
- •2) Objects and methods of animal biotechnology
- •3) Totipotent, multipotent, pluripotent animal cells
- •4.Allophenic animals. Genetic chimers
- •5)The principles of genetic cloning
- •6.Allophenic animals. Genetic chimers
- •8) Methods for introducing foreign dna into animal cells
- •9)Cryopreservation of reproductive and germ cells of animals and humans
- •11)The principles and methods of plant cells cultivation in vitro
- •12. The types of medium. Physiological means of compounds medium (as an example you can use the composition of Murashige-Skug medium)
- •14)Differentiation and dedifferentiation in plant cell culture. The obtaining callus mass and cultivation of callus tissue .
- •15)The influence of phytohormons on morphogenesis and regeneration in plant cells culture
- •16.The main path of morphogenesis processes in plant cells culture
- •18.The growth stages in suspension culture
- •20) The factors influenced on microclonal propagation in plant cell culture.
- •21) What is Biotechnology? Various definitions of “Biotechnology”. History of Biotechnology
- •22.Microbial Biotechnology: fundamentals of applied microbiology
- •24.Sterilization in Biotechnology: Methods and principles
- •26) Somaclonal and gametoclonal variation in plant cells culture.
- •27) Artificial seeds". Embryo culture in vitro
- •28. Culture of apical meristem cells
- •29)Cell reconstruction. Theoretical means of cell reconstruction
- •30.Basics of phytopathology. The main diagnostics methods of plant diseases
- •32) Main objects of animal biotechnology:
- •33) Morphological and functional features of gametes - eggs and sperm
- •34Hormonal regulation of mammalian reproduction
- •35)The history of investigations of the genetic transformation of animal cells
- •36.The principles of genetic engineering in animal biotechnology
- •53)Genetic engineering. Methods of genetic transformation
- •54. Methods of receiving plant materials without viruses
- •56) The vector systems used in the genetic engineering
- •57) Methods of genetic engineering: agrobacterial genetic transformation
- •58)Methods of genetic engineering: bioballistics methods
- •60.Apply cell technology and cryopreservation technology for safe gene bank
- •62) Methods of producing chimeras
- •63) Collection and cultivation of oocytes in vivo and in vitro
- •64 Collection and cultivation of embryos in vivo and in vitro
- •66.Fertilization of oocytes in vitro, environment and conditions
- •68) Draw a diagram of the structure of plasmid pBr322
- •69) Draw a diagram of an experiment in genetic engineering (design recDna) and give a description of the main stages
- •70)Describe the calcium-phosphate method for introducing foreign dna into mammalian cells.
- •72 Methods of cryopreservation of sperm and oocytes of mammals
- •74) Modes of freezing and thawing of gametes and embryos
- •75) Methods of artificial fertilization: gamete insemination fallopian tube (gift), zygosity insemination fallopian tubes (zift).
- •76) Stem cells and prospects for their use in practice
- •78.Technical equipment of experiments on artificial insemination
- •80) Methods of animal cloning, reproductive and therapeutic cloning
- •81) Microorganisms in water and wastewater treatment
- •82 Microbial fermentations in food products
- •84.Bacterial examination of water and standard water analysis
- •86) Use of e.Coli for the biotechnological production
- •87) Microbes in milk and dairy products
- •88) What is the benefit of microorganisms in industry
- •90. Algae, their applications
4.Allophenic animals. Genetic chimers
Chimera is the animal consisting of different genotype cells which originated more than 1 zygotes.
Different cell populations can be combined in one organism during any stage of development
Methods of creating chimeras.
Embryonic aggregation chimeras
Injection of embryonic cells to blastocyst
Therato-carcinomas (for example, the introducton of embryonic cells to the adult)
Xenotransplantation (transplantations of cells, tissue, organs from one adult to another)
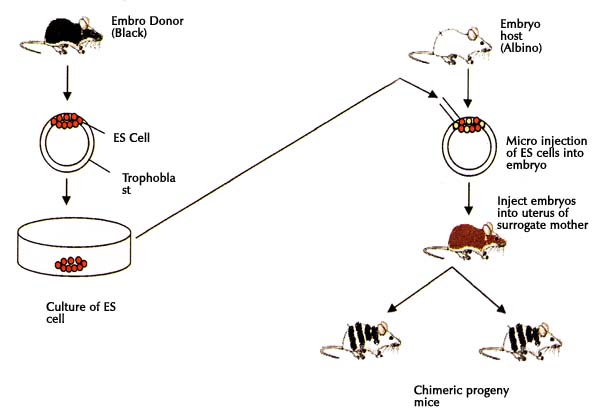
Methods of creating chimerical mouse
Isolation of eggs from donors with different genotypes;
Embryos should be cultivated on standard culture media (base-buffered saline, STC and lactate, glucose, albumin) to stage of 8 blastomeres;
8-cells morula aggregation (aggregation method), and cultivation in vitro to the blastocyst stage;
chimeric embryo should be implanted into the uterus of female recipient
One of the promising areas of biotechnology - art ¬ tively obtaining chimeras (allofennyh animals). The concept of Chi ¬ measure is a composite animal. The essence of the method is to produce chimeras combining artificial ¬ embryonic cells of two or more animals. Animals can be either single species or different species and even of different kinds. ¬ mennaya modern microsurgery produces chimeras having 3-4 or more parents. Chimera possess features animals once ¬ genotypes. There are two primary methods for obtaining artificial chimeras ¬ vennym by: 1) aggregation - combining two or more morulae or blastocysts in one embryo, 2) injecting ¬ s - microinjection of intracellular cell mass (ICM) of blastocyst embryo donors in the blastocoel of the recipient. In both cases, individuals receive, tissues and organs are constructed ¬ enes of cell clones combined (two or more) embryos . The first set of laboratory mice chimeras between the lines of the agouti (cream) and agouti (black). They looked mottled. Their colors combined features of both parents pigmented hair bands alternated with light, each bar represents a clone of cells ancestors. Their use helps to study fundamental problems of cell differentiation during ontogeny, many questions ¬ joint mechanism of cell development and origin of the individual tissues, immunological interactions in the development, etc.
5)The principles of genetic cloning


6.Allophenic animals. Genetic chimers
Chimera is the animal consisting of different genotype cells which originated more than 1 zygotes.
Different cell populations can be combined in one organism during any stage of development
Methods of creating chimeras.
Embryonic aggregation chimeras
Injection of embryonic cells to blastocyst
Therato-carcinomas (for example, the introducton of embryonic cells to the adult)
Xenotransplantation (transplantations of cells, tissue, organs from one adult to another)
Methods of creating chimerical mouse
Isolation of eggs from donors with different genotypes;
Embryos should be cultivated on standard culture media (base-buffered saline, STC and lactate, glucose, albumin) to stage of 8 blastomeres;
8-cells morula aggregation (aggregation method), and cultivation in vitro to the blastocyst stage;
chimeric embryo should be implanted into the uterus of female recipient
Одно из перспективных направлений биотехнологии — искусственное получение химер (аллофенных животных). Понятие химера означает составное животное. Сущность метода получения химер заключается в искусственном объединении эмбриональных клеток двух и более животных. Животные могут быть как одной породы, так и разных пород и даже разных видов. Современная микрохирургия позволяет получать химер, имеющих 3—4 и более родителей. Химеры обладают признаками животных разных генотипов. Существует два основных метода получения химер искусственным путем: 1) агрегационный — объединение двух и более морул или бластоцист в один эмбрион; 2) инъекционный — микроинъекция клеток внутриклеточной массы (ВКМ) бластоцисты доноров в бластоцель эмбриона-реципиента. В обоих случаях получают особей, ткани и органы которых построены из клонов клеток объединенных (двух или более) эмбрионов (рис. 30). Первыми созданы химеры лабораторных мышей между линиями агути (кремовые) и не агути (черные). Они выглядели крапчатыми. Их окраска сочетала признаки обоих родителей: полосы пигментированной шерсти чередовались со светлыми, каждая полоса представляла клон клетки-родоначальницы. Их использование помогает изучению фундаментальных проблем дифференцировки клеток в процессе онтогенеза, многих вопросов механизма клеточного развития и происхождения отдельных тканей, иммунологического взаимодействия в развитии и т. д.
7 The main stages of in vitro fertilization in animals. IVF is the basic assisted reproduction technique, in which fertilization occurs in vitro. The sperm and the egg are combined in a laboratory dish, and after fertilization, the resulting embryo is then transferred to the female's uterus. The first successful IVF offspring were rabbits born in 1959. The basic requirements for IVF are healthy ova, sperm that can fertilize, and a uterus that can maintain a pregnancy. Five general steps are followed for IVF : 1Superovulation: Normally, a female ovulates just one or more egg per cycle. With the use of fertility drugs, she may be able to produce many eggs, which can then be retrieved from the ovaries prior to ovulation to be used for artificial semination of another female unable to produce eggs or that quality of egg. Spontaneous ovulation during the cycle is typically prevented by the use of GnRH agonists or GnRH antagonists, which block the natural surge of luteinising hormone (LH). 2. Egg Retrieval: When follicular maturation is judged to be adequate, chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is given. This agent would cause ovulation about 42 hours after injection. The eggs are retrieved using a transvaginal technique involving an ultrasound-guided needle piercing the vaginal wall to reach the ovaries. Through this needle follicles can be aspirated. It is common to remove between ten and thirty eggs.3. Fertilization: In the laboratory, the identified eggs are stripped of surrounding cells and prepared for fertilization. In the meantime, semen is prepared for fertilization by removing inactive cells and seminal fluid. The sperm and the egg are incubated together (at a ratio of about 75,000:1) in the culture media for about 18 hours. In most cases, the egg will be fertilized by that time and the fertilized egg will show two pronuclei. In certain situations, such as low sperm count or motility, a single sperm may be injected directly into the egg using intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). The fertilized egg is passed to a special growth medium and left for about 48 hours until the egg has reached the 6-8 cell stage. 4. Selection: Laboratories have developed grading methods to judge oocyte and embryo quality. Typically, embryos that have reached the 6-8 cell stage are transferred three days after retrieval. 5. Embryo Transfer: Embryos are graded by the embryologist based on the number of cells, evenness of growth and degree of fragmentation.The embryos judged to be the "best" are transferred to the patient's uterus through a thin, plastic catheter, which goes through her vagina and cervix. Several embryos may be passed into the uterus to improve chances of implantation and pregnancy
