fill in the words listed below.
- •2. Make up the texts using the sentences below. Note how certain words refer forward and back to other words in the texts.
- •3. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •4. Answer the following questions and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Printing problem led to first air conditioner
- •5. Complete the following table according to the text.
- •6. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions.
- •8. Make an abstract on Text 1.
- •9. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •14. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the intensifying construction “it is ___ that (who) ___”.
- •15. Continue the following sentences paying attention to the intensifying construction “it is ___ that (who) ___”.
- •16. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •17. Answer the following questions and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Types of Air Conditioning Units
- •Industrial and Residential Air Conditioning Systems
- •18. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •19. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •20. Answer the following questions.
- •21. Fill in the table using the information of Text 1.
- •22. Make an oral report on Text 2 using the table in exercise 21.
- •23. Combine the words from the column on the left with the suitable nouns from the column on the right. Translate them into Russian.
- •24. Match the words with their synonyms.
- •25. Say in other words.
- •26. Fill in the correct prepositions, translate the phrases, then choose any five items and make up the sentences of your own.
- •27. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the function of the infinitive.
- •28. Give Russian equivalents of the following words and phrases. Try to memorize them.
- •Verbs and verbal phrases
- •29. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •How Does an Air Conditioner Work?
- •30. Answer the following questions.
- •31. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •32. Choose the underlined words and phrases which have mistakes.
- •37. Translate the following words and phrases into English using the vocabulary of the text.
- •38. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the word as at the beginning of the sentence.
- •39. Read the following texts and fill in the missing words from the list below.
- •Undersized Air Conditioners
- •Oversized Air Conditioners
- •40. Translate the following texts into English. Кондиционеры
- •Как устроены кондиционеры?
- •Как происходит охлаждение воздуха в кондиционере?
- •41. Read the texts of Unit 5 again and make notes under the following headings. Then use your notes to talk about Conditioning.
- •1. Fill in the gaps with the derivatives of the given words:
- •Reverse cycle air conditioning
- •2. Choose the contextual meanings of the words written in bold in the text above.
- •3. Translate in written form the paragraph given in bold.
- •4. Fill in the table using the information of the Text.
- •5. Choose the best option.
- •6. Translate the following words and phrases into English using the vocabulary of the unit.
- •Supplementary texts
- •What is Infrared Radiation?
- •Infrared: How does It Work?
- •Introduction to Infrared Process Heating
- •Heating
- •How To Compare Types of Heating Systems
- •Ventilating
- •Air Conditioning Capacity
- •Sources
- •References
Heat Transfer
Here are three easy things to know about the way heat flows:
1) There has to be a temperature difference. Energy only flows as heat if there is a temperature difference.
2) Energy as heat flows from a higher temperature to a lower temperature.
3) The greater or larger the difference in temperature, the faster the energy flows.
Heat can be transferred from place to place by conduction [conduction: The transfer of heat energy through a material - without the material itself moving. ], convection [convection: The transfer of heat energy through a moving liquid or gas. ] and radiation [infrared radiation: Electromagnetic radiation emitted from a hot object. ]. Conduction and convection involve particles, but radiation involves electromagnetic waves.Dark matt surfaces are better at absorbing heat energy than light shiny surfaces. Heat energy can be lost from homes in many different ways and there are ways of reducing these heat losses.
Conduction
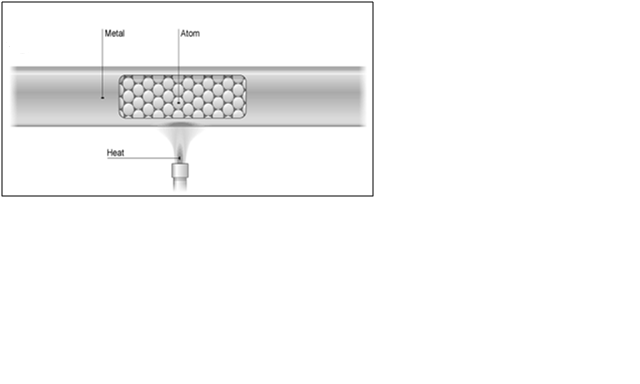
Heat energy can move through a substance by conduction. Metals are good conductors of heat, but non-metals and gases are usually poor conductors of heat. Poor conductors of heat are called insulators. Heat energy is conducted from the hot end of an object to the cold end.
The electrons in piece of metal can leave their atoms and move about in the metal as free electrons. The parts of the metal atoms left behind are now charged metal ions. The ions are packed closely together and they vibrate continually. The hotter the metal, the more kinetic energy these vibrations have. This kinetic energy is transferred from hot parts of the metal to cooler parts by the free electrons. These move through the structure of the metal, colliding with ions as they go.
Convection
Liquids and gases are fluids. The particles in these fluids can move from place to place. Convection occurs when particles with a lot of heat energy in a liquid or gas move and take the place of particles with less heat energy. Heat energy is transferred from hot places to cooler places by convection.
Liquids and gases expand when they are heated. This is because the particles in liquids and gases move faster when they are heated than they do when they are cold. As a result, the particles take up more volume. This is because the gap between particles widens, while the particles themselves stay the same size.
 The
liquid or gas in hot areas is less dense than the liquid or gas in
cold areas, so it rises into the cold areas. The denser cold liquid
or gas falls into the warm areas. In this way, convection currents
that transfer heat from place to place are set up.
The
liquid or gas in hot areas is less dense than the liquid or gas in
cold areas, so it rises into the cold areas. The denser cold liquid
or gas falls into the warm areas. In this way, convection currents
that transfer heat from place to place are set up.
Radiation
All objects give out and take in thermal radiation, which is also called infrared radiation. The hotter an object is, the more infrared radiation it emits.
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that involves waves. No particles are involved, unlike in the processes of conduction and convection, so radiation can even work through the vacuum of space. This is why we can still feel the heat of the Sun, although it is 150 million km away from the Earth.
Some surfaces are better than others at reflecting and absorbing infrared radiation. If two objects made from the same material have identical volumes, a thin, flat object will radiate heat energy faster than a fat object. This is one reason why domestic radiators are thin and flat. Radiators are often painted with white gloss paint. They would be better at radiating heat if they were painted with black matt paint, but in fact, despite their name, radiators transfer most of their heat to a room by convection.
Radiation or Conduction or Both?
When you stand near hot molten lava, the heat you feel on your skin is mostly radiant heat. This type of heat doesn't need air to travel through. Even if you were standing in a vacuum (no air) you would feel the heat (except you'd be unconscious, or worse, from lack of air).
Almost all of the energy from the sun that travels 93 million miles in 8 and 1/2 minutes through the vacuum of space is radiant energy. When you stand outside on a sunny day feeling the warm rays, remember that only 8 and 1/2 minutes ago it left the sun. Scientists call it electromagnetic radiation. Infrared, ultraviolet, and visible light are examples of electromagnetic radiation that can transfer energy from one object to another object.
Believe it or not, your body and all other objects are always giving off or absorbing heat by radiation. Heat transfer by radiation goes from a hotter object to a cooler object - like from the sun to earth, or from hot coals to you, or from your body to the cold walls of a lonely castle on a dark and stormy night.
Conduction is the type of heat flow that results when things are actually touching. Energy traveling as heat by conduction needs matter to flow through. If you touch a hot object the heat is conducted by physical contact with your skin. The energized atoms in the object transmit their energy to the atoms in your hand. If you are standing in cold air, the heat from your body flows from the molecules in your body into the cold air molecules that are touching your body. If you are floating in cold water, the heat flows from your body into the cold water molecules that are touching your skin. If you fry vegetables on a stove you are relying on conduction to cook your vegetables. Heat from the flame flows through the metal by conduction, into and through the cooking oil by conduction, and into and throughout the vegetables by conduction.
 Conduction
cannot travel through a vacuum because in a vacuum there are no atoms
or molecules making contacting with other atoms or molecules.
Something made of atoms or molecules has to touch something else made
of atoms or molecules in order for there to be conduction.
Conduction
cannot travel through a vacuum because in a vacuum there are no atoms
or molecules making contacting with other atoms or molecules.
Something made of atoms or molecules has to touch something else made
of atoms or molecules in order for there to be conduction.
Heat from a wood stove is radiated to cooler surfaces like walls, floors, ceilings, furniture, and people.
Energy as heat is also conducted into the air and circulated naturally by a process called convection from the hot metal surfaces to the air surrounding the stove.
COMPREHENSION CHECK
