- •Project consultation pointing to relevant chapters
- •Annotation
- •Аннотация
- •Түйіндеме
- •1.5Final Goals
- •2Application architecture
- •2.1Enterprise JavaBeans (ejb)
- •2.2Bpm Process Engine
- •2.2.1Introduction
- •2.2.2What is bpmn?
- •2.2.3Bpmn 2.0 constructs Custom extensions
- •2.2.4Engine api
- •2.2.5Business archives
- •2.2.6Versioning of process definitions
- •2.2.7Generating a process diagram
- •2.3Integrating bpm into project
- •2.4Web Services
- •2.5Application Design
- •3Database Architecture
- •3.1Dbms
- •3.2Schemas Design
- •3.3Data Model Overview Table «Catalog» - Catalog of subjects which would be available in a faculty on certain term with some number of credits
- •Table «Class» - a set of lessons which will be tough by some instructor
- •Table «Class_Enroll» - Enroll for a class
- •Table «Class_Grades» - Grades of student for some class
- •Table «Student_Schedule» - Student Schedule of classes
- •Table «Subject» - Some area of study in education
- •Table «Term» - Special Period of time, which has name, start date and end date
- •3.4Activiti Database tables
- •Benefits
- •4Network and Servers
- •4.1Design
- •Benefits
- •5Bpmn usage in Middleware
- •6Conclusion
- •7References
Table «Student_Schedule» - Student Schedule of classes
Relationships
Columns |
Association |
Notes |
|
0..* Student_Schedule.student_id 1 Student.PK_Student |
|
|
0..* Student_Schedule.class_id 1 Class.PK_Class |
|
|
0..* Student_Schedule.term_id 1 Term.PK_Term |
|
Table «Subject» - Some area of study in education
Relationships
Columns |
Association |
Notes |
|
0..* Subject.course_id 1 Course.PK_Course |
|
|
0..* Catalog.subject_id 1 Subject.PK_Subject |
|
Table «Term» - Special Period of time, which has name, start date and end date
Relationships
Columns |
Association |
Notes |
|
0..* Class.term_id 1 Term.PK_Term |
|
|
0..* Catalog.term_id 1 Term.PK_Term |
|
|
0..* Student_Schedule.term_id 1 Term.PK_Term |
|
3.4Activiti Database tables
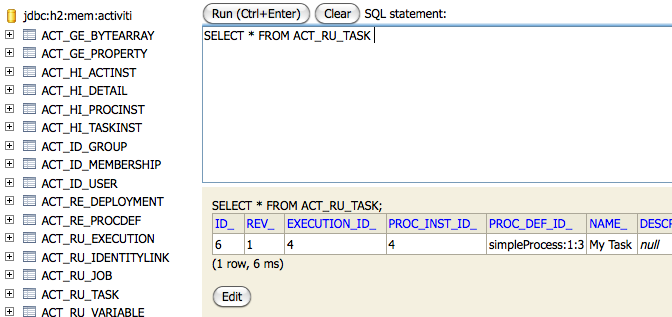
The database names of Activiti all start with ACT_ (Figure 3.2). The second part is a two-character identification of use case of the table. This use case will also roughly match the service API.
ACT_RE_*: 'RE' stands for repository. Tables with this prefix will contain 'static'' information such as process definitions and, process resources (images, rules, etc.).
ACT_RU_*: 'RE' stands for runtime. These are the runtime tables, that contain the runtime data of process instances, user tasks,variables, jobs, etc. Activiti only stores the runtime data during process instance execution, and removes the records when a process instance ends. This keeps the runtime tables small and fast.
ACT_ID_*: 'ID' stands for identity. These tables contain identity information, suchas users, groups, etc.
ACT_HI_*: 'HI' stands for history. These are the tables that contain historic data, such as past process instances, variables, tasks, etc.
ACT_GE_*: general data, which is used in various use cases.
Figure 3.2 – Activiti database tables
Benefits
There are several benefits of this design:
Normalized (each table has primary key)
The weight of row in tables are low
Tables have foreign keys
4Network and Servers
4.1Design
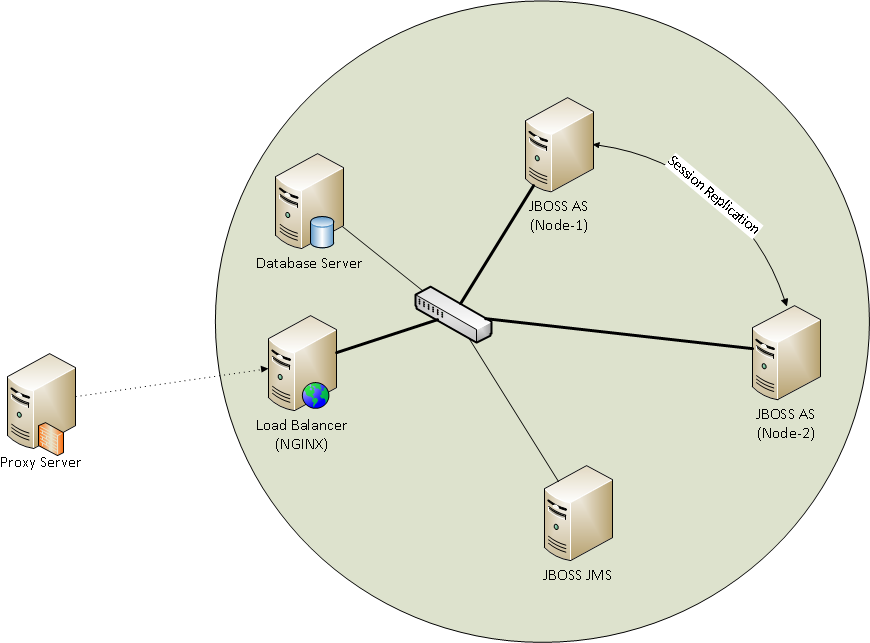
At Figure 4.1 we have a network grid diagram of the servers.
Let’s discover parts of network grid:
Proxy Server - is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers.
The purposes of using proxy server are:
To keep machines behind it anonymous (mainly for security).
To speed up access to resources (using caching). Web proxies are commonly used to cache web pages from a web server.
To apply access policy to network services or content, e.g. to block undesired sites.
To log / audit usage, i.e. to provide company employee Internet usage reporting.
To bypass security/ parental controls.
To scan transmitted content for malware before delivery.
To scan outbound content, e.g., for data leak protection.
To circumvent regional restrictions.
Types of proxy servers:
Forward proxy – is a proxy where the client server names the target server to connect to (Figure 4.2).
Open proxy – is a forward proxy server that is accessible by any Internet user (Figure 4.3).
Reverse proxies – is a proxy server that appears to clients to be an ordinary server (Figure 4.4).
We are using reverse proxy for our case of network design.
Figure 4.2 – Forward proxy
Figure 4.3 – Open proxy

Figure 4.4 – reverse proxy
Load Balancer(NGINX) – is distributing service requests across a group of servers. The following diagram shows load balancing within a server. Addresses several requirements:
Increased scalability
High performance
High availability and disaster recovery
Database Server – an independently functioning computer in a local-area network that holds and manages the database.
JBOSS AS – is a free software/open-source Java EE-based application server. There two nodes of JBOSS AS:
Node-1
Node-2
These Nodes operates between each other by round robin load balancing algorithm with session replication. Round robin – a simple algorithm that distributes each new connection/session to the next available server.
Figure 4.1 – Network grid diagram